- Cart 0
- English
Typing and identification of immune cell culture strategies (3)
September 22, 2025
Clicks:143
overview
There are six basic processes of immune cell culture: sample preparation, cell sorting, typing and identification, expansion & culture, quality optimization and follow-up research. Xiao Ai has given you a detailed introduction to "Sample Preparation of Immune Cell Culture Customs Clearance Techniques" and "Cell Sorting of Immune Cell Culture Customs Clearance Techniques". Today, we will continue to learn the relevant content of typing and identification together.
Phenotyping: Cell surface markers are used for cell identification. At present, the commonly used method is flow cytometry.
If we use flow sorting to obtain the target cells, generally speaking, after sorting, we need to back test the cells to verify the purity of the target cells, that is, typing identification, that is to say, the typing identification of the target cells after flow sorting is the same as The cell markers used for sorting are basically the same.
If we use magnetic bead sorting to obtain the target cells, it means that we need to design another flow cytometry experiment for typing and identification.
Method
Below, Xiao Ai introduces you to the [six aspects] that need to be determined for immune cell typing identification by flow cytometry:
01 Cell Number
The sorted cell suspension needs to be counted, generally 5 ~ 10 * 106/mL, to ensure that there are enough cells to be put on the machine.
02 Cell surface markers
The importance of cell surface markers is self-evident, and it will also be involved in cell sorting. During typing and identification, we also need to use cell surface markers to set the logic of the circle gate. It should be noted that the cells after typing and identification need to be expanded and cultured in vitro, and the intracellular markers of the cells cannot be selected (intracellular detection requires fixed membrane breaking treatment of the cells, and the final result is dead cells).
For example, the logic of flow cytometry identification after sorting mouse spleen Treg cells with magnetic beads is as follows:
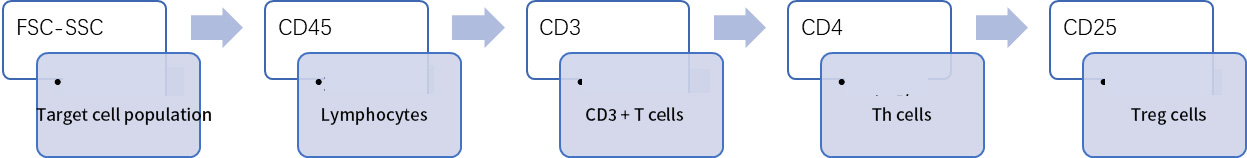
Figure 1 Flow cytometry identification of mouse spleen Treg cell circle gate logic
03 Fluorescein labeling
The color matching principles of flow sorting and flow identification are the same. Xiaoai has summarized the selection principles of antibody-conjugated fluorescein for everyone in [Cell Sorting], and friends can check them as needed.
04 Live and dead dyes
If the sorted cells are typed and identified immediately, it is generally not necessary to stain them alive or dead. It is recommended to add live or dead dye to stain frozen cells.
At present, live and dead dyes used in flow cytometry are divided into two categories: amine dyes and nucleic acid dyes. The principles, usage stages, and corresponding specific channels of the two are also summarized for everyone. Since there are few products available for nucleic acid dyes, which occupy some important fluorescence channels, Xiaoai also recommends that everyone give priority to antibody color matching before choosing the fluorescence matching of nucleic acid dyes.
|
Type |
Principle |
Stage of use |
Name |
Detection channel |
Laser |
|
Nucleic acid dyes |
It is a nucleic acid fluorescent dye with cell membrane impermeability. Dead cells have incomplete membranes and enter the nucleus to reversibly bind to DNAVRNA. |
After the surface dyeing is completed, add 5-10 min before loading |
P1 |
PE/PE-CF594 |
Blue/YG |
|
7-ADD |
PerCP/PerCP-Cy5.5 |
BlueNYG |
|||
|
DAPI |
BV421/BUV |
UV/Violet |
|||
|
Via-Probe Green |
FITC/AF488 |
Blue |
|||
|
DRAQ7 Tm |
APCIAF647 |
Red |
|||
|
Via-Probe Red |
APCJAF647 |
Red |
|||
|
Amine-based dyes |
Is a cell membrane impermeable amine-based fluorescent dye. Dead cells leave the incomplete correctional membrane and enter the cell to irreversibly bind to protein-free amines. |
Before all staining begins, the first step adds |
FVS450 |
BV421/Pacifc Blue |
Violet |
|
FVS510 |
BV510VAmycan |
Violet |
|||
|
FVS575V |
BV605/Qdot605 |
Violet |
|||
|
FVS520 |
FITCIAF488 |
Blue |
|||
|
FVS570 |
PE |
Blue/YG |
|||
|
FVS620 |
PE-CF594 |
Blue/YG |
|||
|
FVS660 |
APCJAF647 |
Red |
|||
|
FVS700 |
AF700 |
Red |
Fig. 2 Principle of live and dead dyes and corresponding specific channels
Tips:
① When using amine-based dyes such as FVS, it is necessary to use sodium azide-free and protein-free DPBS solution to wash and resuspend cells;
② After dyeing FVS, it is necessary to wash twice with dyeing solution containing protein (FBS, BSA) to make the free FVS dye invalid and facilitate subsequent dyeing;
③ The addition of nucleic acid dyes is the last step of all operations, and it can be added 5-10 minutes before getting on the machine without washing;
④ Nucleic acid dyes are covalently bound to nucleic acid space, and the fluorescence is weak. After staining, avoid washing, violent vortexing or excessive force blowing to avoid the shedding of nucleic acid dyes, resulting in false negatives;
⑤ After staining with nucleic acid live and dead dyes, it should be put on the machine in time (within 1 hour) to avoid the toxic and side effects of the dyes leading to additional dead cells;
⑥ Nucleic acid dyes are stored at 4 ℃ and cannot be frozen.
05 Flow control
Flow control is also crucial to the success of the experiment. Xiaoai also lists some functions of control and their application scenarios.
|
Flow Cytometer Control |
effect |
Application scenarios |
|
Blank control |
Cells only, without any staining, served as a reference for voltage regulation |
Required |
|
Isotype control |
Observe the binding of fluorescent dye to cell, the binding of antibody Fc fragment to cell FCR, and the non-specific binding of antibody to cell |
In particular cases, such as when monocytes are stained with antibodies labeled with tandem dyes such as PEICy7, APCICy7, APC/Fire750, APC-H7 or PE-CF594 |
|
Single stain control |
Samples stained with cells alone are mainly used to modulate compensation and cooperatively regulate voltage to prevent positive signals from exceeding the received range |
Required |
|
FMO Control |
Also known as fluorescence subtraction, it refers to samples that do not stain a certain channel alone and stain everything else. Used to eliminate the background influence of full dyeing and circle the door more accurately |
In the absence of other non-specific staining, FMO controls are generally more referential than isotype controls when setting the circle gate |
|
Biological controls |
Sample controls with known negative or positive results |
Biological controls are important for all staining, especially for intracellular staining with higher background fluorescence |
Figure 3 Summary of flow control
Tips:
Fc receptor blockers are recommended to reduce the non-specific binding of antigens and antibodies and produce excessive background signals. You can use:
① Commercial Fc Block;
② Serum of the sample species or the fluid resistance source species;
③ IgG of the sample species or the source species.
06 Dyeing Protocol
Staining protocols can also be determined by pre-experiments, mainly to prevent improper fluorescence selection, resulting in too strong or too weak staining signals. Factors to be considered include, but are not limited to, the amount of antibody used, chromosome volume, incubation time, incubation temperature, number of washes, and the like.
Tips:
① Different detection indicators, antibody brands, fluorescein labels, and antibody batches will lead to different titers of antibodies. To obtain the best experimental plan and results, we must perform antibody titration experiments on each antibody to determine the best antibody dosage (For specific operation plans, please refer to the video tutorial: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13t4y1B7Ch/?spm _ id _ from = 333.999.0. 0&vd _ source = 1aa714d23cbae1f961f525e8197e9960);
② Generally speaking, the chromosome product remains unchanged, and the antibody dosage remains unchanged (the floating range of about 10 times the number of cells is stable); If the chromosome volume increases, the amount of antibody must be increased to keep the antibody concentration stable;
③ The chromosome volume is generally 50-100μL;
④ Antibody incubation time and temperature: the most commonly used is 4 ℃, 30-60min, which can reduce non-specific binding, and the fluorescence is the most stable and not easy to quench; Room temperature (about 20 ℃) is the most commonly used for clinical testing, 15-30min;
⑤ Cell centrifugation, recommended 300g-500g, 5min, antibody washing is recommended directly using flow tube operation, and the dosage of one washing solution is 2mL;
⑥ In order to ensure the vitality of cells, it is necessary to put on the machine as soon as possible after staining.
Written at the end:
If we can't immediately type and identify the cells sorted by magnetic beads, it involves cell preservation and viability measurement.
Short-term storage: The sorted cells were resuspended to an appropriate density with an appropriate amount of Hanks, Tc-199, RPMI1640 or other medium containing 10%-20% inactivated calf serum, and stored at 4 °C.
Long-term storage: Cells are stored in liquid nitrogen at low temperature (-196 ℃), and 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) can be added as protective agent.
Viability determination: The simplest and commonly used method is trypan blue staining. Trypan blue is an anionic dye. This dye cannot penetrate the normal and complete cell membrane of living cells, so living cells are not stained; The cell membrane permeability of dead cells increases, and the dye can enter the cell through the cell membrane, so the dead cells are colored blue.
After doing a good job of cell preservation, resuscitation and viability measurement after resuscitation, you can follow the above steps and then perform cell typing and identification by flow cytometry!
That's it for today's explanation, the next expansion & culture!
Recommended by Xiaoai in this issue
|
Item number |
Product name |
Specifications |
|
abs9358 |
PI staining solution |
10mL |
|
abs9104 |
7-AAD |
1mg |
|
abs47047616 |
DAPI staining solution |
50mL |
|
abs7011 |
25 cm ² cell culture flask (50mL, air permeable cap) |
200 pcs/box |
|
abs7033 |
Cell culture plate (standard clear 6-well plate) |
50 pcs/box |
|
abs7054 |
25mL disposable serum pipette |
200 pcs/box |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
