- Cart 0
- English
Breaking Immunotherapy Resistance: Absin mIHC Kit Powers PVR-Targeted Therapy That Reprograms the Tumor Microenvironment and Doubles PD-1 Blockade Efficacy
January 20, 2026
Clicks:91
In the field of tumor immunotherapy, "cold tumors" exhibit low response rates, monotherapies targeting single molecules readily acquire resistance, and the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) is governed by highly complex mechanisms—bottlenecks that have long impeded both bench-to-bedside translation and fundamental research. A recent landmark study published in Cell Death & Differentiation identifies the poliovirus receptor (PVR, CD155) as a novel target and successfully dismantles myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC)-mediated immune escape within the TME, offering a breakthrough rationale for combinatorial immunotherapy. Absin's tyramide signal amplification (TSA) multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC) kit served as the core experimental tool throughout the investigation, enabling high-resolution dissection of the immune microenvironment and providing critical technical support for data validation.
Title: Targeting the poliovirus receptor to activate T cells and induce myeloid-derived suppressor cells to differentiate to proinflammatory macrophages via the IFN-γ–p-STAT1–IRF8 axis in cancer therapy
Journal: Cell Death & Differentiation (IF 15.4) | DOI: 10.1038/s41418-025-01496-6
Absin product used: Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody)(abs50029)

In the field of tumor immunotherapy, "cold tumors" exhibit low response rates, monotherapies targeting single molecules readily acquire resistance, and the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) is governed by highly complex mechanisms—bottlenecks that have long impeded both bench-to-bedside translation and fundamental research. A recent landmark study published in Cell Death & Differentiation identifies the poliovirus receptor (PVR, CD155) as a novel target and successfully dismantles myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC)-mediated immune escape within the TME, offering a breakthrough rationale for combinatorial immunotherapy. Absin's tyramide signal amplification (TSA) multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC) kit served as the core experimental tool throughout the investigation, enabling high-resolution dissection of the immune microenvironment and providing critical technical support for data validation.
I. Research Strategy: Addressing Immunotherapy Pain Points via Innovative Targeting of PVR
Core Pain Points Resolved
- Anti-TIGIT therapies yield contradictory clinical outcomes and fail to durably reverse immunosuppression;
- Cold tumors display poor responsiveness to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade owing to MDSC enrichment and consequent immune tolerance;
- Intercellular crosstalk within the TME remains poorly defined, hampering rational combinatorial regimen design.
Study Design Logic
- Target validation: Clinical specimens plus public databases confirm pan-cancer PVR overexpression and association with poor prognosis, establishing therapeutic potential;
- Functional validation: PVR-knockout tumor cell lines generated; growth curves and immune infiltrates assessed in LLC (cold), CT26 (intermediate), and MC38 (hot) syngeneic models;
- Mechanistic dissection: Single-cell RNA-seq and multiparameter flow cytometry delineate the PVR-regulated axis governing MDSC differentiation and T-cell activation;
- Therapeutic evaluation: Anti-PVR monotherapy and anti-PVR + anti-PD-1 combination tested across tumor models to overcome cold-tumor refractoriness.
II. Key Findings: PVR-Targeted Therapy Overcomes Multifaceted Treatment Barriers
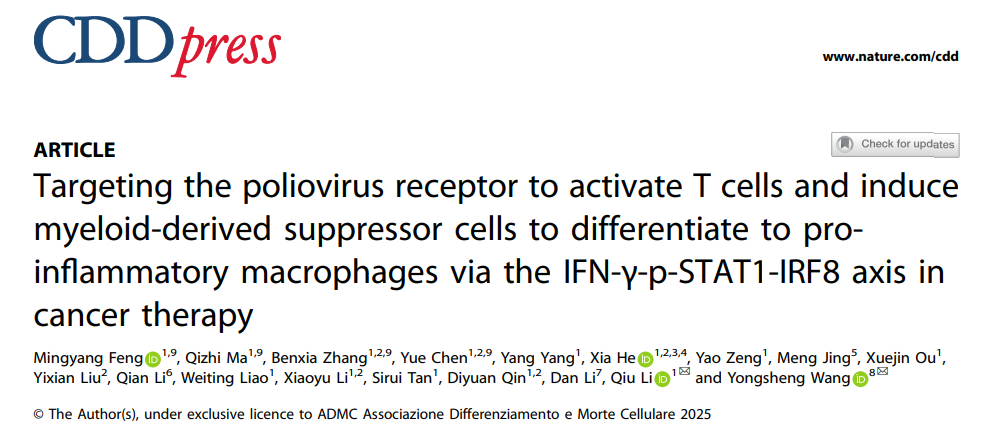
1. High PVR Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis—A Pan-Cancer "King-Slayer" Target
- IHC of clinical samples shows broad PVR expression in lung, ovarian, pancreatic and other malignancies (sFigure 1a,b), with high expression correlating with shortened survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients (sFigure 1c,d);
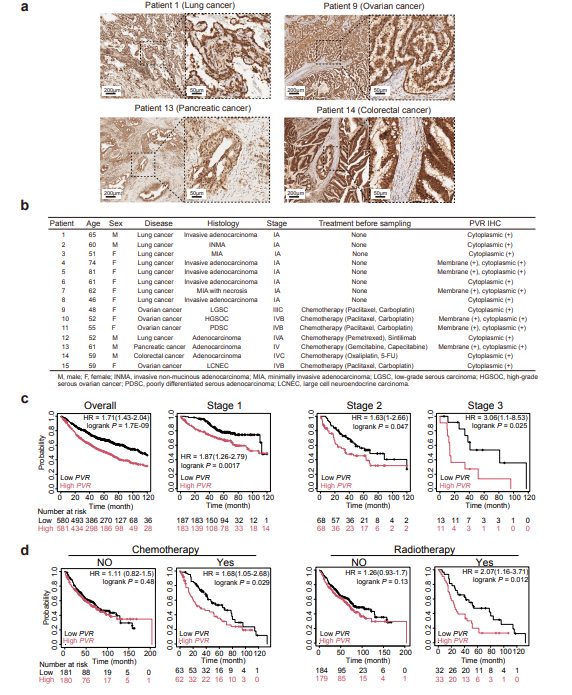
- TCGA data confirm positive correlation between PVR transcript levels and intratumoral MDSC infiltration, intensifying immunosuppression (Fig. 1j).
Correlation between PVR expression and MDSC infiltration in LUAD (Rho = 0.399, P = 3.23 × 10⁻²⁰)
2. PVR Ablation Reprograms the TME from Immunosuppressive to Pro-inflammatory
- PVR knockout reduces monocytic MDSC (M-MDSC) frequency while enriching CD8⁺ central-memory and effector T cells (Fig. 2a,f,h), tilting the TME toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype;
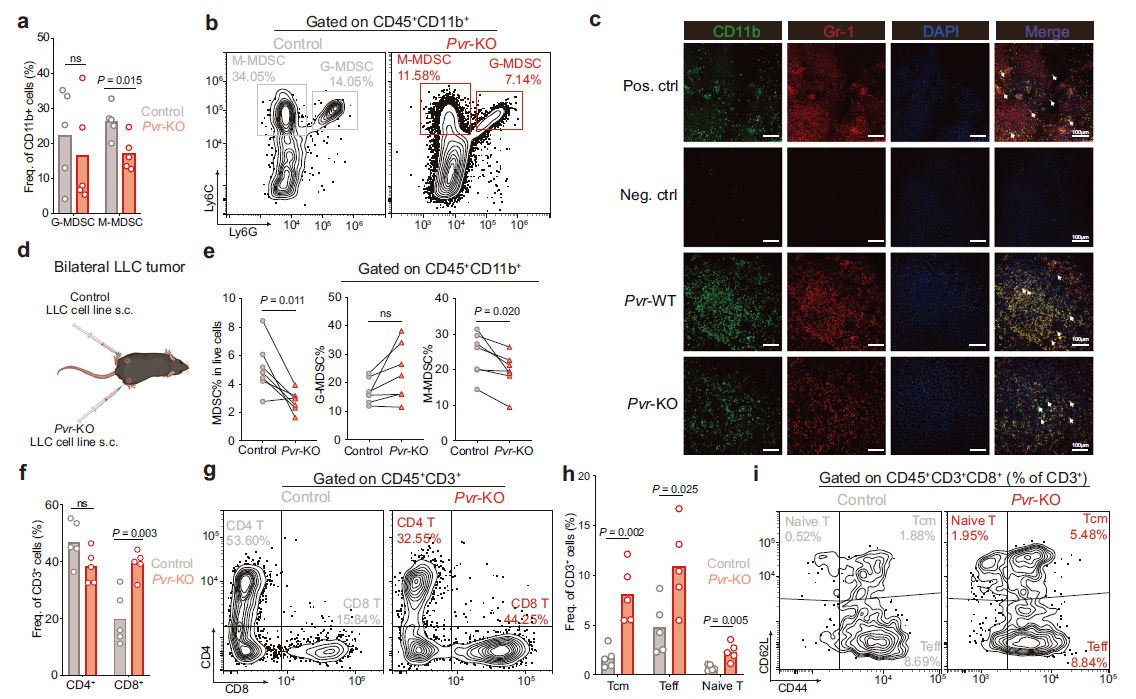
PVR deletion decreases M-MDSCs and increases CD8⁺ central-memory and effector T cells
- Single-cell profiling reveals expansion of CD8⁺ progenitor-exhausted T (Tpex) and Th1 cells alongside reduced Tregs, reinforcing anti-tumor immunity (Fig. 6b,c);
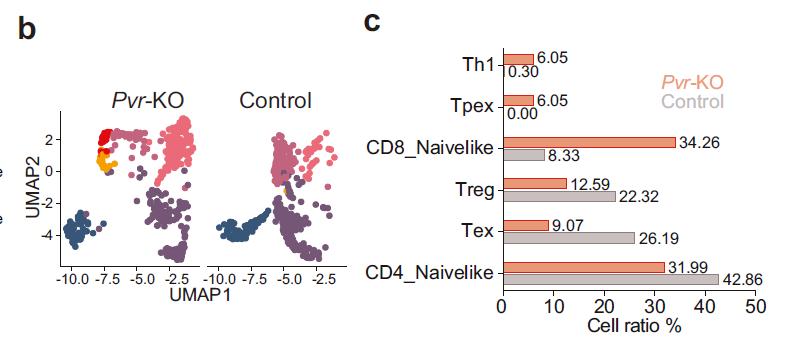
UMAP analysis and quantification of T-cell subsets in Pvr-KO vs control tumors
- Key mechanism: PVR blockade activates T cells to secrete IFN-γ, which via the IFN-γ–p-STAT1–IRF8 axis drives M-MDSC differentiation into pro-inflammatory macrophages, dismantling immune suppression (Fig. 7h).
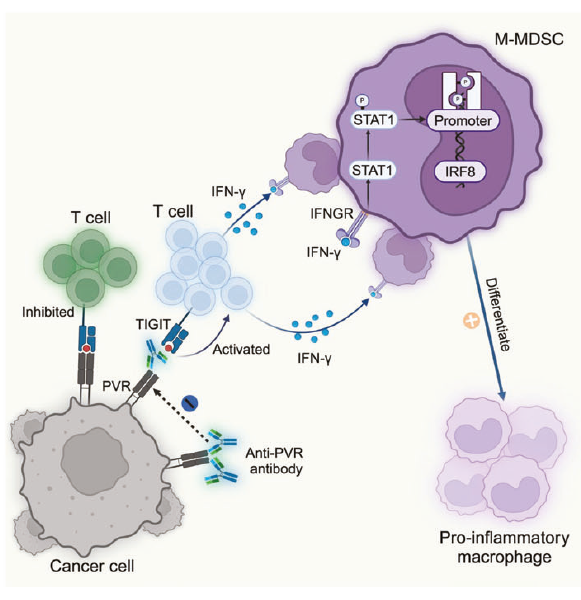
PVR blockade induces T-cell-derived IFN-γ, which triggers M-MDSC-to-macrophage conversion via IFN-γ–p-STAT1–IRF8 signaling
3. Combination Therapy Breaks Cold-Tumor Resistance: Anti-PVR + Anti-PD-1 Achieves Pan-spectrum Tumor Control
- Cold tumor (LLC): Neither anti-PD-1 nor anti-PVR alone is effective; combination significantly reduces tumor burden (sFigure 2a);
- Intermediate tumor (CT26): Anti-PVR monotherapy shows efficacy, further amplified by combination (sFigure 2d);
- Hot tumor (MC38): Both monotherapies and combination potently inhibit growth without overt toxicity (sFigure 2f);
- Multiplex IHC confirms increased CD8⁺ T cells, CD86⁺F4/80⁺ pro-inflammatory macrophages and IFN-γ secretion post anti-PVR treatment (sFigure 2g,h), directly evidencing TME reprogramming.
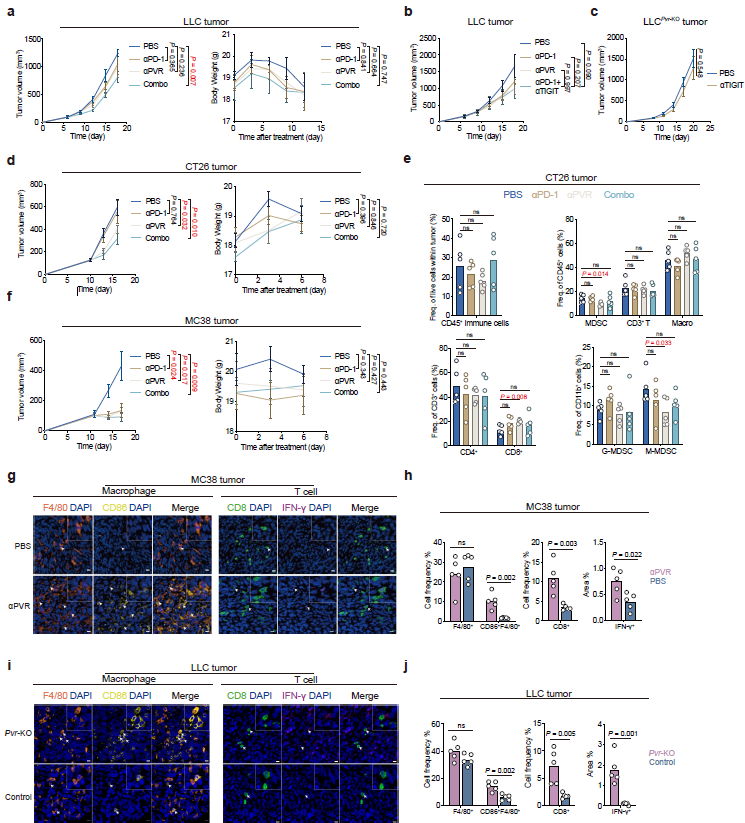
Increased immune infiltrates and cytokine expression after anti-PVR therapy
4. Core mIHC Readouts and Conclusions
Using Absin TSA 7-color mIHC on 4-μm FFPE sections of MC38 tumors, four key parameters plus DAPI nuclear counterstain were simultaneously profiled and quantified:
- Effector lymphocyte marker: CD8 (core metric of cytotoxic T-cell function);
- Pro-inflammatory macrophage signature: CD86⁺F4/80⁺ (F4/80 = pan-macrophage; high CD86 indicates pro-inflammatory activation);
- Key cytokine: IFN-γ (central driver of immune activation and MDSC differentiation).
- Anti-PVR treatment significantly elevates intratumoral CD8⁺ T-cell infiltration, reinforcing tumoricidal activity (sFigure 2g);
- CD86⁺F4/80⁺ pro-inflammatory macrophages are markedly expanded, confirming successful M-MDSC-to-macrophage conversion (sFigure 2g);
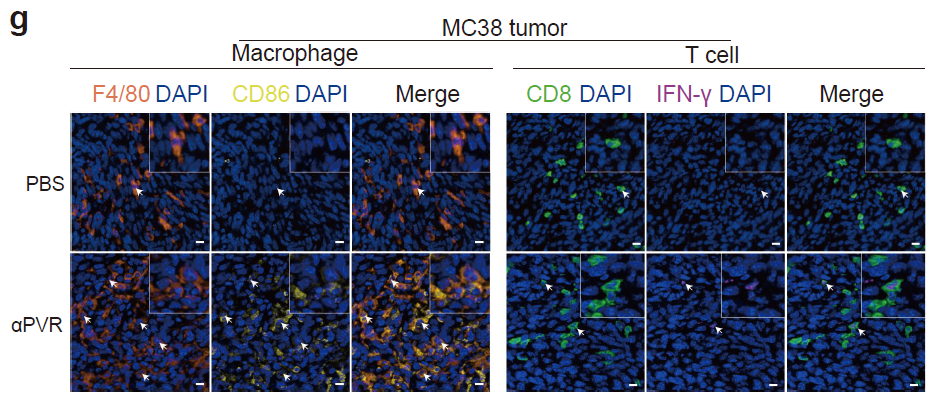
Detection of F4/80⁺CD86⁺ pro-inflammatory macrophages and CD8⁺IFN-γ⁺ T cells in MC38 tumors
- IFN-γ-positive area fraction increases, validating the pivotal pathway "PVR blockade → T-cell activation → IFN-γ secretion" (sFigure 2h);
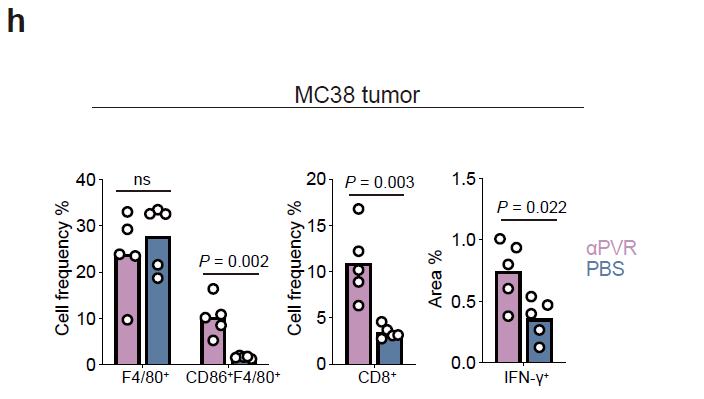
Significant increase in IFN-γ-positive area after anti-PVR therapy (P = 0.002)
- Spatial distribution and quantification provide direct visual evidence that PVR targeting reshapes the TME into a pro-inflammatory phenotype, underpinning the efficacy of combination therapy.
III. Absin Product at the Core: TSA Multiplex IHC Kit Solves Detection Bottlenecks
In this study, the Absin TSA 7-color multiplex IHC kit (cat# abs50029) became the cornerstone for immune-microenvironment profiling. Its high sensitivity and multi-target capability overcome the limitations of conventional IHC, which cannot simultaneously quantify distinct immune populations.
| Product | Cat# | Core use | Experimental workflow |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSA 7-color mIHC kit | abs50029 | Simultaneous localization & quantification of CD8⁺ T cells, IFN-γ⁺ cells, F4/80⁺ macrophages, and CD86⁺ cells | 1. 4-μm FFPE sections: deparaffinization & antigen retrieval; 2. Sequential incubation with CD8, IFN-γ, F4/80, CD86 primaries and HRP secondaries; 3. TSA fluorophore labeling (CD8-TSA520, IFN-γ-TSA620, F4/80-TSA700, CD86-TSA570); 4. DAPI counterstain, PANNORAMIC MIDI II scan |
- Multi-target detection: single staining run yields data on four critical immune readouts, efficiently validating pro-inflammatory TME formation;
- High sensitivity: TSA signal amplification reliably captures low-abundance targets (e.g. IFN-γ), preventing false negatives;
- Precise spatial resolution: clearly displays immune-cell distribution patterns, visually confirming enhanced infiltration after anti-PVR therapy (sFigure 2g,h);
- Quantifiable output: SlideViewer software enables accurate statistics on positive-rate and expression intensity, providing numerical support for conclusions.
IV. Implications & Translational Outlook
This study establishes PVR as a pan-cancer immunotherapeutic target and unveils the IFN-γ–p-STAT1–IRF8 axis as a previously unrecognized pathway capable of reversing MDSC-mediated suppression. The anti-PVR + anti-PD-1 regimen successfully resolves the longstanding cold-tumor resistance dilemma, exhibiting broad translational potential.
As a research-tool provider, Absin remains committed to cost-effective, high-performance solutions that accelerate scientific breakthroughs. The successful deployment of the TSA multiplex IHC kit in this top-tier journal article—delivering precise quantification of CD8, CD86, F4/80 and IFN-γ—supplies the decisive visual evidence validating PVR-targeted therapy and reaffirms the kit's premier role in immune-microenvironment interrogation. Going forward, Absin will continue to supply optimized reagents for tumor immunology and cell biology, empowering researchers to overcome emerging technical challenges.
Content is based on the article published in Cell Death & Differentiation (DOI: 10.1038/s41418-025-01496-6). All original figures and data are the intellectual property of the journal and the corresponding authors. Should any infringement arise, please contact us for prompt removal; we will cooperate fully.
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Antibody eluent (for mIHC) |
30ml |
Contact Absin
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
