- Cart 0
- English
Breaking the AAA Research Bottleneck: Absin Tools Decipher the IRF8–cDC1–CD8 T-Cell Pathogenic Axis
January 20, 2026
Clicks:102
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), a globally prevalent and lethal vascular disorder, is characterized by a complex pathogenesis and lacks effective pharmacological interventions. A landmark study recently published in Advanced Science has, for the first time, delineated that interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) exacerbates aortic wall injury by driving conventional type 1 dendritic cell (cDC1) differentiation and CD8+ T-cell activation, thereby offering a novel therapeutic target for AAA. The Absin mIHC kit underpinned a pivotal experimental step in this work and witnessed this major scientific breakthrough.
Title: IRF8 Drives Conventional Type 1 Dendritic Cell Differentiation and CD8+ T Cell Activation to Aggravate Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Development
Journal: Advanced Science (IF 14.1) | DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202416238
Absin product used: 7-color multiplex immunofluorescence staining kit (universal anti-mouse/rabbit secondary) (abs50015)
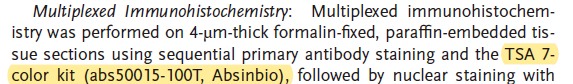
I. Research Rationale: Targeting the Immune-Cell Axis to Decode AAA Pathogenesis
1. Scientific question: Although dendritic cells (DCs) are known to critically regulate AAA progression, the precise subtype(s) and upstream transcriptional control remain elusive. Does IRF8—a master regulator of cDC1 development—participate in AAA pathobiology?
2. Framework: A step-wise pipeline—“clinical specimen validation → animal-model perturbation → cellular/molecular mechanism → human-data corroboration”—was adopted to dissect IRF8 function and its downstream circuitry.
3. Core logic: IRF8 over-expression (Irf8-OE) and DC-specific knockout (Irf8ΔDC) mice, together with cDC1-deficient Batf3−/− animals and ex-vivo assays, were used to establish the IRF8–cDC1–CD8+ T-cell axis as a disease driver.
II. Key Findings: Four Breakthroughs Reshaping AAA Immunotherapy
1. IRF8 is markedly up-regulated in AAA
Both human AAA lesions and murine models displayed prominent IRF8 enrichment within HLA-DR+ DCs, and expression intensity positively correlated with aneurysm severity (Fig. 1D–F). This first demonstration of IRF8–AAA association laid the groundwork for mechanistic dissection.
2. Bidirectional control of AAA by IRF8
- Irf8-OE mice: exhibited aggravated AAA dilation, extensive elastin fragmentation, increased collagen deposition and pronounced inflammatory infiltration (Fig. 2A–E).
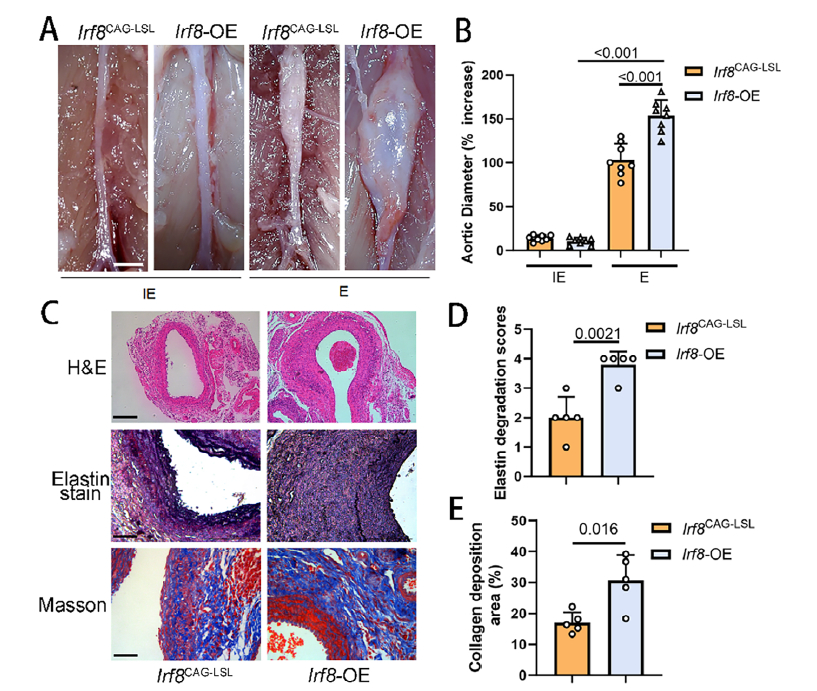
Phenotypic analysis of Irf8-OE AAA mice (Fig. 2A–E)
- Irf8ΔDC mice: displayed markedly attenuated AAA expansion, preserved aortic architecture and diminished inflammation (Fig. 2F–J).
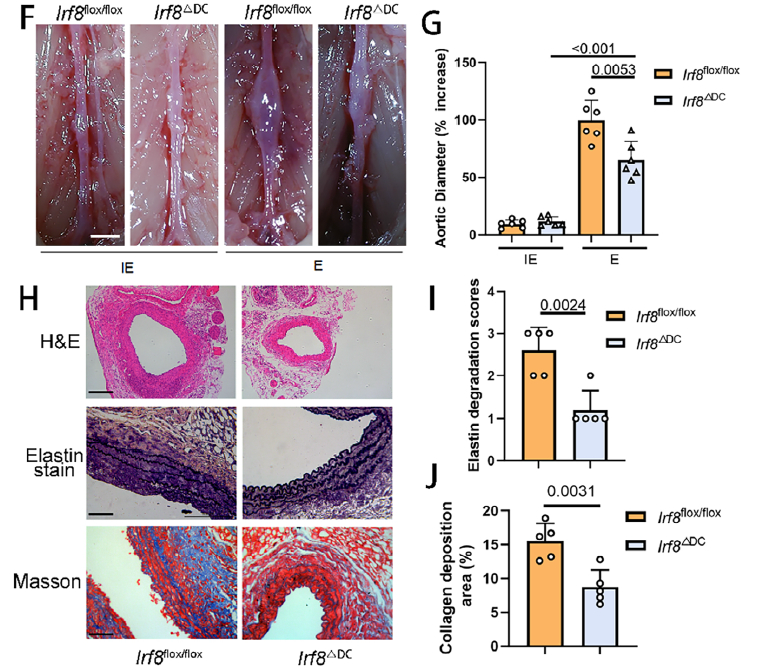
Phenotypic analysis of Irf8ΔDC AAA mice (Fig. 2F–J)
3. cDC1 is the key downstream executor of IRF8
Single-cell RNA-seq and flow cytometry identified cDC1 as the dominant IRF8-expressing population within AAA lesions (Fig. 3A–D). Batf3−/− mice, lacking cDC1, mirrored the protective phenotype of Irf8ΔDC animals, formally demonstrating that IRF8 operates via cDC1 (Fig. 3E–F).
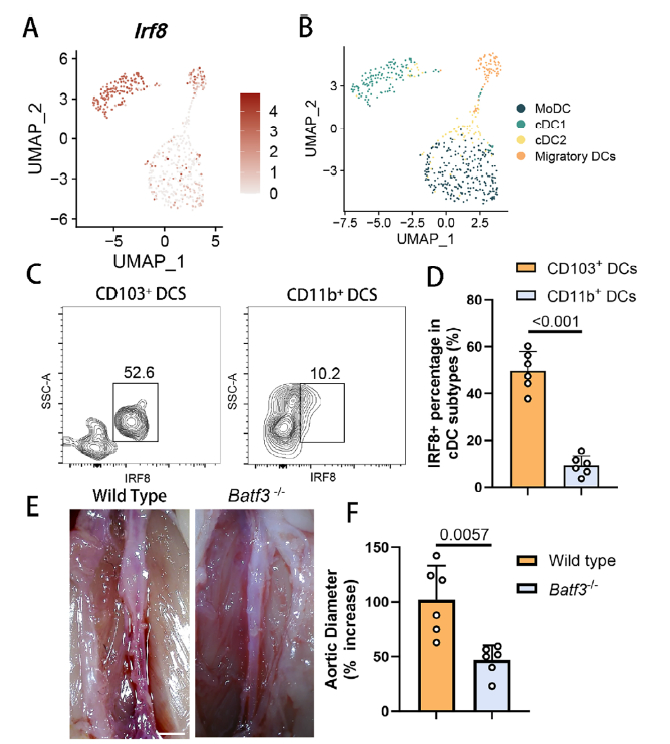
Validation of cDC1 as IRF8 downstream executor (Fig. 3A–F)
4. The IRF8–cDC1–CD8+ T-cell axis mediates aortic injury
- cDC1 activate CD8+ T cells: Irf8-OE animals showed elevated CD8+ T-cell maturation marker CD69 and increased TNF-α/IFN-γ production (Fig. 4A–F), whereas these responses were blunted in Irf8ΔDC mice (Fig. 4G–H).
- Axis blockade ameliorates AAA: Disrupting cDC1–CD8+ T-cell interaction (Clec9a−/− mice or CLEC9A-neutralizing antibody) significantly reduced aneurysmal dilation (Fig. 4I–L).
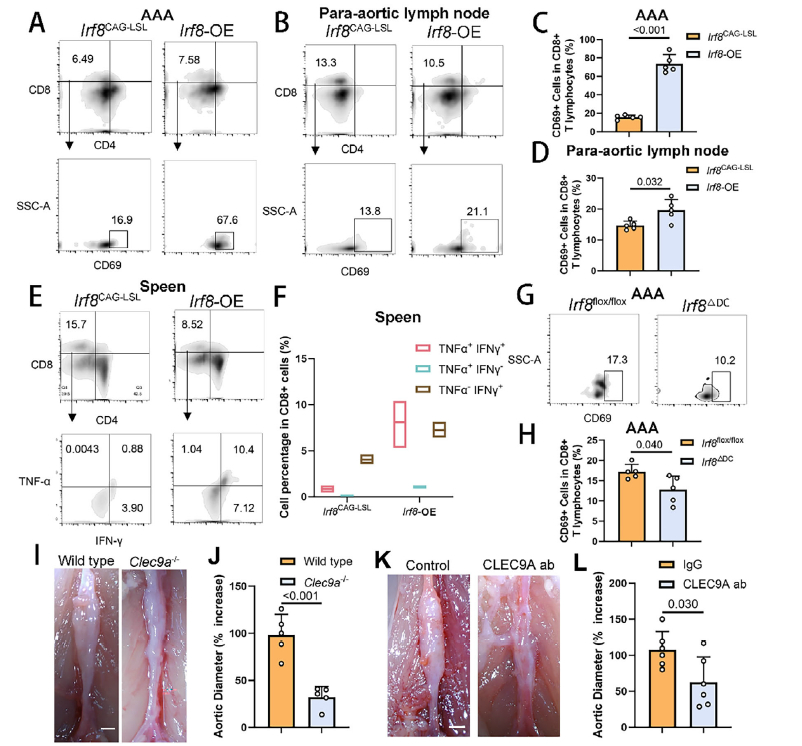
IRF8–cDC1–CD8+ T-cell axis governs AAA progression (Fig. 4A–L)
- Final effector mechanism: Activated CD8+ T cells trigger vascular smooth-muscle-cell apoptosis, thereby destabilizing the aortic wall (Fig. 5A–F).
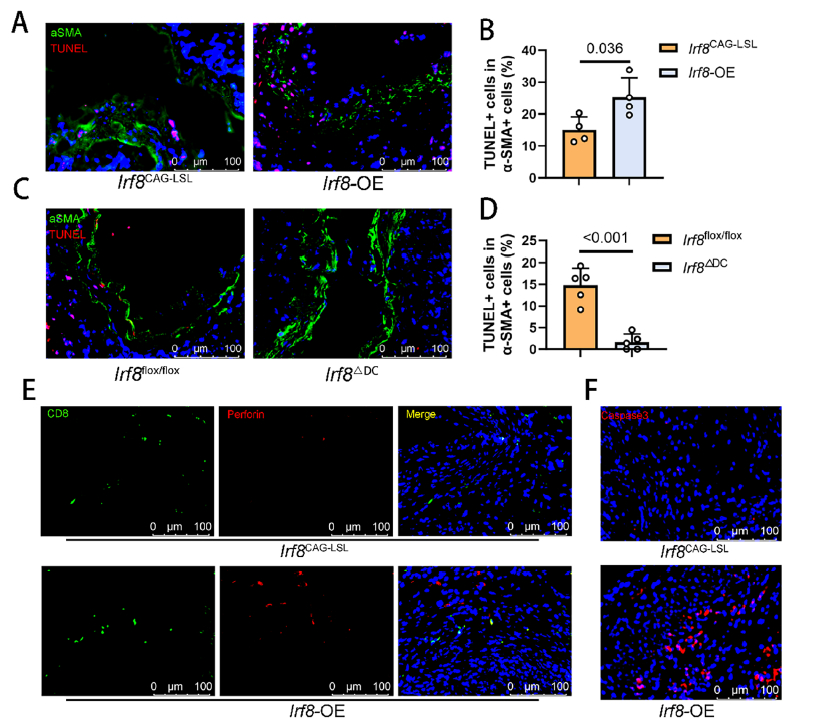
CD8+ T-cell-induced aortic SMC apoptosis (Fig. 5A–F)
III. Absin Products: Core Enablers of Critical Experiments
1. Product list
| Product | Cat. No. | Application |
|---|---|---|
| TSA 7-color kit | abs50015 | Multiplex immunohistochemistry |
2. Experimental role
To map the distribution of IRF8 and perforin (a CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity marker) in human AAA specimens, the authors employed the Absin TSA 7-color kit (abs50015-100T) together with HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit/mouse secondary antibodies for multiplex immunostaining.
- Simultaneous multi-marker detection: IRF8 (green) and perforin (yellow) were co-visualized on a single section, revealing their colocalization in AAA lesions (Fig. 7A).
- Signal amplification & specificity: HRP-secondary antibodies and TSA-mediated tyramide deposition ensured robust fluorescence, enabling precise detection of low-abundance targets and providing direct visual evidence that “IRF8 expression is elevated in human AAA and correlates with enhanced cytotoxicity” (Fig. 7C).
- Data reliability: These human data corroborated murine findings, consolidating the translational relevance of the IRF8–cDC1–CD8+ T-cell axis.
IV. Illustration: How Absin Empowered the Key Result
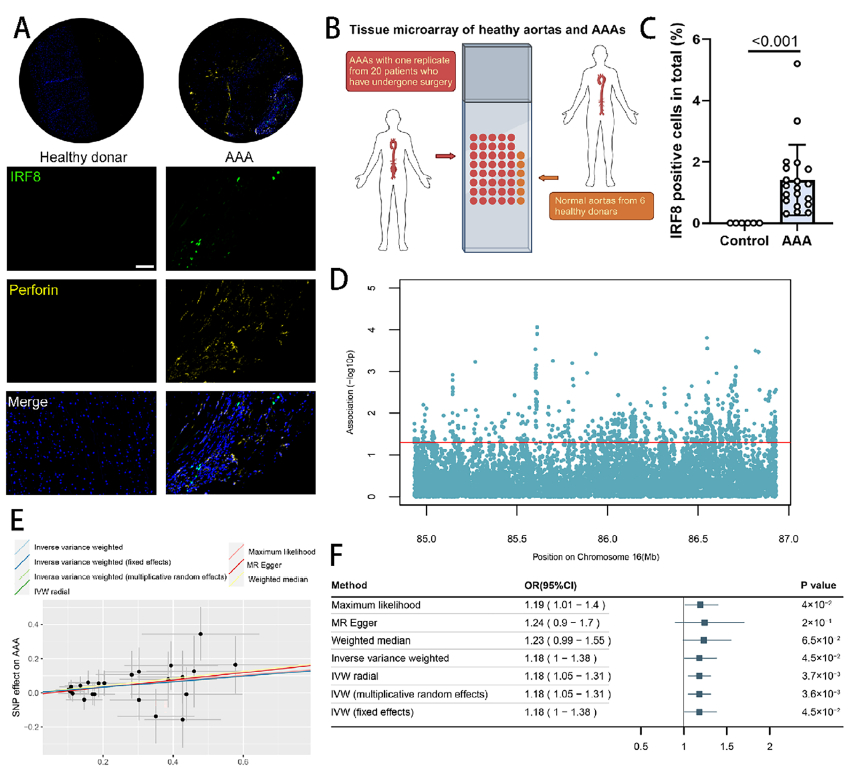
IRF8 and perforin expression in human AAA tissue (Fig. 7A)
As shown, multiplex IHC with the Absin kit revealed extensive overlap between IRF8- and perforin-positive areas, with IRF8 abundance significantly higher in AAA than in normal aorta (P<0.001). This direct visual evidence supports the conclusion that “IRF8 fuels CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity and thereby AAA progression,” forming a cornerstone of the study’s clinical dataset.
V. Empowering Discovery: Absin Walks with Scientific Innovation
As a life-science tool provider dedicated to high-quality reagents, Absin offers integrated solutions spanning immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and molecular biology. Our participation in this AAA breakthrough highlights the superior sensitivity and specificity of Absin products and underscores their value in deciphering mechanisms of major diseases.
Moving forward, Absin will continue to focus on unmet research needs, iterate product portfolios, and deliver ever more efficient and precise tools for cardiovascular, cancer and immunology studies—exploring the unknown frontiers of life science together with the global research community.
Content is based on the Advanced Science article (DOI: 10.1002/advs.202416238); all original figures and data are the intellectual property of the journal and the authors. Should any infringement occur, please contact us for prompt removal.
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Antibody eluent (for mIHC) |
30ml |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
