- Cart 0
- English
Breakthrough in Top-Tier Journal: Absin mIHC Kit Facilitates Discovery of Novel Anti-Myocardial Fibrosis Target, Decoding SARM1 Palmitoylation Regulatory Mechanism
February 03, 2026
Clicks:71
Myocardial fibrosis serves as the common pathological substrate for various cardiovascular diseases progressing to heart failure, with complex pathogenesis and a lack of precise therapeutic targets in clinical practice. Recently, a landmark study was published in the prestigious international journal Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, revealing for the first time that ZDHHC17-mediated SARM1 palmitoylation promotes collagen deposition and myocardial fibrosis by targeting the collagen synthesis key enzyme P4HA1, and identified potential therapeutic agents. In this breakthrough research, Absin core products provided comprehensive support for critical mechanistic validation, offering reliable experimental backing for the smooth progression of the study.
Title: Palmitoylated SARM1 targeting P4HA1 promotes collagen deposition and myocardial fibrosis: A new target for anti-myocardial fibrosis
Journal: Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (IF=14.6)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2025.07.011
Absin Products Used: Four-Color Multi-Label Immunofluorescence Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) (Cat. No.: abs50028)


I. Core Focus: Layered Research Strategy Deciphering the Fibrosis Puzzle
The research team led by Academician Bao-Feng Yang designed a progressive experimental approach centered on "identifying key regulatory factors of myocardial fibrosis," systematically uncovering the role and regulatory mechanisms of SARM1 in fibrotic progression:
- Step 1: Establishing the Association Between SARM1 and Myocardial Fibrosis: Bioinformatic analysis of the GSE116250 dataset revealed significantly elevated SARM1 expression in cardiac tissues from cardiomyopathy patients. Subsequently, mouse myocardial infarction (MI) models and TGF-β1-induced neonatal mouse cardiac fibroblast (NMCFs) models were employed to validate SARM1 expression characteristics in fibrotic tissues/cells, preliminarily establishing the "elevated SARM1 expression - myocardial fibrosis" association.
- Step 2: Functional Validation of SARM1: Gene knockdown and overexpression techniques were applied both in vivo (mouse models) and in vitro (NMCFs) to systematically evaluate SARM1 effects on cardiac function, collagen deposition, and fibroblast proliferation/migration, confirming the core function that "SARM1 promotes myocardial fibrosis."
- Step 3: Screening and Validation of SARM1 Downstream Targets: Co-immunoprecipitation/mass spectrometry (Co-IP/MS) was utilized to screen SARM1-interacting proteins, identifying the collagen synthesis key enzyme P4HA1. Immunofluorescence, Co-IP, and rescue experiments confirmed direct SARM1-P4HA1 binding and functional regulation, establishing their upstream-downstream relationship.
- Step 4: Elucidating Upstream Regulatory Mechanisms of SARM1: Combining bioinformatic prediction with click chemistry, SARM1 palmitoylation was confirmed. Candidate enzyme screening and functional validation identified ZDHHC17 as the key enzyme mediating SARM1 palmitoylation, with CYS13 as the core modification site. The complete pathway "ZDHHC17→SARM1(C13) palmitoylation→enhanced SARM1 stability→P4HA1 binding→collagen deposition→myocardial fibrosis" was ultimately elucidated.
- Step 5: Screening SARM1-Targeted Anti-Fibrotic Agents: Screening of potential SARM1 inhibitors revealed that berberine (BBC) binds to the SARM1 palmitoylation site to inhibit its function. Additionally, the clinical-stage drug Selonsertib was confirmed to ameliorate myocardial fibrosis by downregulating the SARM1-P4HA1 pathway, offering potential for clinical translation.
II. Landmark Findings: Unlocking Novel Anti-Fibrotic Targets and Therapeutic Strategies
Through systematic in vivo and in vitro experiments, this study achieved multiple breakthrough findings, providing novel directions for myocardial fibrosis treatment:
- First identification of SARM1 as a key pro-fibrotic regulatory factor, with expression levels positively correlated with fibrosis severity; SARM1 knockdown significantly improves cardiac function and reduces collagen deposition.
- P4HA1 was established as the core downstream target of SARM1. SARM1 activates collagen synthesis pathways through direct P4HA1 binding, accelerating fibrotic progression. The binding sites are highly conserved across species, providing a foundation for cross-species research.
- ZDHHC17-mediated SARM1(C13) palmitoylation was revealed as the critical mechanism regulating SARM1 function, significantly enhancing SARM1 protein stability. This site provides a precise target for anti-fibrotic drug development.
- Two classes of potential therapeutic agents were identified: berberine (BBC) directly binds the SARM1 palmitoylation site to inhibit its activity; the Phase III clinical drug Selonsertib exerts anti-fibrotic effects by downregulating the SARM1-P4HA1 pathway, providing evidence for drug repurposing.
III. Absin Support: Core Products Enabling Critical Experiments and Precise Mechanistic Validation
In this high-impact study, the Absin Four-Color Multi-Label Immunofluorescence Kit (Cat. No.: abs50028), with its high specificity and sensitivity, participated throughout the co-localization and expression validation of SARM1 with key proteins, serving as an important guarantee for experimental success.
1. Core Application: mIHC Detection Indicators and Experimental Conclusions
The research team utilized the Absin Four-Color Multi-Label Immunofluorescence Kit (abs50028) to examine myocardial tissues from the infarct border zone of MI mice. Core detection targets included three key proteins: ZDHHC17, SARM1, and α-SMA, with DAPI nuclear counterstaining for cellular localization.
Through multi-color labeling and co-localization analysis with this kit, definitive conclusions were reached: ZDHHC17 and SARM1 exhibit significant co-expression in cardiac fibroblasts, with their co-localization regions highly overlapping with the expression zones of the fibrosis marker α-SMA. These results directly demonstrate that ZDHHC17 and SARM1 undergo direct interaction at critical fibrotic sites (cardiac fibroblasts) during MI-induced fibrosis, providing histological evidence for the core mechanism of "ZDHHC17-mediated SARM1 palmitoylation."
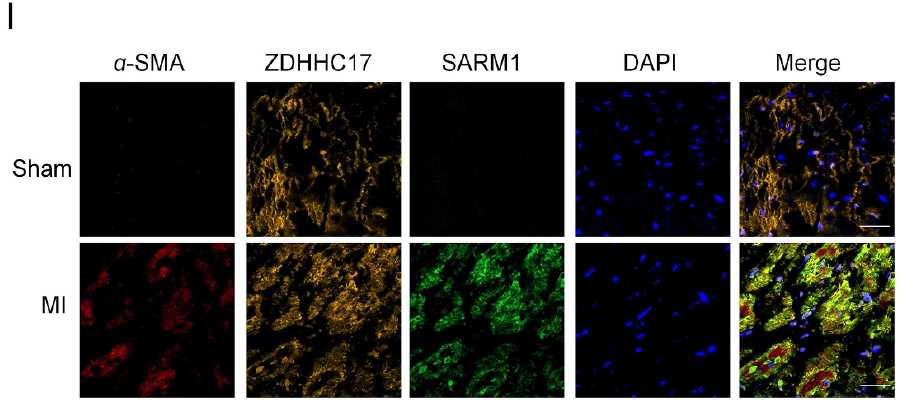
Figure 6I (Four-color multi-label immunofluorescence staining of ZDHHC17, SARM1, and α-SMA in cardiac fibroblasts from the infarct border zone of MI tissue)
2. Core Product Advantages: Empowering Multi-Target Joint Detection
The Absin Four-Color Multi-Label Immunofluorescence Kit (abs50028) earned the favor of top-tier journal research due to three core advantages:
- Multi-Color Compatibility: Supports simultaneous detection of 4 target proteins, obtaining multi-target co-localization information without repeated staining, significantly improving experimental efficiency.
- Signal Stability: Optimized staining system effectively reduces non-specific binding, with clear fluorescence signals and low background, ensuring result accuracy and reproducibility.
- Broad Applicability: Compatible with various sample types including tissue sections and cell coverslips, meeting unified detection requirements for in vivo and in vitro experiments, providing comprehensive support for mechanistic validation.
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Research Application |
|---|---|---|
| Four-Color Multi-Label Immunofluorescence Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) | abs50028 | Co-localization detection of ZDHHC17, SARM1, and α-SMA proteins |
V. Summary: Mechanistic Breakthroughs Leading Clinical Translation, Research Tools Empowering Innovative Discovery
Through systematic layered investigation, this study first completely elucidated the "ZDHHC17-SARM1(C13) palmitoylation-P4HA1" molecular pathway regulating myocardial fibrosis. This not only fills gaps in mechanistic research in this field but also successfully identifies the SARM1 palmitoylation site as a precise therapeutic target, providing clear direction for anti-myocardial fibrosis drug development. The discovery of two potential agents, berberine and Selonsertib, further accelerates the translation from basic research to clinical application, bringing new therapeutic hope to cardiovascular disease patients.
Notably, the Absin Four-Color Multi-Label Immunofluorescence Kit (abs50028) played an indispensable role in critical mechanistic validation. Its high specificity and multi-color compatibility provided precise and reliable data support for key experiments such as protein co-localization, fully demonstrating the empowering value of high-quality research reagents for major scientific breakthroughs. Moving forward, Absin will continue to uphold the "quality first" philosophy, continuously optimizing product performance to provide superior experimental tools for global researchers, facilitating more innovative discoveries and clinical translations in life sciences.
This article is based on the original publication in Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.07.011); images and data referenced herein are intellectual property of the original journal and research team. Should any infringement occur, please contact us promptly for removal, and we will actively cooperate.
