- Cart 0
- English
Protein/Antibody Labeling Solutions
1. Introduction
Antibody/protein labeling technology is a method that utilizes specific labeling agents (such as fluorescent dyes, enzymes, metal ions, etc.) to label antibodies or proteins, thereby facilitating the tracking, localization, and quantitative analysis of target molecules through various detection methods. This technology has extensive applications in the fields of biomedical research, clinical diagnostics, and drug development.
Protein and Dye Preparation → Protein and Dye Ratios and Incubation → Protein Purification → Detection
2. Biotin Labeling Scheme
The biotin and avidin system is a biomolecular recognition system with extremely high affinity. The binding constant between biotin and avidin is at least 10,000 times higher than that of antigen-antibody interactions, representing the strongest non-covalent interaction known to date. Biotinylated proteins can be used for studies of protein-protein interactions and protein purification, while biotinylated antibodies are applicable in techniques such as Western Blot (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
2.1 Avi-Tag Protein Biotinylation
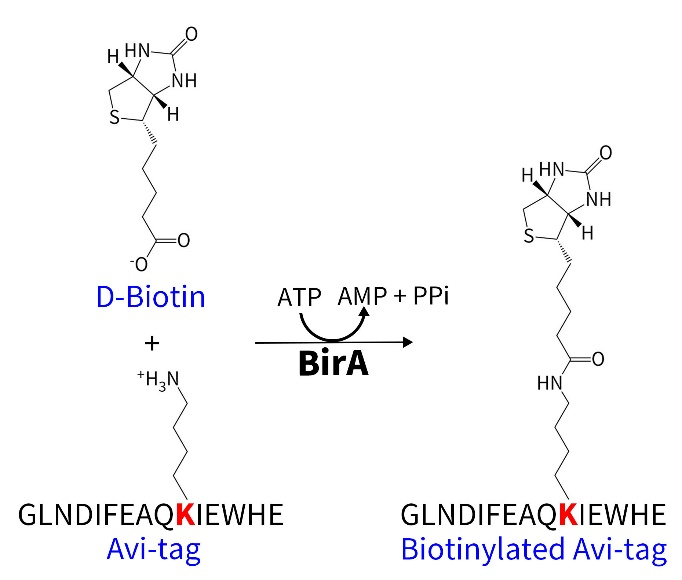
The Avi tag is a short peptide tag composed of 15 amino acid residues (GLNDIFEAQKIEWHE), which contains a biotinylatable lysine residue. The biotin ligase (BirA) can specifically recognize the Avi tag and, in the presence of ATP, covalently link biotin to the lysine residue of the Avi tag. In the presence of ATP, the biotin ligase (BirA) first activates biotin to form biotinyl-5'-adenylate. The activated biotin is then conjugated to the lysine residue within the Avi tag, thereby completing the biotinylation. This method is highly specific, acting only on the Avi tag sequence without labeling other proteins or amino acid residues. Moreover, the reaction conditions are mild and have minimal impact on protein activity.
|
CatalogNumber |
Product Name |
Specification |
|
Biotin Labeling for Avitag Protein Kit |
200ug/1mg |
Product Features:
1) Site-specific labeling, with minimal impact on protein activity;
2) BirA derived from coli, with purity > 95%, endotoxin < 0.5 EU/µg.
Results Display:

2.2 Chemical Biotinylation of Proteins
Chemical labeling is a method that involves the conjugation of biotin molecules to the free amino groups at the N-terminus of proteins and the amino groups on the side chains of internal lysine residues. Typically, multiple biotin molecules are attached to a single protein molecule. This method is characterized by high sensitivity and the absence of a tag, making it one of the commonly used approaches in biological research.
|
CatalogNumber |
Product Name |
Specification |
Features |
|
Biotin Microscale Protein Labeling Kit |
1kit |
A single conjugation reaction is capable of labeling up to 200 µg of protein. The entire reaction can be completed in as little as 30 minutes. |
|
|
Biotin Labeling Kit |
1T/2T/3T |
It is applicable for labeling both antibodies and proteins, with an optimized biotin-to-antibody labeling ratio for antibody labeling, allowing up to 1 mg of antibody to be labeled per reaction, and the labeling process can be completed in approximately 1 hour. |
3. Antibody HRP Conjugation Scheme
Sodium periodate (NaIO₄) is capable of oxidizing the carbohydrate chains of glycoproteins, converting the dihydroxy groups within these chains into aldehyde groups. These aldehyde groups can subsequently react with the amino groups present on antibodies to form Schiff bases. Following this, through a reduction reaction with sodium borohydride (NaBH₄), the Schiff bases are transformed into stable secondary amine bonds, thereby achieving covalent conjugation between horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and the antibody.
|
CatalogNumber |
Product Name |
Specification |
HRP Quantity |
Antibody Labeling Capacity |
Recommended Antibody Labeling Concentration |
|
HRP Rapid Conjugation Kit |
100ug |
100ug |
67ug-100ug |
3~6mg/mL |
|
|
300ug |
300ug |
201ug-300ug |
|||
|
500ug |
500ug |
333ug-500ug |
4. Antibody (Protein) FITC Conjugation Scheme
The isothiocyanate group in FITC molecules is a reactive group that can react with the amino groups present in proteins. By dissolving FITC in an appropriate solvent (such as dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO) and then adding it to a protein solution, the isothiocyanate group of FITC reacts with the amino groups in the protein to form a thiourea bond (-NH-CO-NH-), thereby covalently attaching FITC to the protein.
|
CatalogNumber |
Product Name |
Specification |
|
Quick FITC Antibody(protein) Labeling Kit |
3T |
Product Features:
1 )Simple operation, with protein labeling and purification completed in approximately one hour.
2) Optimized F/P ratio, with each T capable of labeling approximately 1 mg of protein.
3) No need to weigh small amounts of powder; the kit includes disposable reagent vials.
4) Includes purification resin and centrifugal columns to ensure rapid and efficient removal of unreacted dye and achieve excellent protein recovery.

Immunofluorescence microscopy of A549-GAPDH cell slides, with FITC-IgG (goat anti-rabbit) secondary antibody labeled with abs90007.
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
July 28, 2025
Clicks:92
