- Cart 0
- English
[IF 16.6] PRMT3 Regulates IDO1 Metabolic Axis: Novel Mechanism of Radioresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
February 09, 2026
Clicks:78
Recently, a study on radioresistance mechanisms in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) published in Cancer Research not only revealed the central role of the PRMT3-TFAP2A-IDO1-Kyn axis in radioresistance and immunosuppression in lung cancer, but also provided novel therapeutic targets for clinical treatment. Notably, the mIHC experiments in this study relied on the absin mIHC kit for precise protein localization and expression analysis, fully demonstrating the supporting value of absin tools for high-quality scientific research.
Publication Title: PRMT3 Drives IDO1-Dependent Radioresistance and Immunosuppression by Promoting Kynurenine Metabolism in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
Journal: Cancer Research (IF=16.6)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-4162
Absin Products Used: Extracellular Matrix (High Concentration, Phenol Red-free) (abs955), Four-Color Multiplex Immunofluorescence Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary) (abs50028)



I. Research Strategy: Decoding the "Metabolism-Immunity" Dual Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Radioresistance
Radioresistance in NSCLC is one of the primary causes of clinical treatment failure, with metabolic reprogramming and immune microenvironment dysregulation being two core drivers of tumor resistance. The research team initiated with "identifying key regulators of radioresistance" and explored through the following logical framework:
1. Screening Key Regulatory Factors: By comparing PRMT family gene expression between NSCLC patients with radioresponsive and non-responsive tumors, PRMT3 was found to be significantly overexpressed in the non-responsive group and associated with poor patient prognosis, initially identifying PRMT3 as the core research target.2. Investigating Metabolic Regulatory Pathways: Through 4D-Fast DIA proteomics and untargeted metabolomics analysis, PRMT3 overexpression was found to significantly activate the tryptophan-kynurenine (Kyn) metabolic pathway, with Kyn being the most significantly upregulated metabolite, suggesting that PRMT3 may influence radiosensitivity through regulation of Kyn metabolism.
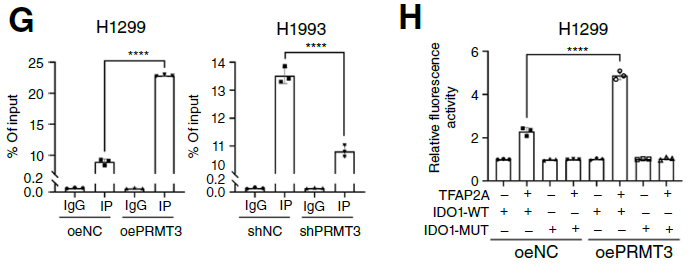
3. Elucidating Molecular Mechanisms: Further through transcription factor prediction, Co-IP, and dual-luciferase reporter assays, the study confirmed that PRMT3 methylates transcription factor TFAP2A, prolonging its half-life, promoting nuclear localization and dimerization, thereby enhancing the transcriptional activity of IDO1 (the key enzyme in Kyn metabolism), forming the "PRMT3-TFAP2A-IDO1-Kyn" regulatory axis.
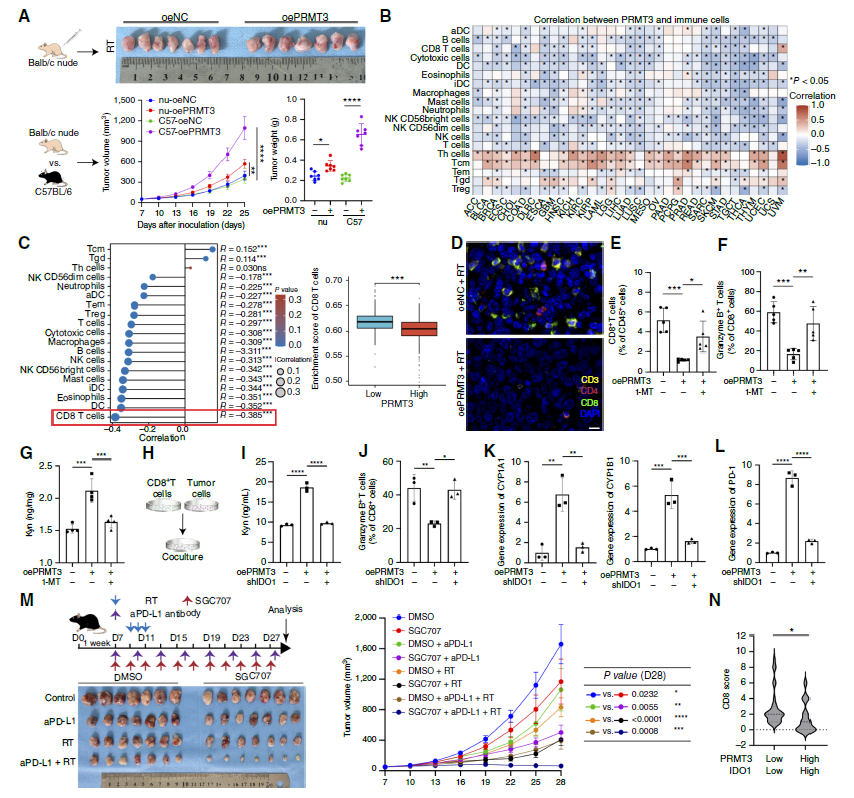
4. Correlating with Immune Microenvironment: Combining animal models and clinical sample analysis, PRMT3-mediated Kyn accumulation was found to activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in CD8+ T cells, leading to T cell exhaustion (high PD-1 expression) and functional suppression, forming a "metabolic dysregulation-immunosuppression" vicious cycle that exacerbates radioresistance.
5. Validating Therapeutic Strategies: In PDX models and patient-derived organoids (PDO), combined inhibition of PRMT3 (SGC707) and IDO1 (1-MT) was confirmed to effectively block the above regulatory axis, reverse radioresistance and activate anti-tumor immunity, providing evidence for clinical combination therapy.
II. Research Findings: Three Core Discoveries Providing New Directions for Lung Cancer Treatment
Through rigorous cellular experiments, animal models, and clinical sample validation, this study achieved three key outcomes:
1. PRMT3 is the "Culprit" of NSCLC Radioresistance: PRMT3 overexpression significantly enhanced clonogenic capacity, migration, and proliferation of NSCLC cells, reduced radiation-induced ROS production and apoptosis rates (Fig. 1I), and decreased accumulation of DNA damage marker γH2AX (Fig. 1J, K); conversely, PRMT3 knockdown or inhibitor SGC707 significantly enhanced radiosensitivity, significantly reducing tumor volume in PDX models (Fig. 1M).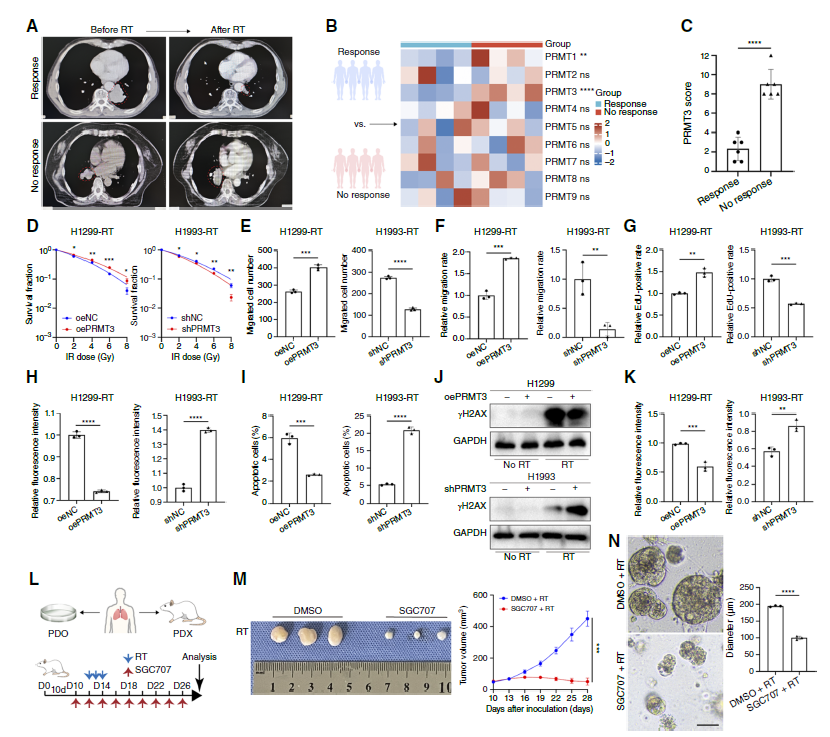
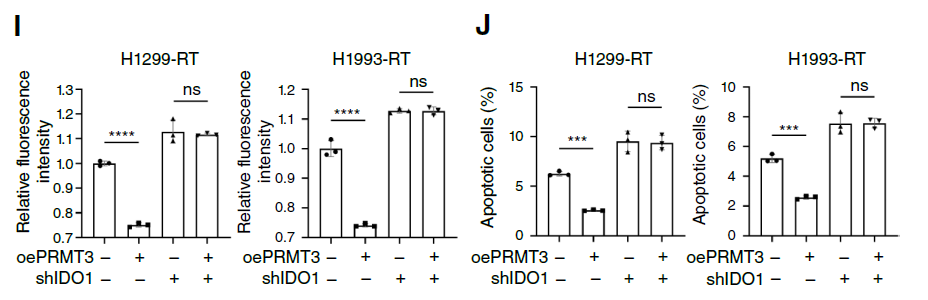
3. Kyn-AhR Pathway Mediates Immunosuppression, Combined Targeted Therapy Shows Efficacy: PRMT3-mediated Kyn accumulation significantly reduced CD8+ T cell infiltration (Fig. 4C, D) and inhibited their cytotoxic function (reduced granzyme B expression, Fig. 4J); combined use of PRMT3 inhibitor, IDO1 inhibitor, and radiotherapy significantly enhanced CD8+ T cell activity in mouse models (Fig. 4M), and this effect disappeared after CD8+ T cell depletion, confirming immune activation as the key mechanism of combined therapy efficacy. Furthermore, clinical sample analysis showed that PRMT3(high)/IDO1(high) patients had significantly lower radiotherapy response rates than PRMT3(low)/IDO1(low) patients (Fig. 8F, G), suggesting this axis as a biomarker for predicting radiotherapy efficacy.
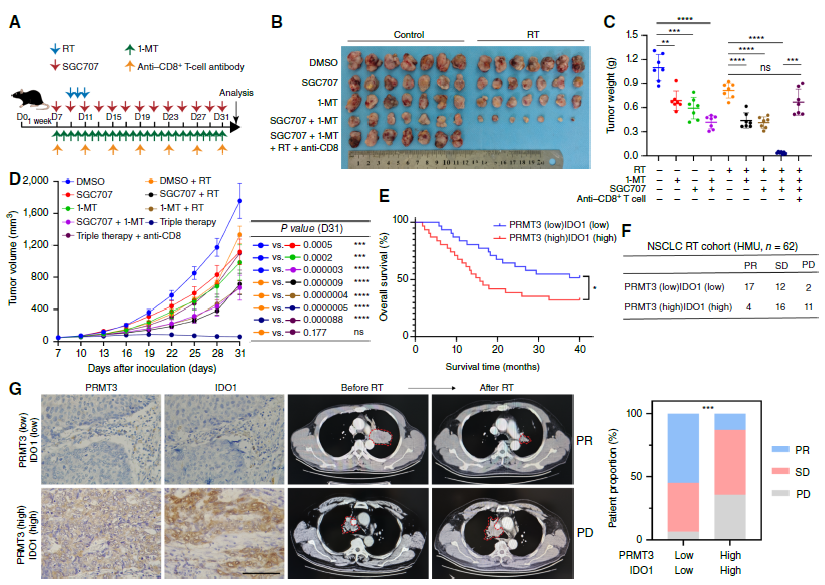
III. Absin Product Applications: "Precision Localization Tools" for Immunofluorescence Experiments
In elucidating the interaction and protein localization of PRMT3 and TFAP2A, immunofluorescence (IF) experiments were key technical approaches. This study utilized absin's Four-Color Multiplex Immunofluorescence IHC Kit (abs50028) to complete the following core experiments, providing direct visual evidence for mechanism validation:
1. Colocalization Validation of PRMT3 and TFAP2A: Through staining of H1299 and H1993 cells with this kit, clear colocalization signals of PRMT3 and TFAP2A in the nucleus were observed (Fig. 5D), directly confirming their intracellular interaction and providing prerequisite evidence for subsequent Co-IP experiments.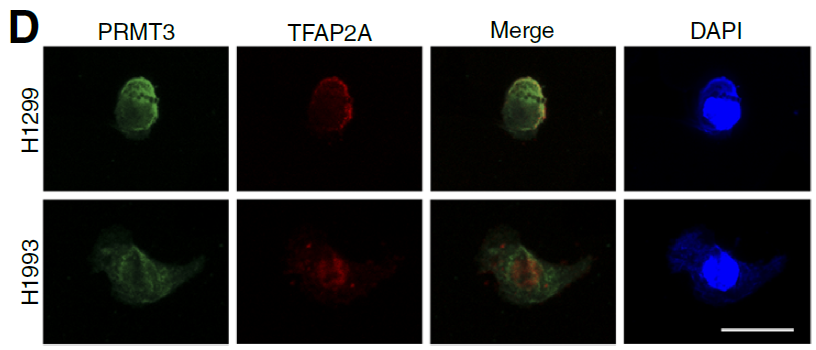


IV. Summary and Outlook: From Basic Research to Clinical Translation, Absin Provides Comprehensive Support
This study not only revealed novel mechanisms of NSCLC radioresistance but also proposed a "targeting metabolism-immunity axis" combination therapy strategy, providing new directions for clinical precision treatment. As a "partner" in life science research, absin consistently supports scientific innovation with high-quality reagent products—from immunofluorescence, Western blot to flow cytometry analysis, absin's product portfolio can meet research needs in tumor metabolism, immune microenvironment, signal transduction, and other fields.
This article is based on the original publication in Cancer Research (DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-4162); original figures, data, and intellectual property rights belong to the original journal and research team. If any infringement exists, please contact us promptly for removal, and we will actively cooperate in handling the matter.
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| abs50028 | Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) | 20T/50T/100T |
| abs955 | Immunoprecipitation (IP/CoIP) kit | 50T |
Contact Absin
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
