- Cart 0
- English
Early- vs Late-Onset Prostate Cancer: Drastically Different Prognoses? Absin mIHC Kit Unlocks Age-Specific Tumor Microenvironment Codes!
January 06, 2026
Clicks:103
Prostate cancer, a malignancy with high incidence in men, exhibits markedly disparate clinical outcomes and therapeutic responses between early-onset (≤55 y) and late-onset (>55 y) patients. Younger individuals present with more aggressive disease and higher mortality, yet lack tailored therapeutic strategies, whereas elderly patients frequently develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) with limited efficacy of conventional therapies. This long-standing clinical dilemma has perplexed both researchers and clinicians. A landmark study recently published in Nature Aging employed integrated single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and spatial transcriptomics (ST-seq) to systematically delineate age-specific progression trajectories and tumor microenvironment (TME) regulatory circuits, providing unprecedented molecular targets for precision therapy. Absin multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC) kits served as the critical enabling tool throughout tissue staining and mechanistic validation, underpinning the scientific breakthrough.
Journal: Nature Aging (IF 19.4) | DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00842-0
Absin products: 6-Color Multiplex Fluorescence IHC Kit (mouse/rabbit universal secondary) (abs50014); 6-Color Multiplex Fluorescence IHC Kit (anti-rabbit secondary) (abs50030)
I. Experimental Design: Multi-dimensional sequencing + cross-level validation deciphers age-related heterogeneity
To address the central question of whether chronological age drives prostate-cancer progression, the authors devised a “discovery–validation–translation” pipeline:
- Cohort construction: 10 treatment-naïve aggressive prostate cancers (4 EOPC, 6 LOPC), 31 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) archival samples, and complementary murine models, spanning diverse clinical contexts.
- Technology integration: scRNA-seq for single-cell resolution, ST-seq for spatial architecture, plus GWAS, flow cytometry, conventional IHC and mIHC, forming a seamless molecular-to-functional continuum.
- Core objectives: Define age-specific tumor-cell states, TME composition, and regulatory pathways; identify actionable, age-stratified therapeutic targets.
II. Key Findings: Age-defined “progression blueprints” illuminate prognosis
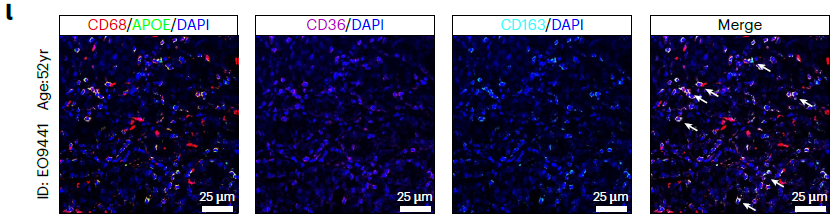
- EOPC: Enriched T cells, myeloid cells and smooth-muscle cells create a hypoxic, lipid-reprogrammed niche. APOE+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) dominate, fostering immunosuppression and rapid progression (Fig. 1 & 2) — explaining the high Gleason score and early metastasis in young patients.
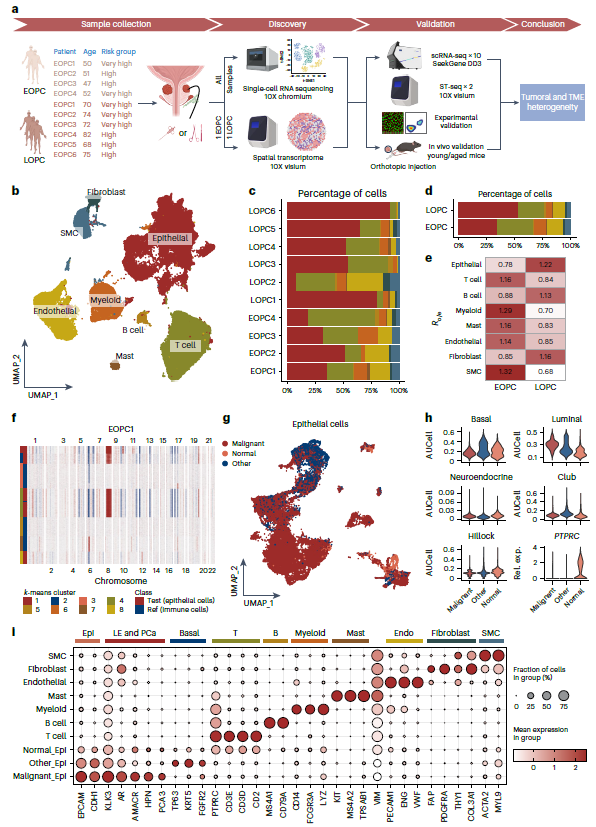

- LOPC: Epithelial and fibroblast fractions expand; inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts (iCAFs) accumulate, potentiating epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and castration resistance, with smoking-associated signatures (Fig. 5 & 6) — clarifying why elderly patients readily progress on androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT).
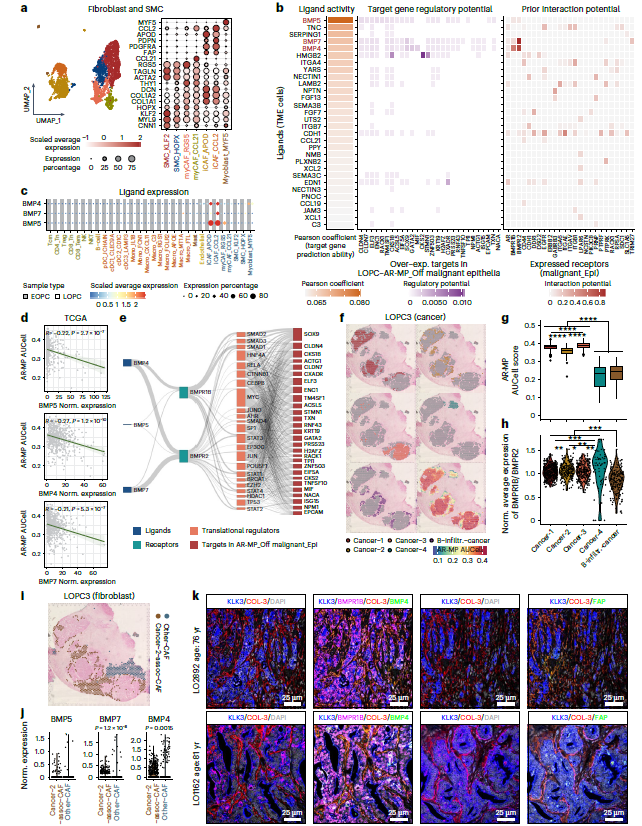
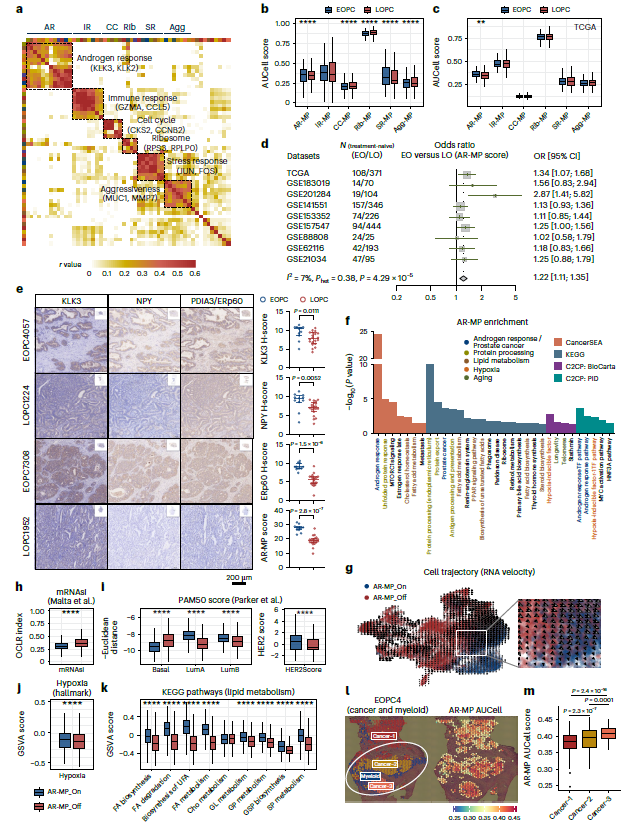
- EOPC: AR-MP is hyper-activated, synergizing with lipid-metabolism and ErbB signaling to fuel proliferation (Fig. 3) — suggesting that AR, lipid-metabolism or ErbB inhibitors could benefit younger patients.
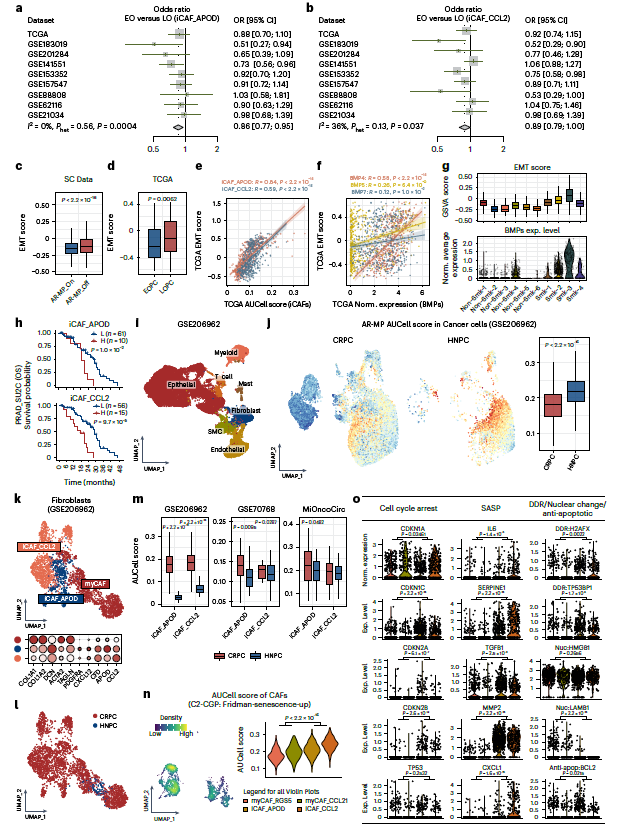
- LOPC: AR-MP is down-regulated; iCAFs repress AR-MP via BMP–BMPR–SMAD signaling while activating EMT, fostering invasion and ADT resistance (Fig. 5) — revealing BMPs/BMPRs and iCAFs as novel therapeutic targets for elderly CRPC.
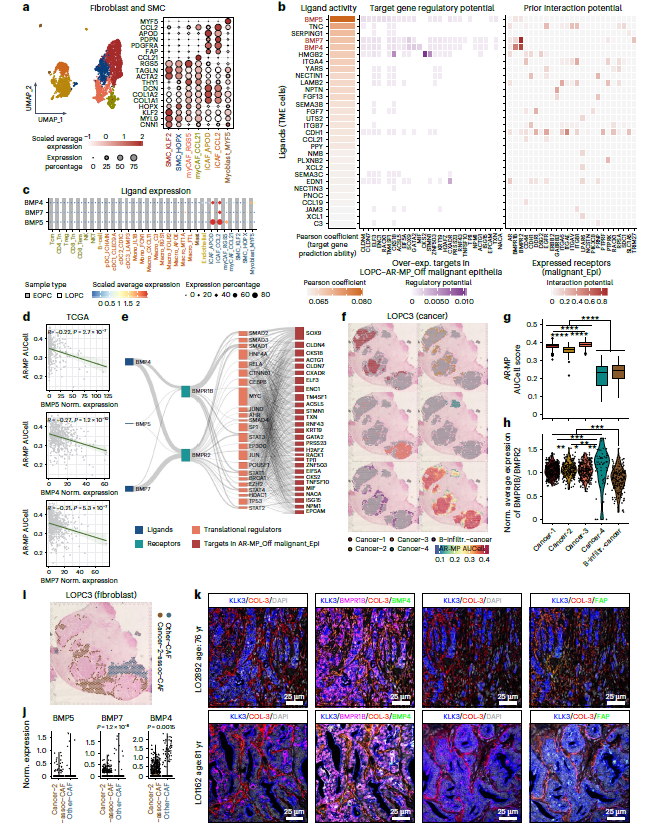
- EOPC: Target AR signaling, APOE+ TAMs, lipid metabolism or ErbB pathway.
- LOPC: Target iCAFs, BMP–BMPR crosstalk or EMT signaling.
III. Absin Products: Core “toolkit” for mechanistic validation
Throughout IHC and mIHC assays, Absin 6-color kits (cat# abs50014 human, abs50030 mouse) delivered high specificity and robustness, enabling:
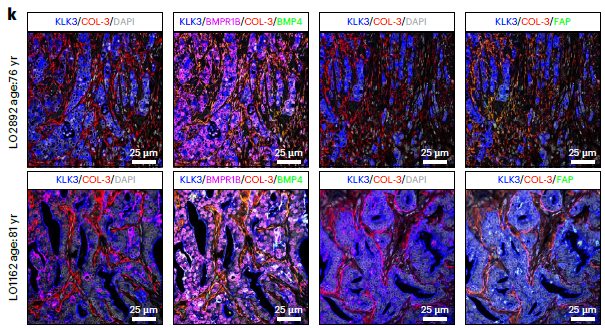
- Human prostate-cancer staining: multiplex immunofluorescence on FFPE/fresh-frozen sections for KLK3 (AR-MP), APOE (TAMs), CD68 (macrophages), BMP4 (iCAF secretome) (Fig. 4j, 5k, 7f).
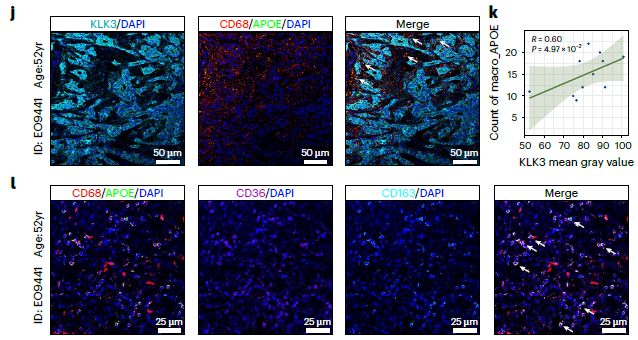
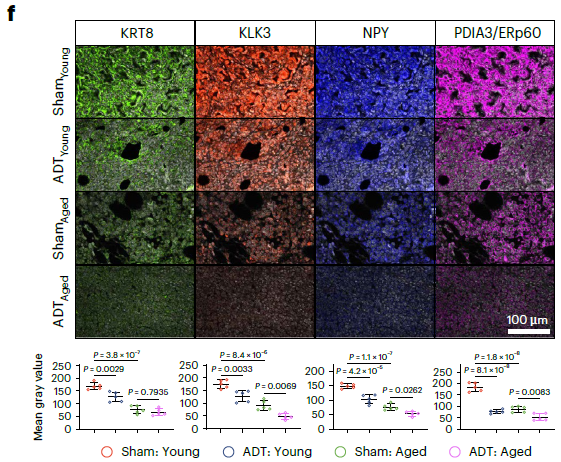
- Murine model validation: in situ C57BL/6 orthotopic tumors to monitor ADT-induced AR-MP inhibition, APOE+ TAM infiltration and iCAF redistribution (Fig. 7g–j).
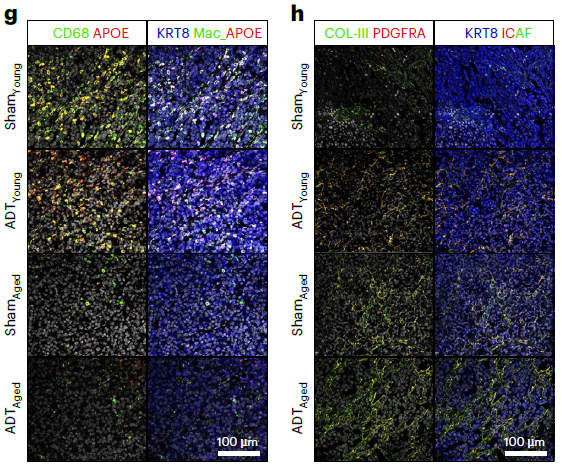
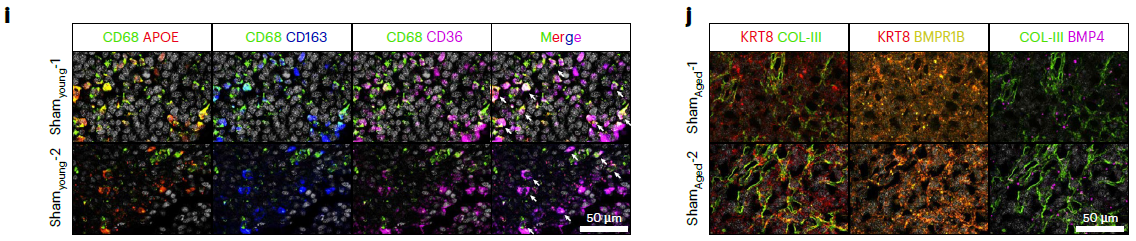
- Spatial co-localization: simultaneous 6-marker labeling revealed APOE+ TAMs juxtaposed to AR-MPhigh tumor cells (Fig. 4j) and iCAFs adjacent to BMPR1B+ epithelia (Fig. 5k), substantiating inter-cellular circuitries driving progression.
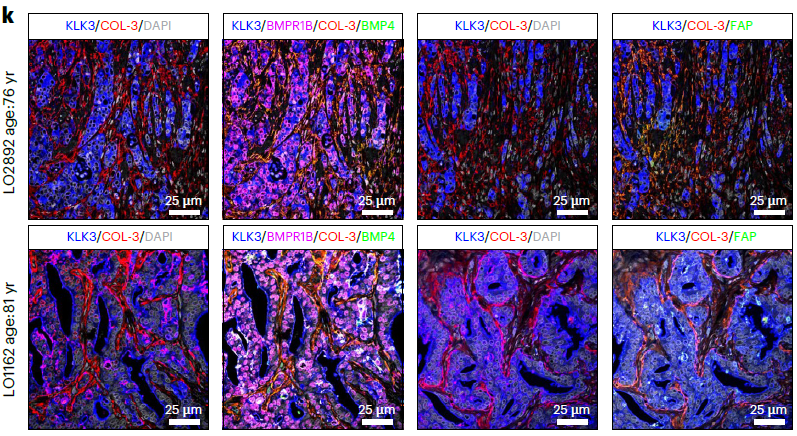
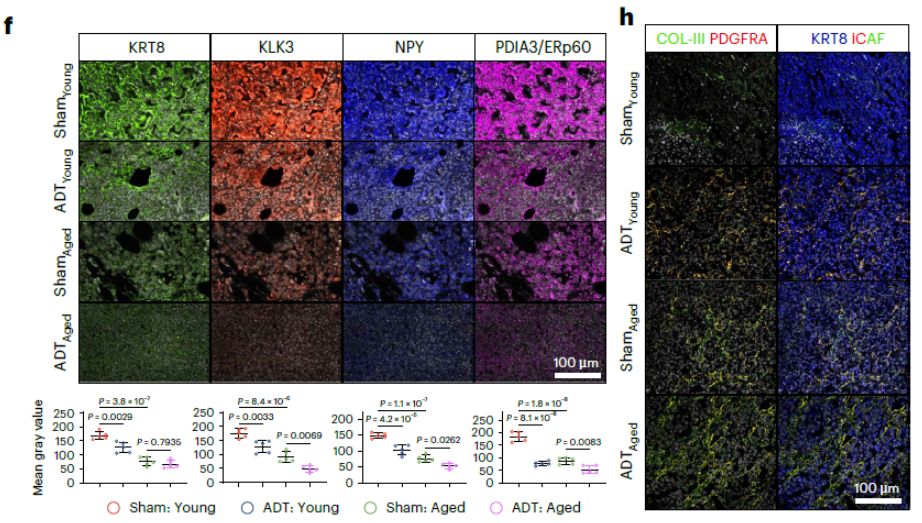
- Quantitative validation: mean-fluorescence quantification confirmed higher KLK3 and NPY (AR-MP) in EOPC vs LOPC, and enrichment of BMP4 and FAP (iCAF) in LOPC (Fig. 3e, 5k).

- Therapeutic-response evaluation: visualized ADT-induced AR-MP suppression and iCAF dynamics in young vs aged mice (Fig. 7f, 7h), offering a translational read-out.
CD68, CD163, Collagen type III and other primary antibodies used in the study are fully compatible with Absin kits, ensuring specificity and reproducibility.
IV. Product advantages — empowering high-impact research
- Multiplex capacity: 6-color panel interrogates tumor, immune and stromal compartments plus cytokines in a single slide, eliminating serial-sectioning artifacts and accelerating discovery.
- Broad sample compatibility: validated on both FFPE and fresh-frozen specimens, seamlessly bridging scRNA-seq/ST-seq data to protein-level confirmation.
- Tyramide signal amplification: delivers low-background, high-sensitivity detection of low-abundance targets, generating publication-grade images (all mIF micrographs in the paper were acquired with Absin kits).
V. Conclusion — innovative tools crack age-specific clinical pain points
This study not only deciphers the age-driven heterogeneity of prostate cancer but also offers clear therapeutic avenues for the long-standing clinical predicament of “aggressive disease in the young, resistant disease in the elderly”. Leveraging multiplex compatibility, sample versatility and signal robustness, Absin 6-color IHC kits function as the essential bridge from molecular discovery to functional validation, empowering researchers to traverse the complete workflow from “finding disparities” to “validating mechanisms”.
Content is based on the original article in Nature Aging (DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00842-0). All images and data rights belong to the journal and the authors. If any infringement occurs, please contact us for prompt removal.
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Antibody eluent (for mIHC) |
30ml |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
