- Cart 0
- English
A Guide to Selecting WB Internal Control Antibody
1. What are Internal References?
Internal references are a class of proteins used for normalization and correction of experimental errors in Western Blot experiments. They are typically proteins encoded by housekeeping genes, expressed relatively constantly in different tissues and cells, and commonly used as reference markers for detecting changes in the expression levels of target proteins.
2. What is the Role of Internal References in WB?
Correction of Experimental Errors: Internal references are used to correct experimental errors in protein quantification and loading processes to ensure the accuracy of experimental results. Since different samples may have operational errors in protein extraction, quantification, and loading, using internal references can correct these errors.
Semi-Quantitative Analysis: By comparing the signal intensities of internal references and target proteins, semi-quantitative analysis of experimental results can be performed. When sample protein quantities are limited and only sufficient for a single electrophoresis and transfer experiment, the internal reference and target protein levels of the samples can be detected separately. Then, the target protein levels of each sample are divided by their respective internal reference levels to obtain the relative content of the target protein in each sample after internal reference correction. This value can be used for comparison and analysis between samples.
Blank Control: Internal references can serve as blank controls to check whether protein transfer is complete and whether the entire Western Blot detection system (colorimetric or luminescent) is functioning properly.
Ensuring Comparability of Results: When comparing the relative expression levels of target proteins under different conditions or in different tissues, internal references provide a standard for comparison, ensuring the comparability of experimental results.
3. Common Internal References in WB
β-Actin: β-Actin is a cytoskeletal protein with a molecular weight of approximately 42 kDa, widely distributed in various tissues with relatively constant and abundant expression. It is commonly used as a total protein reference, especially in non-muscle tissues. However, it should be noted that the expression of β-Actin may be lower in certain specific tissues (such as cardiac muscle), and thus it is not suitable in all cases. Additionally, different β-Actin isoforms are distributed differently in various tissues, which should be considered when selecting antibodies.

Rat brain lysate 20μg

Human colorectal cancer tissue

Hela cells
abs171598 Rabbit anti-β-Actin Monoclonal Antibody
GAPDH (Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase): Approximately 36 kDa, GAPDH is a widely expressed protein suitable for various cell types. However, under certain conditions, such as hypoxia or diabetes, the expression of GAPDH may be affected and should be chosen carefully based on experimental conditions.
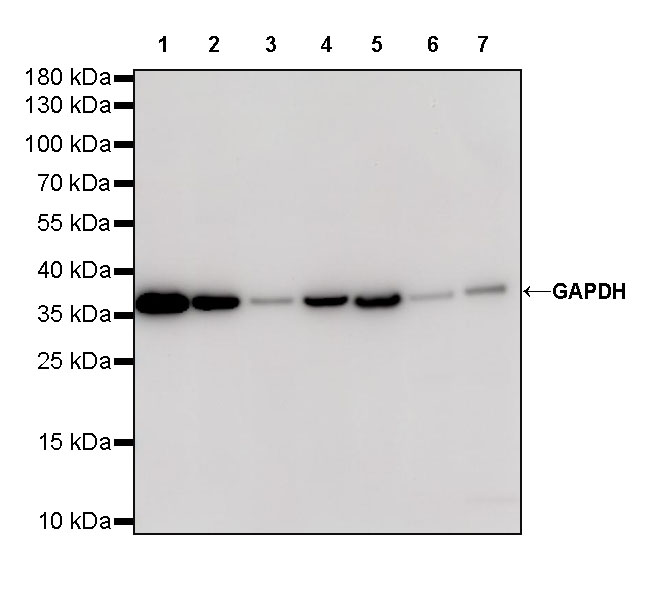
abs132004 Rabbit anti-GAPDH Polyclonal Antibody
β-Tubulin: Approximately 55 kDa, β-Tubulin is a type of microtubule protein involved in the formation of the cytoskeleton. Due to its stable expression in cells, it is particularly used for detecting cytoskeletal proteins. The expression of β-Tubulin is relatively constant in various cell types, but changes in expression under specific conditions, such as in apoptotic cells, should also be considered.

Hela cell lysate

Rat kidney tissue

NIH3T3 cells
abs171597 Rabbit anti-β-Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody
In addition to the internal references mentioned above, there are also α-Tubulin, Hsp90, etc. Each internal reference has different molecular weights and application scenarios, and it is recommended to do some research before making a selection.
4. How to Choose the Right Internal Reference and What Factors to Consider?
Molecular Weight of Target Protein: The molecular weight of the internal reference protein should differ from that of the target protein by at least 5 kDa to ensure clear separation of the bands of the target protein and internal reference in gel electrophoresis and Western Blot.
Sample Species: Different species of samples may require different internal reference proteins. For example, mammalian tissue or cell samples often choose β-actin, β-tubulin, GAPDH, etc., while plant samples may choose plant actin, Rubisco, etc.
Cellular Localization: Select internal references based on the subcellular localization of the target protein. For example, for detecting whole-cell or cytoplasmic proteins, β-actin, β-tubulin, GAPDH, etc., can be chosen; for nuclear proteins, Lamin B, Histone H3, etc., may be used as internal references.
Experimental Conditions: The choice of internal references should also consider the actual experimental environment and sample pretreatment. Under certain special conditions, the expression of some internal reference proteins may change, affecting their stability and reliability as internal references. For example, the expression of GAPDH may increase under hypoxic or diabetic conditions, making it unsuitable as an internal reference.
Tissue Specificity: Different tissues may require different internal references. For example, in muscle tissue, specific actin isoforms may be chosen as internal references, while in non-muscle tissues, β-actin may be selected.
5. How to Incubate Internal Reference Antibodies and Target Antibodies?
Sequential Incubation: After detecting the target protein, use a strip buffer to wash off the antibodies on the membrane, and then re-incubate with the internal reference antibody and perform detection. This method requires using the same membrane for both incubations.
Double Membrane Method: After protein transfer, cut the membrane into two parts based on the size of the pre-stained protein marker to separate the internal reference protein from the target protein. Then, incubate and detect the two membranes separately with internal reference and target protein antibodies.
Simultaneous Incubation (if molecular weights differ significantly): If the molecular weights of the target protein and internal reference protein differ significantly, both antibodies can be incubated simultaneously on the same membrane after transfer. Due to the difference in band positions, both internal reference and target proteins can be detected on the same membrane.
Use of Pre-Labeled Internal Reference Antibodies: Some laboratories use pre-labeled internal reference antibodies (e.g., with HRP). These can be added during the secondary antibody incubation and detected following the normal procedure.
|
Catalog Number |
Product Name |
Specification |
|
Rabbit anti-β-Actin Monoclonal Antibody |
100 μL |
|
|
Rabbit anti-GAPDH Polyclonal Antibody |
100 μg |
|
|
Rabbit anti-β-Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody |
100 μL |
|
|
Mouse anti-β-Actin Monoclonal Antibody |
100 μL |
|
|
Mouse anti-GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
100 μL |
|
|
Rabbit anti-α-Tubulin Polyclonal Antibody |
100 μg |
|
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
April 16, 2025
Clicks:433
