- Cart 0
- English
Architectural and Functional Atlas of the Human Immune System: From Cells to Organs and mIHC Applications
November 21, 2025
Clicks:141
The immune system is the body's “defensive network” against pathogens and for maintaining internal-environmental homeostasis. Composed of immune cells, immune tissues and immune organs, it precisely discriminates “self” from “non-self” and fulfils the three core tasks of immune defense, immune surveillance and immune homeostasis, thereby safeguarding health.
I. Architectural Framework of the Immune System
Core Components
Immune cells: Include lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells), macrophages, etc.; they are the executive agents of immune responses.
Immune tissues: Use reticular tissue as a scaffold and are packed with lymphocytes plus a few other immune cells; morphologically divided into diffuse lymphoid tissue, lymphoid nodules and lymphoid cords.
Immune organs: Classified into central lymphoid organs (thymus, bone marrow) and peripheral lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils); the former support lymphocyte development and maturation, the latter are sites where immune responses are initiated.
II. Key Immune Cells and Their Functions
Lymphocytes (Core of Adaptive Immunity)
T cells (thymus-dependent lymphocytes): Generated in the thymus and, after entering the periphery, subdivided into naïve T cells, effector T cells and memory T cells. Effector T cells perform cell-mediated immunity by directly killing abnormal cells; memory T cells provide long-term immunological memory and mount rapid responses upon re-exposure to antigen.
B cells (bone-marrow-dependent lymphocytes): Generated in the bone marrow; upon antigenic stimulation they differentiate into plasma cells and memory B cells. Plasma cells secrete antibodies that eliminate antigens via humoral immunity; memory B cells likewise provide long-term memory.
NK cells (natural killer cells): Kill virus-infected and tumour cells directly without the need for antigen presentation or antibody mediation; they are a key component of innate immunity.
Accessory Immune Cells
Macrophages: Phagocytose pathogens and senescent cells, process antigens and present them to lymphocytes, thereby initiating adaptive immune responses.
| Cell type | Core role | Key functions |
|---|---|---|
| Macrophage | “Scavenger + alarm” | Phagocytose pathogens/senescent cells, present antigen, release cytokines to trigger downstream responses |
| NK cell | “Patrol guard” | Kill virus-infected and tumour cells without prior antigen activation; first line of innate defence |
| T cell | “Special force + commander” | Helper T cells coordinate responses; cytotoxic T cells kill abnormal cells; regulatory T cells maintain tolerance |
| B cell | “Arsenal + memory bank” | Differentiate into plasma cells secreting antibodies; memory B cells store antigenic information for secondary responses |
| Dendritic cell | “Intelligence officer” | Capture and process antigen, migrate to lymph nodes and present to T cells; bridge innate and adaptive immunity |
III. Structure and Function of Major Immune Organs
Central Lymphoid Organs
Bone marrow: Generates naïve B lymphocytes. Red marrow (in flat, irregular bones and epiphyses of long bones) consists of hematopoietic tissue and blood sinusoids; yellow marrow is fat-rich but retains hematopoietic potential.
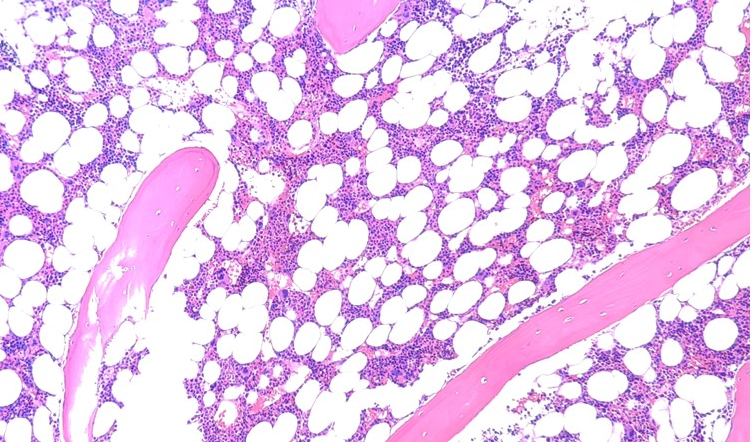
Thymus: Generates naïve T lymphocytes. Located in the anterior superior mediastinum, it is largest during childhood and gradually involutes after puberty. Each lobe has an outer cortex (thymic epithelial cells, thymocytes) and an inner medulla (Hassall’s corpuscles). The blood–thymus barrier maintains a stable microenvironment for thymocyte development.
Peripheral Lymphoid Organs
Lymph node: Size and architecture vary with immune status. Parenchyma is divided into cortex (superficial cortex/B-cell zone, paracortex/T-cell/thymus-dependent zone, cortical sinuses) and medulla (medullary cords/B-cell zones, medullary sinuses).
Spleen: Largest lymphoid organ; embryonic hematopoietic site. Parenchyma comprises red pulp (splenic cords rich in blood cells, blood sinusoids) and white pulp (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath/T-cell zone, lymphoid follicles, marginal zone/B-cell rich).
Tonsils: Include palatine, pharyngeal and lingual tonsils, together with scattered pharyngeal lymphoid tissue forming Waldeyer’s ring. Composed of stratified squamous epithelium, numerous lymphoid follicles and diffuse lymphoid tissue.
IV. Three Core Functions of the Immune System
- Immune defense: Recognise and eliminate invading antigens (pathogens, foreign cells) to prevent infection.
- Immune surveillance: Recognise and destroy antigenically altered cells (e.g. tumour cells, virus-infected cells) to prevent neoplasia and viral spread.
- Immune homeostasis: Recognise and clear aged/dead cells to maintain internal stability.
Recommended mIHC Markers for Immune Studies
| Organ category | Specific organ | Resident immune cells | Core mIHC markers | Accessory markers | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | Bone marrow | Hematopoietic stem cell | CD34, CD117 | CD45 | Identify HSCs, trace differentiation |
| Immature B cell | CD19, CD20 | CD45R | Assess B-cell maturation | ||
| NK-cell progenitor | CD56, CD16 | CD3⁻ | Track NK differentiation | ||
| Central | Thymus | Immature T cell | CD3, CD4, CD8 | CD2 | Detect DP thymocytes, monitor selection |
| Mature T cell | CD3⁺CD4⁺, CD3⁺CD8⁺ | Foxp3 | Distinguish Th vs Tc subsets | ||
| Thymic stromal cell | CK18, HLA-DR | CD40 | Evaluate thymic microenvironment | ||
| Peripheral | Lymph node | T-cell subsets | CD3, CD4, CD8, Foxp3 | CD45RO | Map total T, Th, Treg activation |
| B cell | CD19, CD20, CD138 | Ki67 | Gauge humoral response | ||
| Macrophage | CD68, CD163, CD86 | PD-L1 | Distinguish M1/M2 polarity | ||
| Dendritic cell | CD11c, HLA-DR | CD83 | Assess antigen-presentation capacity | ||
| Peripheral | Spleen | Cytotoxic T cell | CD3, CD8, Granzyme B | Perforin | Detect killer T cells and cytolytic proteins |
| NK cell | CD56, CD16 | NKG2D | Quantify and assess activation | ||
| Splenic parenchyma | CD35 (FDC), CK19 (epithelium) | DAPI | Localise white-pulp compartments | ||
| Peripheral | Tonsil | Germinal-centre cells | CD20, CD3, CD21 | Ki67 | Mirror mucosal immune response |
| Macrophage | CD68, CD163 | IL-10 | Evaluate local inflammation/regulation | ||
| Peripheral | MALT | Intra-epithelial lymphocyte | CD3, CD8 | TCRγδ | Survey mucosal surface T cells |
| B cell | CD19, CD20 | IgA | Assess IgA-secreting B-cell function |
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Antibody eluent (for mIHC) |
30ml |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
