- Cart 0
- English
Absin Kit Powers mEVs-SKAP2 Therapy for Asthenoteratozoospermia
January 16, 2026
Clicks:110
Against the backdrop of globally rising infertility rates, asthenoteratozoospermia—characterized by impaired sperm motility and abnormal morphology—has emerged as a leading etiology of male infertility, imposing a heavy burden on affected couples and representing a critical diagnostic and therapeutic bottleneck in reproductive medicine. A breakthrough study recently published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2025, 10:416) unveiled the pivotal regulatory role of the hnRNPR–SKAP2 axis during spermatogenesis and developed an exosome-based SKAP2-targeted therapeutic strategy, offering a novel direction for asthenoteratozoospermia treatment. absin biochemical assay kits provided essential support throughout the investigation, enabling the research team to overcome technical hurdles.
Title: Targeting SKAP2 restores sperm motility and morphology through modulating mitochondrial organization and cytoskeletal remodeling
Journal: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (IF 52.1) | DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-025-02513-3
absin Product Used: Bradford Protein Assay Kit (abs580304)

I. Research Rationale: A Stepwise Decoding of the Core Defects Underlying Sperm Abnormalities
The team adopted a closed-loop framework of “clinical challenge → mechanistic dissection → therapeutic development”:
- Pathogenic culprit identification: To address the clinical dilemma of “unknown etiology and lack of therapy,” 572 asthenoteratozoospermia patients were enrolled. Whole-exome sequencing identified pathogenic HNRNPR mutations directly linked to human male infertility.
- Animal-model validation: Hnrnpr knock-in (KI) and germ-cell-specific conditional knockout (cKO) mice were generated, faithfully recapitulating the human phenotype and confirming the indispensable role of hnRNPR during spermatogenesis.
- Molecular-mechanism elucidation: Integrating scRNA-seq, proteomics, and RIP-seq revealed a “mutation → splicing aberration → functional defect” axis: hnRNPR, in an m6A-dependent manner, regulates alternative splicing of Skap2 pre-mRNA, thereby controlling cytoskeletal remodeling and mitochondrial alignment in spermatids.
- Targeted-therapy development: To overcome the difficulty of restoring sperm function, milk-derived exosomes (mEVs) were engineered to carry SKAP2 protein; both in-vivo injection and in-vitro co-culture validated therapeutic efficacy, providing a clinically translatable regimen.
II. Key Findings: Three Breakthroughs Tackling the Asthenoteratozoospermia Conundrum
1. Novel Pathogenic Gene Identified
HNRNPR mutations were formally established as a significant genetic cause of asthenoteratozoospermia. Mutations precipitate acrosome loss and neck-structure disorganization, leading to markedly reduced progressive motility (Fig. 1i–j).
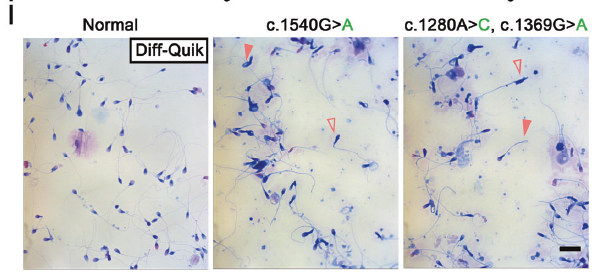
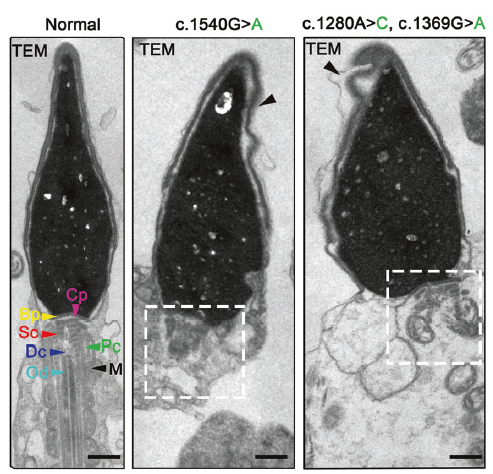
Fig. 1: HNRNPR mutation-induced acrosome loss and morphological anomalies (original Fig. 1i–j)
2. Regulatory Mechanism Deciphered
The hnRNPR–SKAP2 axis was revealed as a central coordinator: hnRNPR acts as an m6A-dependent splicing mediator that directly binds m6A-modified sites within Skap2 mRNA, ensuring correct splicing and thereby maintaining F-actin assembly and microtubule stability—offering a critical molecular target for intervention (Fig. 5).
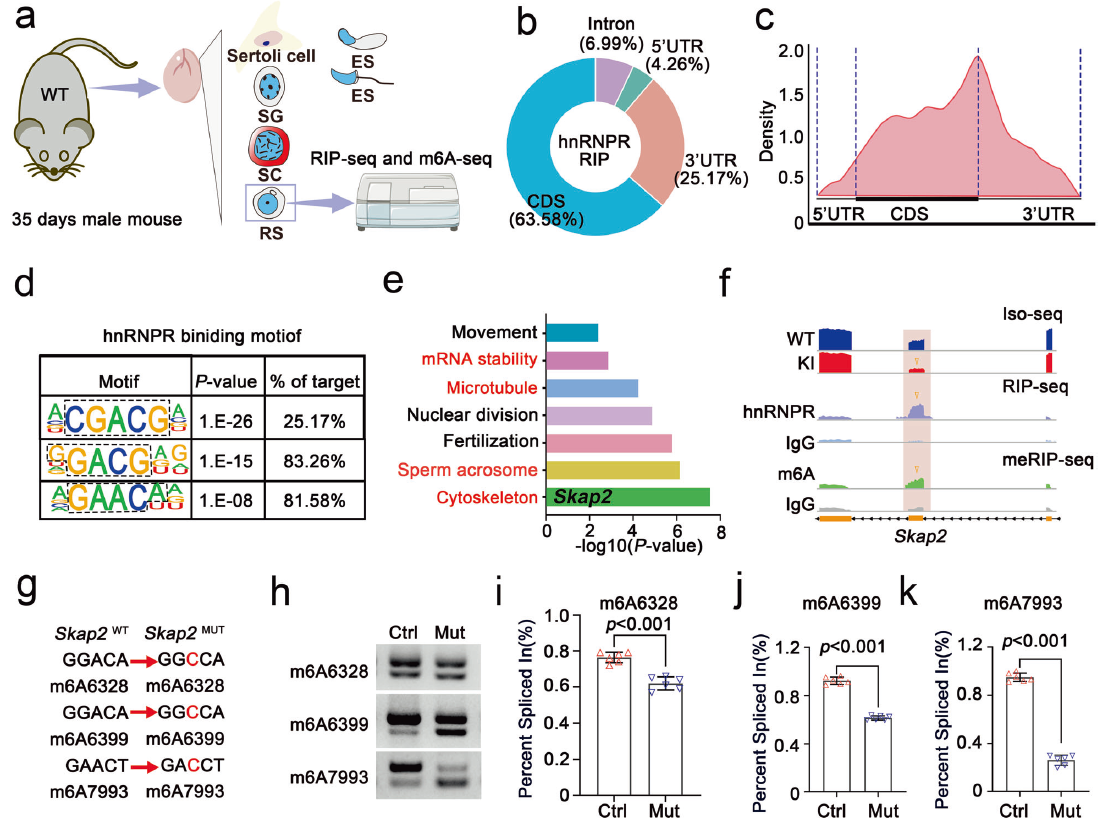
Fig. 5: hnRNPR modulates Skap2 alternative splicing in an m6A-dependent manner (original Fig. 5)
3. Innovative Therapeutic Strategy Developed
An mEVs-SKAP2 delivery system was successfully constructed. In vivo administration significantly improved sperm motility (Fig. 7c–d) and reduced morphological defects in KI mice (Fig. 7e), whereas in-vitro co-culture enhanced total and progressive motility of human asthenoteratozoospermic sperm (Fig. 9b–c) and restored disorganized mitochondrial alignment (Fig. 8), breaking the deadlock of limited therapeutic efficacy.
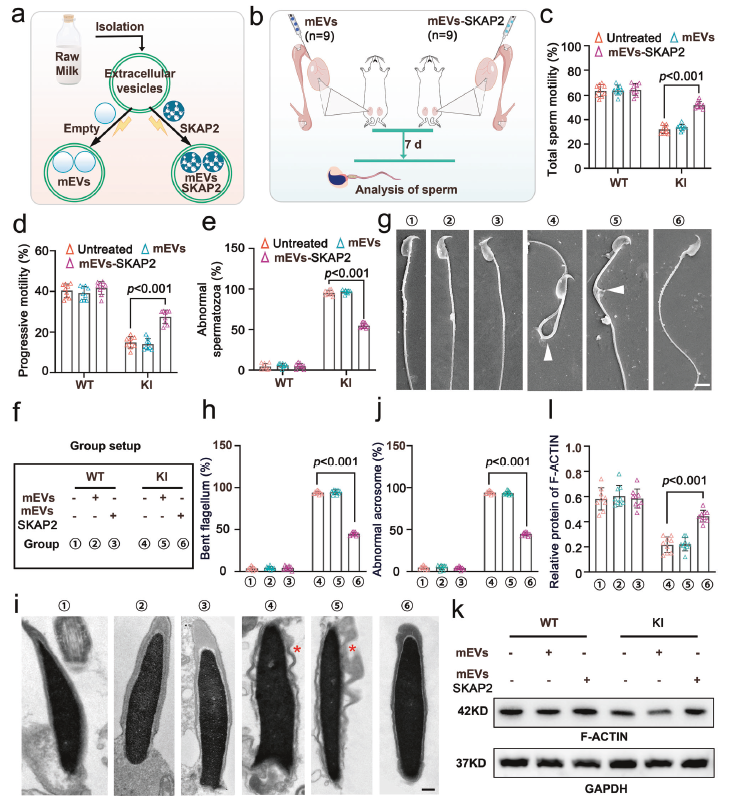
Fig. 7: mEVs-SKAP2 improves sperm motility and morphology in KI mice (original Fig. 7c–e)
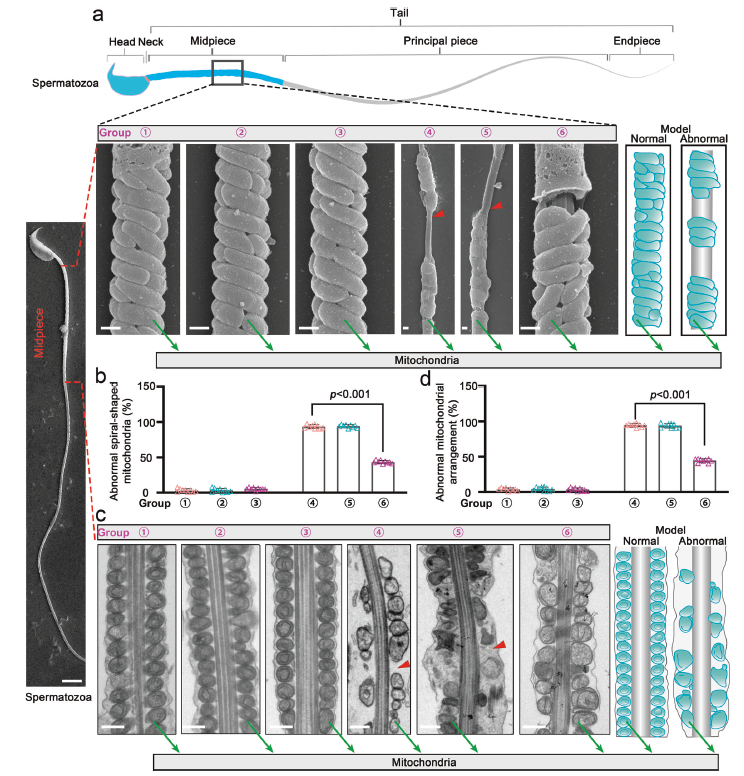
Fig. 8: mEVs-SKAP2 rescues disorganized mitochondrial alignment (original Fig. 8)
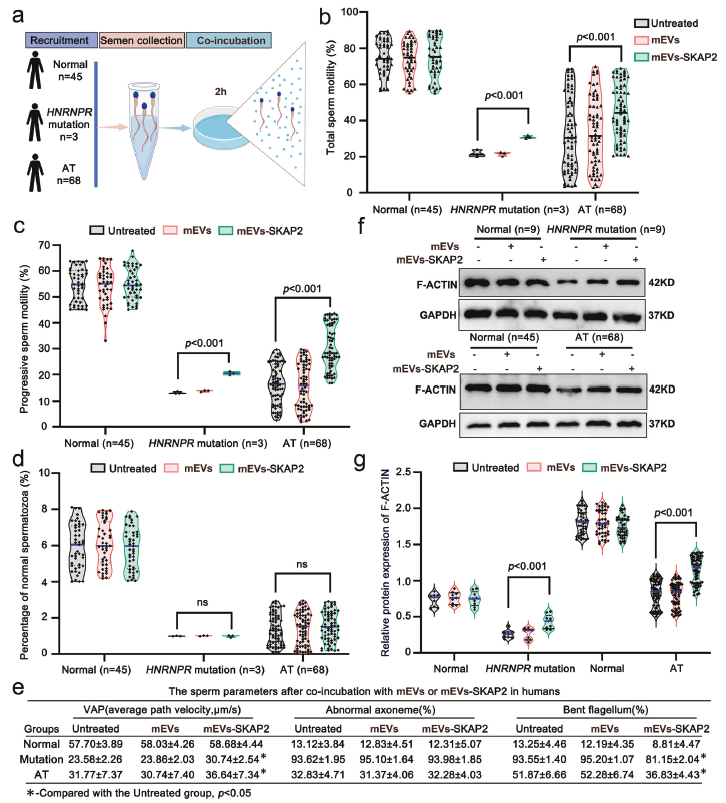
Fig. 9: mEVs-SKAP2 enhances motility of human asthenoteratozoospermic sperm
III. Powered by absin: Critical Reagents Supporting the Full Research Pipeline
In this clinically oriented, high-impact study, absin’s Bradford Protein Assay Kit (Cat. #abs580304) served as the core tool for accurate protein quantification, ensuring data reliability and precision for therapeutic development.
Product Information & Application Scenario
| Product | Catalog # | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Bradford Protein Assay Kit | abs580304 | Precise quantification of SKAP2 loaded into exosomes, ensuring accurate dosing in therapeutic interventions and reliable efficacy validation |
Key Roles in the Study
- Standardization of the therapeutic system: After electroporating SKAP2 into milk-derived exosomes to generate mEVs-SKAP2, the Bradford kit enabled accurate SKAP2 quantification, guaranteeing uniform dosing across in-vivo and in-vitro assays, eliminating concentration-derived experimental bias, and ensuring reproducibility.
- Deep validation of therapeutic mechanism: The kit provided normalized protein loading for Western blot analyses, securing reliable quantification of F-actin, SKAP2, and other key proteins (Fig. 4k), thereby substantiating the conclusion that “mEVs-SKAP2 improves sperm function via cytoskeletal repair” and clarifying the therapeutic pathway.
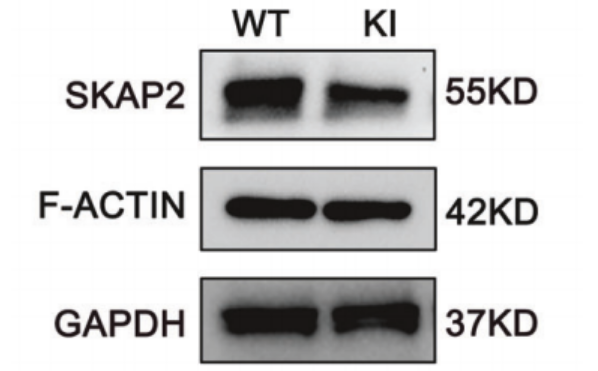
Fig. 4: Validation of SKAP2 and F-actin expression (original Fig. 4k)
IV. Implications & Future Perspectives
This study not only deciphers the molecular pathogenesis of asthenoteratozoospermia but also develops a clinically translatable targeted therapy, providing a brand-new solution to the long-standing clinical challenge of poor sperm quality and limited therapeutic options.
As a dependable partner in research, absin continuously empowers life-science investigations with high-quality reagents, offering solid support for technical breakthroughs in reproductive medicine, molecular biology, and beyond. With ongoing advances in exosome-delivery technology, mEVs-SKAP2 is poised to become a novel biological agent for asthenoteratozoospermia, while absin will remain dedicated to developing premium bio-reagents, supplying core tools for more clinically focused projects and jointly promoting progress in reproductive health!
Content is based on the article published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02513-3). All original figures and data cited remain the intellectual property of the journal and the authors. If any infringement is identified, please contact us for prompt removal; we will cooperate fully.
|
Cat. # |
Product |
Size |
| Bradford Protein Quantification Kit | 1000T/2500T |
Contact Absin
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
