- Cart 0
- English
Breakthrough Study Uncovers the Culprit Behind Pulp-Regeneration Failure—Absin DSPP Antibody Decodes Magnesium-Homeostasis Control
December 29, 2025
Clicks:142
In the field of regenerative endodontics, regeneration failure caused by chronic inflammation has long remained a critical clinical challenge. A recent landmark study published in Advanced Science has, for the first time, unveiled the core mechanism by which lipopolysaccharide (LPS) triggers mitochondrial damage and pyroptosis via SLC41A1-mediated magnesium ion efflux, ultimately leading to regenerative dysfunction of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). The study further demonstrates that exogenous magnesium supplementation can effectively reverse this process. Absin anti-DSPP antibody (Cat#: abs118471) was employed throughout the study for the detection of pulp-regeneration markers, providing reliable support for the validation of research findings.
Title: LPS-Induced Mitochondrial Damage via SLC41A1-Mediated Magnesium Ion Efflux Leads to the Pyroptosis of Dental Stem Cells
Journal: Advanced Science (IF 14.1)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202505666
Absin Reagent Used: Rabbit anti-DSPP Polyclonal Antibody (abs118471)

I. Research Strategy: Stepwise Decoding of Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Regenerative Failure
Targeting an unmet clinical need, the research team constructed an integrated “phenomenon–mechanism–intervention” chain that is both logical and innovative:
- Clinical Phenomenon: In regenerative endodontic therapy, LPS-driven chronic inflammation frequently causes failure, and mitochondrial damage is hypothesized to be the central culprit (pulp regeneration depends on mitochondrial aerobic respiration).
- Transcriptomic Screening: RNA-seq of LPS-challenged DPSCs revealed dysregulated cation homeostasis, with significant enrichment of Mg²⁺ transporter genes, pinpointing SLC41A1 (a Mg²⁺ efflux transporter).
- Mechanistic Validation: The cascade “Mg²⁺ dyshomeostasis → mPTP opening → mtDAMPs release → AIM2 inflammasome activation → pyroptosis” was systematically verified.
- Intervention Verification: Exogenous Mg²⁺ supplementation, gene silencing/over-expression, and antibody-based assays were applied in cellular and animal models to confirm the therapeutic potential of “magnesium rescue”.
- Marker Detection: Dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) served as the gold-standard marker of pulp regeneration and was tracked throughout all experimental groups.
II. Core Findings: Mg²⁺ Dyshomeostasis Is the Key “Stumbling Block” to Regeneration
LPS Disrupts Mg²⁺ Homeostasis: LPS activates transcription factor STAT5A, which binds the SLC41A1 promoter and up-regulates its expression, resulting in a ~40 % intracellular Mg²⁺ loss within 48 h.
Mg²⁺ Deficiency Triggers Mitochondrial Damage: Low intracellular Mg²⁺ strengthens CypD–OSCP interaction (binding energy drops from –6.8 to –3.0 kcal mol⁻¹), leading to aberrant mPTP opening and release of ROS and mtDNA (Fig. 5A/B).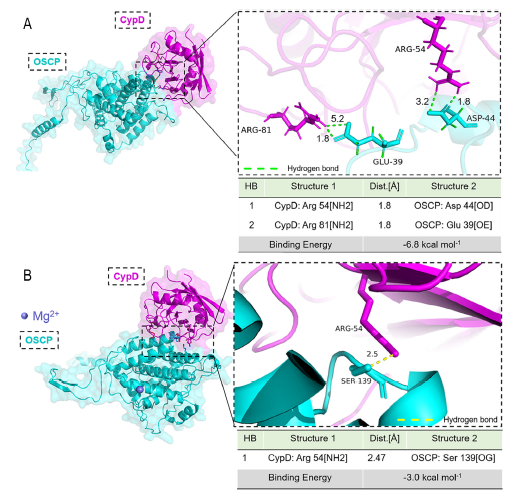
Pyroptotic Pathway Activation: Released mtDNA activates the AIM2 inflammasome, promoting GSDMD cleavage into the pore-forming GSDMD-N fragment and consequent DPSC pyroptosis (Fig. 4N/P).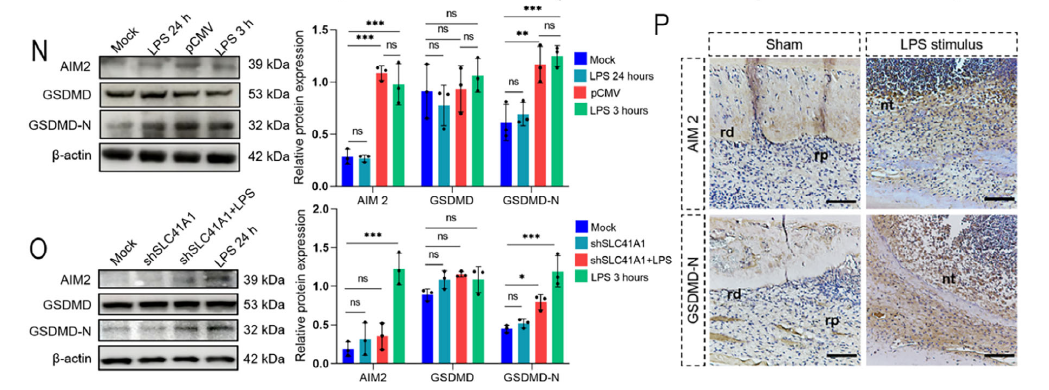
Mg²⁺ Supplementation Reverses Regenerative Failure: Exogenous 5 mM MgCl₂ restores intracellular Mg²⁺, inhibits mPTP opening and pyroptosis, and significantly elevates DSPP expression and pulp-like tissue formation in vivo (Fig. 7E).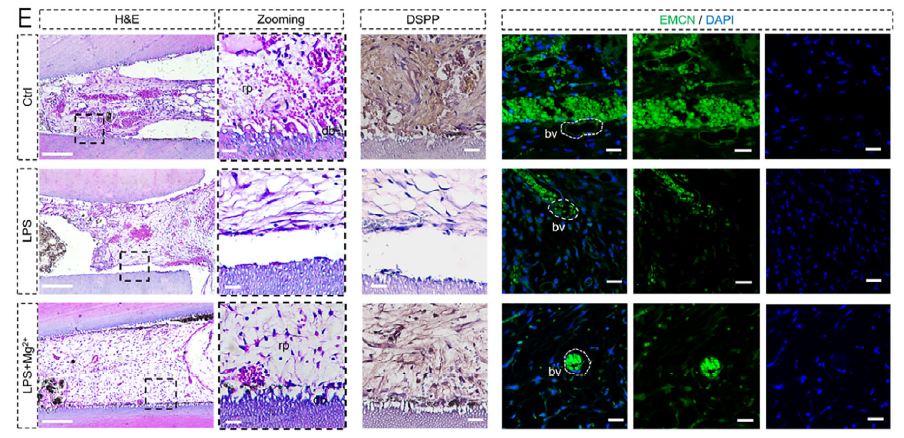
III. Absin Product Spotlight: Pivotal Role of anti-DSPP Antibody (abs118471)
| Product Name | Cat# | Applications | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-DSPP Antibody | abs118471 | IHC, IF | Specific detection of DSPP, the gold-standard marker of pulp regeneration and dentinogenesis |
2. Core Contributions of the Antibody
DSPP is a specific marker of odontoblastic differentiation and pulp regeneration; its expression level directly reflects regenerative capacity. Absin’s anti-DSPP antibody was employed throughout critical validation steps in both cellular and animal experiments, providing direct morphological and molecular evidence:
(1) Validating LPS-Mediated Regeneration Inhibition (Fig. 2C)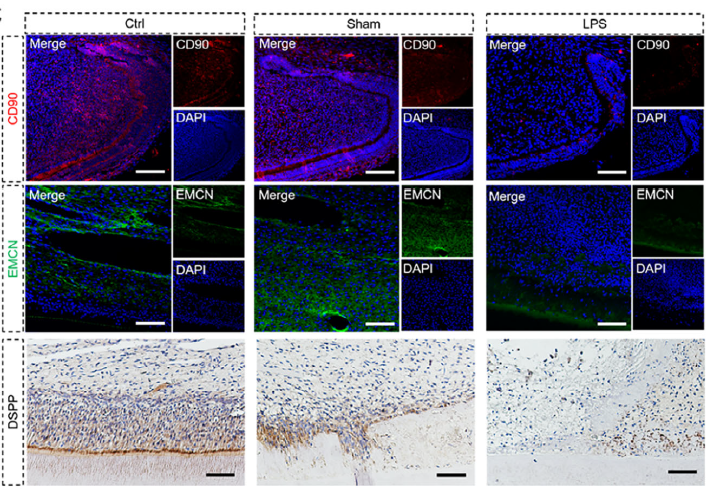
Design: Rat incisor pulp exposure model; LPS was injected into the root canal; DSPP expression was assessed by IHC at day 3.
Antibody Role: Clearly showed reduced DSPP in the LPS group and the appearance of necrotic tissue (nt), confirming LPS inhibition of dentin formation and pulp regeneration.
Value: Provided direct evidence for the initial hypothesis that “LPS induces regenerative failure”.
(2) Validating the Impact of Mg²⁺ Deficiency (Fig. 7A)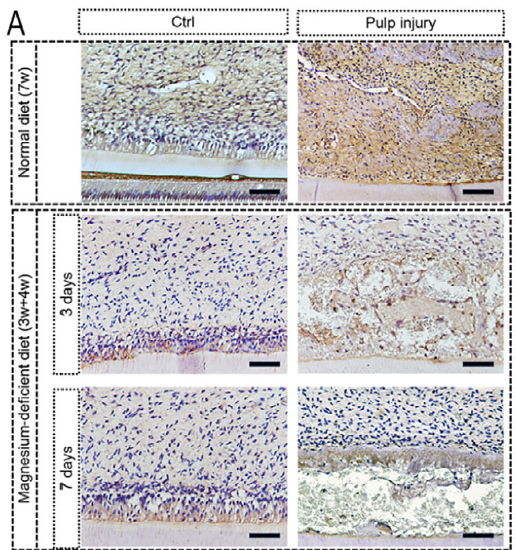
Design: Mg²⁺-deficient rat model; pulp injury was created; DSPP expression was evaluated by IHC.
Antibody Role: Demonstrated negligible DSPP up-regulation and extensive necrosis in Mg²⁺-deficient pulps, proving that Mg²⁺ dyshomeostasis per se suppresses regeneration.
Value: Established Mg²⁺ homeostasis as a prerequisite for pulp regeneration, laying the theoretical ground for subsequent Mg²⁺ rescue.
(3) Validating Therapeutic Efficacy of Mg²⁺ Supplementation (Fig. 7E)
Design: TDM (treated dentin matrix) subcutaneous transplantation; groups: control, LPS, LPS+Mg²⁺; DSPP expression was analyzed by IHC at week 4.
Antibody Role: Showed markedly higher DSPP in the LPS+Mg²⁺ group, with regenerated tissue forming dentin-tubule-like connections to TDM, closely resembling normal pulp DSPP patterns.
Value: Provided direct proof that exogenous Mg²⁺ reverses LPS-induced regenerative failure, offering a potential clinical strategy.
IV. Why Choose Absin’s DSPP Antibody?
- High Specificity: Recognizes DSPP specifically amid the complex pulp-tissue background, with negligible non-specific staining (Figs. 2C/7A/7E).
- High Sensitivity: Detects low-abundance DSPP (e.g., faint expression in LPS group), accurately discriminating among treatment groups.
- Excellent Compatibility: Validated for both IHC (paraffin sections) and IF, fulfilling multi-scenario detection at cellular and animal levels.
- Literature-Endorsed: Adopted by top-tier journals such as Advanced Science, becoming a trusted tool in pulp-regeneration research.
V. Significance and Product Outlook
This study not only unveils a novel mechanism of pulp-regeneration failure but also offers a simple yet effective clinical intervention—“magnesium rescue”—that is expected to standardize and improve the success rate of regenerative endodontics. Absin’s anti-DSPP antibody (abs118471) supported marker validation throughout the project, highlighting the critical value of premium antibodies in both basic research and clinical translation.
【Disclaimer】This article is based on the original publication in Advanced Science (DOI: 10.1002/advs.202505666) and is compiled by AI. All original figures and data rights belong to the journal and the authors. If any infringement occurs, please contact us for immediate removal.
Contact Absin
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
| Absin Bioscience Inc. worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
