- Cart 0
- English
FDFT1: Cholesterol Target in Liver Cancer Unlocked by absin
January 06, 2026
Clicks:193
Title: Targeting FDFT1 Reduces Cholesterol and Bile Acid Production and Delays Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through the HNF4A/ALDOB/AKT1 Axis
Journal: Advanced Science (IF 14.1) | DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202411719
Absin product used: IP/Co-IP Kit (abs955)


I. Background: Unmet needs & new directions in HCC therapy
Liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for ~90 %. Despite molecularly targeted agents, median overall survival for unresectable HCC remains <2 years. Dysregulated cholesterol metabolism is an established driver of hepatocarcinogenesis, yet statins display variable efficacy and dose-limiting toxicities. Identifying druggable nodes in the cholesterol-biosynthetic pathway is therefore urgently needed.
Farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyl-transferase 1 (FDFT1) catalyzes the first committed step of cholesterol synthesis. Its oncogenic role in HCC has remained unexplored. The present study systematically interrogated FDFT1 as a therapeutic target and delineated the underlying molecular circuitry.
II. Experimental design: a stepwise dissection of FDFT1-driven HCC progression
1. Target prioritization
Integration of TCGA, ICGC and GEO datasets nominated 23 cholesterol-biosynthetic genes. Differential-expression and univariate Cox analyses identified FDFT1 as the highest-ranking candidate that is consistently up-regulated in HCC and associated with poor prognosis.
2. Functional validation
CCK-8, colony formation, EdU, Transwell and wound-healing assays plus orthotopic-xenograft, tail-vein metastasis and DEN/CCl₄-induced HCC models were used to test both loss- and gain-of-function phenotypes.
- FDFT1 silencing: suppressed proliferation, migration, invasion and metastasis; reduced tumor burden; improved liver function.
- FDFT1 over-expression: accelerated tumor growth and metastasis.
3. Mechanistic elucidation
RNA-seq, Co-IP, ChIP–qPCR and rescue assays mapped the axis: FDFT1↓ → cholesterol & bile acids↓ → HNF4A transcriptional activity↑ → HNF4A occupies ALDOB promoter → ALDOB transcription↑ → ALDOB binds AKT1 and blocks its phosphorylation → HCC progression restrained.
4. Therapeutic exploration
Combination of FDFT1 knock-down with the AKT inhibitor capivasertib (AZD5363) was evaluated in vitro and in vivo to assess translational potential.
III. Key findings: four breakthroughs illuminating new HCC therapeutics
1. FDFT1 is an independent prognostic biomarker for poor HCC outcome
Multi-cohort analyses (TCGA, ICGC, n=90 IHC cohort) revealed FDFT1 up-regulation positively correlates with tumor size, distant metastasis and BCLC stage. High FDFT1 expression predicts shorter OS (P<0.0001) and higher metastatic risk (P=0.024) (Fig. 1). 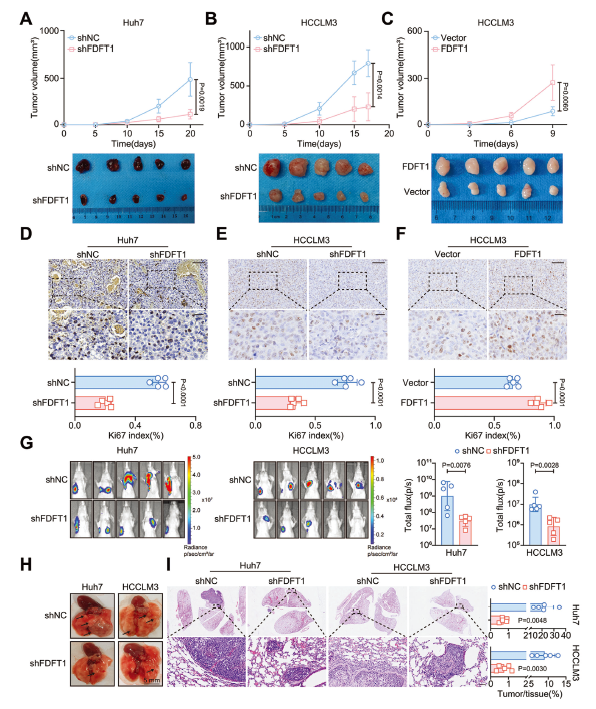
2. FDFT1 reprograms cholesterol & bile-acid metabolism to fuel HCC
FDFT1 silencing decreased intracellular cholesterol and bile-acid pools, relieving their suppression on HNF4A. Exogenous cholesterol or chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) restored AKT phosphorylation and rescued the proliferative defect (Fig. 6). 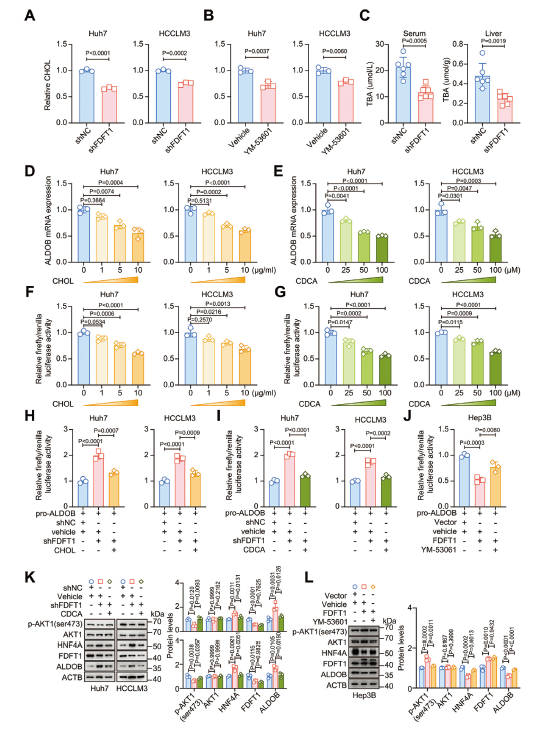
3. HNF4A–ALDOB–AKT1 axis is the core signaling conduit
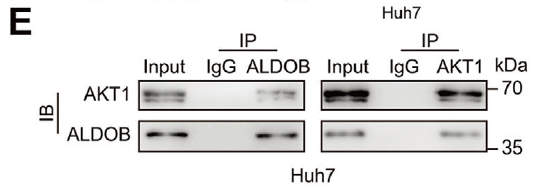
First demonstration that ALDOB acts as a metabolic checkpoint bridging cholesterol biosynthesis and PI3K/AKT signaling. ALDOB physically interacts with AKT1 to block its activating phosphorylation (Figs. 4E, 5G). 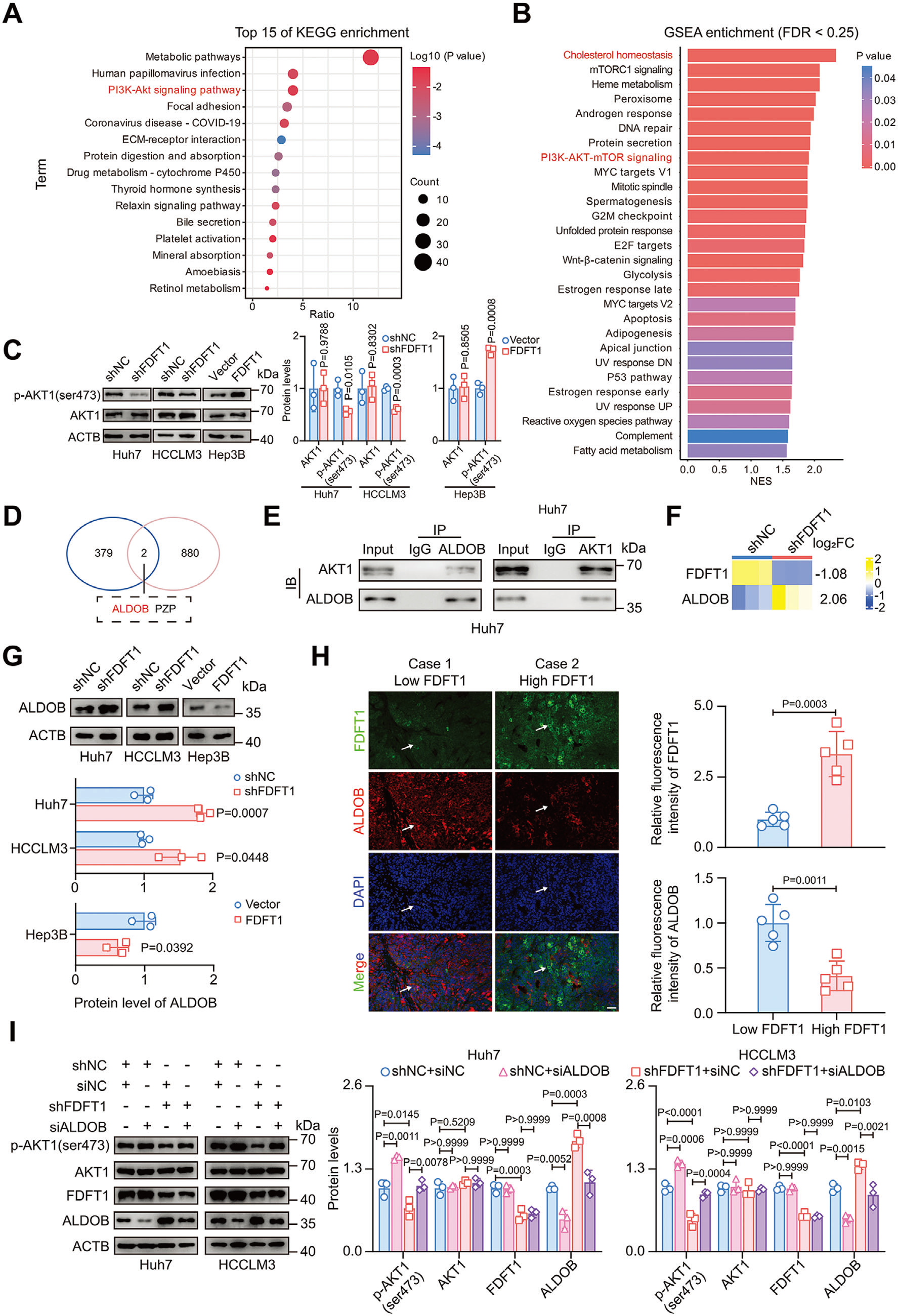

4. FDFT1 targeting synergizes with AKT inhibition
FDFT1 knock-down sensitized HCC cells to capivasertib. Combination therapy produced superior tumor growth inhibition versus single agents in both subcutaneous and orthotopic models (Fig. 7). 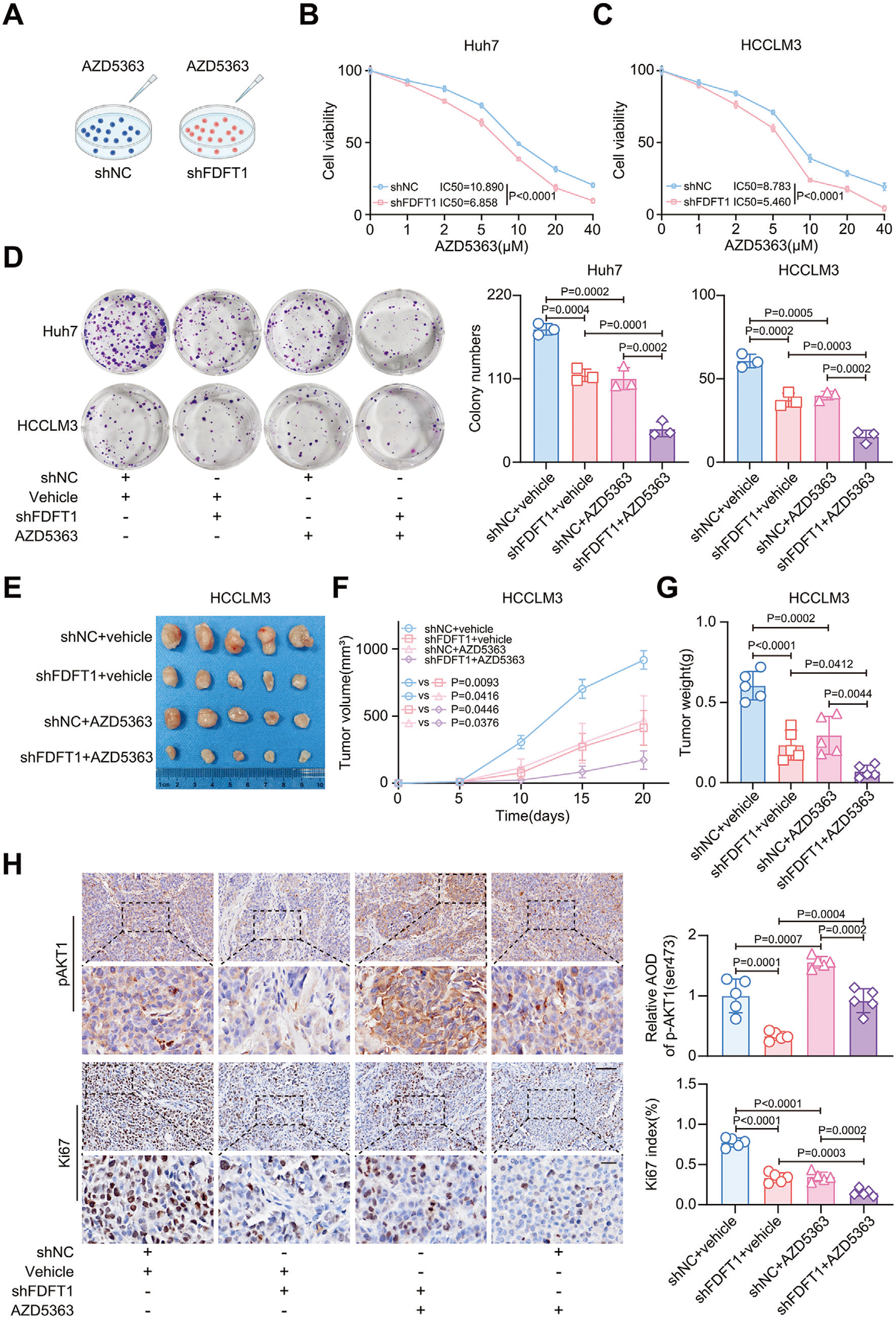
IV. Powered by absin: reliable tools for decisive experiments
Throughout this mechanistically complex study, absin’s IP/Co-IP Kit (cat. abs955) served as a key enabling technology.
Application snapshots:
- Captured endogenous ALDOB in complex with AKT1, demonstrating direct binding (Fig. 4E);
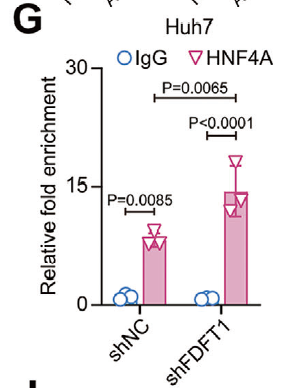
- Verified recruitment of HNF4A to the ALDOB promoter via chromatin immunoprecipitation, establishing transcriptional regulation (Fig. 5G).
 |
 |
Kit highlights:
- High specificity: Protein A/G Plus Agarose minimizes non-specific binding;
- Streamlined workflow: complete reagent set shortens hands-on time;
- Reproducible data: low background ensures confident detection of transient interactions.
V. Conclusions & outlook: from bench to bedside
This study establishes FDFT1 as a druggable metabolic vulnerability in HCC and uncovers the HNF4A–ALDOB–AKT1 axis as a previously unrecognized signaling bridge linking cholesterol biosynthesis to oncogenic PI3K/AKT signaling. FDFT1-targeted therapy, especially in combination with AKT inhibitors, offers a promising precision-oncology strategy that may overcome the limitations of conventional statins.
absin remains committed to supplying researchers with premium tools—from IP kits to antibodies and detection reagents—empowering breakthroughs in tumor metabolism, signaling and targeted therapy. We will continue to optimize product performance and accelerate translational innovation for the benefit of patients worldwide.
This summary is based on the open-access article published in Advanced Science (DOI: 10.1002/advs.202411719). All original figures and data are the intellectual property of the journal and the authors. If any infringement is suspected, please contact us for immediate removal; we will cooperate promptly and assume no legal liability.
|
Cat. # |
Product |
Size |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP/CoIP) kit | 50T | |
| Protein A/G Magnetic IP/Co-IP Kit | 10T/50T | |
| abs50034 | ChIP Kit | 22T |
| abs50074 | DNA Pull Down Kit(Animal) | 6T |
| abs50072 | RNA Pull Down Kit | 6T |
Contact Absin
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
