- Cart 0
- English
【IF 14.1】Dual-checkpoint blockade plus radiotherapy shatters the tumor-therapy ceiling! Absin ELISA kits power the “cold-to-hot” switch and abscopal-effect discovery
October 10, 2025
Clicks:82
In oncology, converting immune-excluded “cold” tumors into inflamed “hot” tumors to ignite systemic anti-tumor immunity and eradicate metastases remains a central challenge. A 2025 Advanced Science paper entitled “Bispecific Antibody Targeting VEGF/TGF-β Synergizes with Local Radiotherapy: Turning Tumors from Cold to Inflamed and Amplifying Abscopal Effects” provides an innovative solution: the VEGF/TGF-β bispecific antibody Y332D cooperates with focal radiotherapy (RT) to re-sculpt the tumor microenvironment (TME) and markedly potentiate abscopal responses, offering a new strategy for solid tumors and their metastases. Absin’s mouse CXCL10/IP-10 ELISA kit (cat.# abs520013) supplied the accurate mechanistic data underpinning this work.


I. Background: The “Double-Edged Sword” of Radiotherapy & Rationale for the Bispecific Approach
Focal RT is a front-line modality for solid tumors. Beyond direct DNA double-strand breaks, RT can initiate an immunostimulatory cascade—cGAS-STING activation, immunogenic cell death (ICD), enhanced antigen presentation, and subsequent T-cell priming—thereby theoretically converting a cold tumor into a hot one.
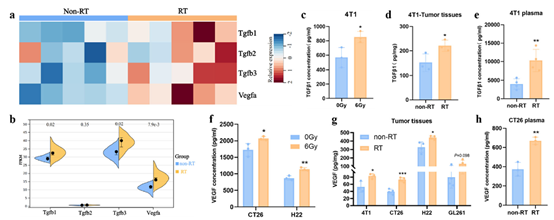
However, RT also elicits compensatory up-regulation of VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) in the TME:
· VEGF drives aberrant angiogenesis, promoting hypoxia and acidosis that suppress cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activity and dendritic cell (DC) maturation;· TGF-β induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), activates cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and recruits immunosuppressive cells (Treg, M2 macrophages), counteracting RT-induced immunity and fostering radioresistance and metastasis.
Therefore, the authors hypothesized that simultaneous blockade of VEGF and TGF-β signaling would neutralize these adverse effects while amplifying RT-mediated immunostimulation.
II. Key Findings: Triple Synergistic Effects of Y332D + RT
Using murine 4T1 breast, CT26 colorectal, H22 hepatocellular, and GL261 glioblastoma models, the team demonstrated three mechanistically distinct but inter-locking benefits:
1. Neutralization of RT-Induced Immunosuppression & Enhanced RadiosensitivityRT elevated VEGF and TGF-β in both tumors and plasma. Y332D dual blockade:
· Inhibited TGF-β–mediated DNA-damage repair (DDR), reducing γ-H2AX foci and tumor-cell radioresistance;
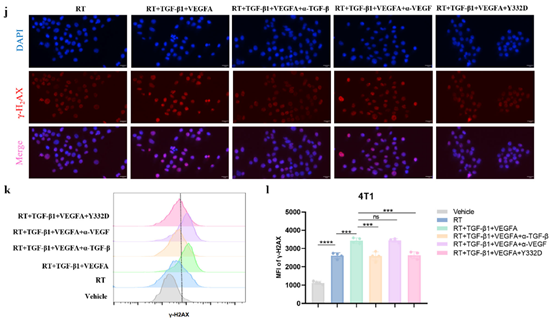
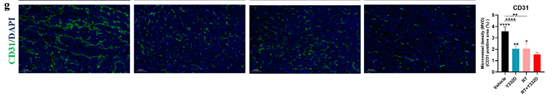
· Normalized VEGF-driven aberrant vasculature: CD31 staining showed reduced micro-vessel density (MVD) and improved oxygenation;
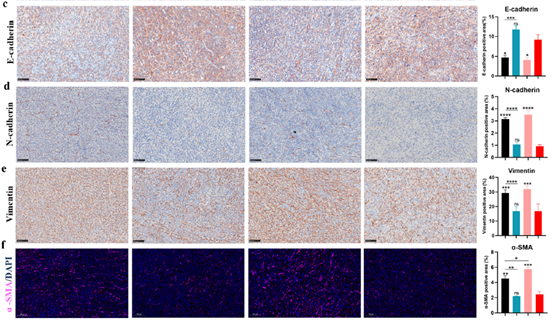
· Suppressed EMT and CAF activation: IHC revealed down-regulation of N-cadherin, Vimentin, and α-SMA, decreasing stromal barriers.
2. Amplification of RT-Induced Immunity: Cold → Hot Conversion
Y332D not only neutralized RT’s negative cues but also boosted its immunostimulatory capacity:
· Promoted DC maturation (CD86+) and M1 macrophage polarization (elevated M1/M2 ratio) by flow cytometry;
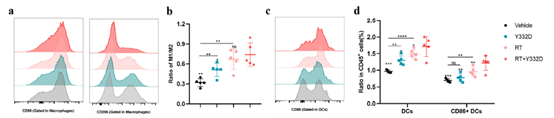
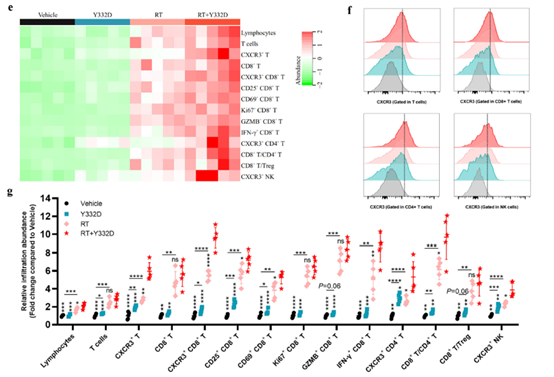
· Enhanced T-cell infiltration and functionality: increased intratumoral CD3+ and CD8+ T cells (activated CD25+/CD69+ and cytolytic GzmB+ subsets) and elevated CD8+/Treg ratio;
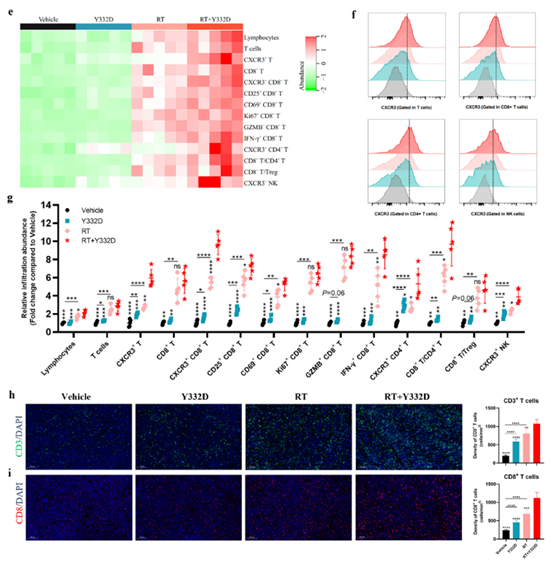
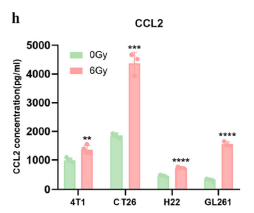
· Activated type-I IFN signaling and chemokine secretion. Absin’s Mouse CXCL10/IP-10 ELISA Kit (abs520013) quantified CXCL10—an IFN-inducible chemokine recruiting CXCR3+ T cells—demonstrating significant up-regulation at both mRNA and protein levels, providing the chemotactic evidence for T-cell trafficking.
3. Elicitation of Abscopal Effects & Metastasis Control
The abscopal effect—regression of non-irradiated metastases via systemic anti-tumor immunity—was evaluated in the 4T1 breast lung-metastasis model:
· RT alone failed to suppress lung metastases, whereas Y332D + RT markedly reduced bioluminescent signals;
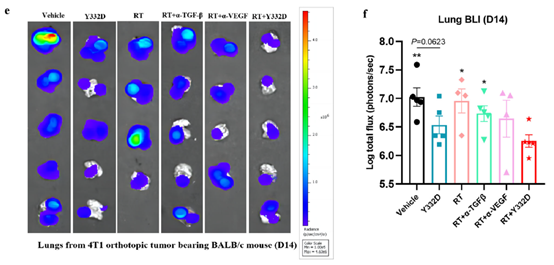
· Mechanistically, the combination augmented CD8+ T-cell and NK-cell infiltration/activation while decreasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in metastatic lungs, providing a cellular explanation for the abscopal response.
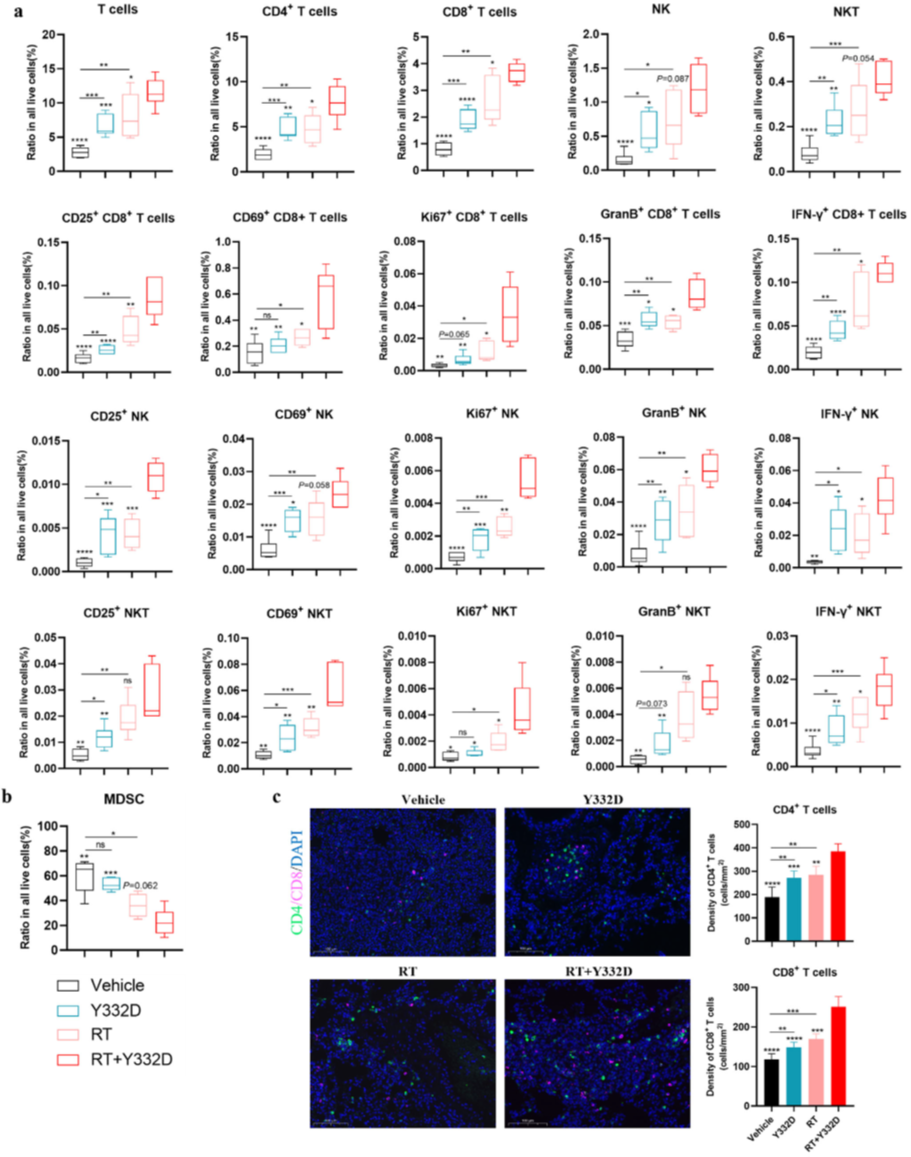
III. abs520013: The “Key Tool” for Chemotaxis Validation
To link IFN signaling to immune-cell recruitment, the authors quantified CXCL10 in:
1. In-vitro tumor-cell supernatants—4T1, CT26, H22, GL261 cells post-RT;
2. In-vivo tumor homogenates—confirming CXCL10 up-regulation within the TME after Y332D + RT.
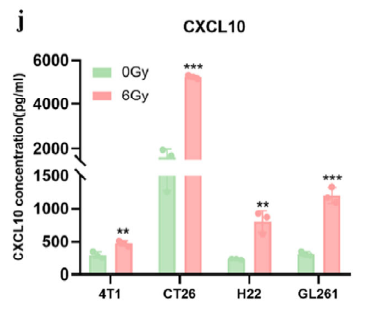
Absin’s high-specificity, high-sensitivity ELISA kit provided the quantitative bridge between pathway activation and T-cell infiltration.
Kit advantages:
· Murine CXCL10-specific antibodies—no cross-reactivity;· pg-level LLoQ—captures subtle RT-induced changes;
· 96-well format—ideal for multi-model, multi-time-point studies.
IV. Significance & Future Directions
This study establishes a “bispecific + RT” paradigm that simultaneously cuts immunosuppressive signaling and amplifies immunostimulatory cues, converting local therapy into systemic anti-tumor immunity against metastatic disease.
Absin continues to support such breakthroughs with high-precision reagents. Beyond abs520013, our portfolio covers ELISAs for IFN-β, TGF-β, VEGF, flow-cytometry antibodies, and integrated tumor-immunology solutions.
Reference:
Bispecific Antibody Targeting VEGF/TGF‐β Synergizes with Local Radiotherapy: Turning Tumors from Cold to Inflamed and Amplifying Abscopal Effects. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun 5.
Product Used
|
Cat.# |
Product Name |
Application |
|
Quantify CXCL10 in serum, plasma, and cell-culture supernatants |
More ELISA Kits
For more product information or technical support, please visit the Absin official website at www.absin.net or contact our technical support team. We are dedicated to providing you with professional services!
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
