- Cart 0
- English
Cell sorting of immune cell culture strategy (2)
September 22, 2025
Clicks:183
overview
There are six basic processes of immune cell culture: sample preparation, cell sorting, typing and identification, expansion & culture, quality optimization and follow-up research. Xiao Ai shared "Sample Preparation of Immune Cell Culture Strategy (1)" with you in detail, and today we will continue to pass the second level: cell sorting.
Cell Sorting: A technique that separates a specific cell subset from a mixed cell sample according to the characteristics of cells. It is the premise and basis of biochemical analysis and functional analysis of a specific cell.
Before sorting cells, we must clarify the proportion of target cells, markers, and sorting method to choose.
Proportion of target cells: It not only involves the selection of samples, but also whether we pre-enrich samples. We have listed this part of the content for you in the sample preparation chapter.
Immune cell markers: The human immune cell typing marker map basically covers all immune cells and identification markers. If you need it, take it away quickly!
Table 1 Table of human immune cell typing markers
|
Cell Type |
Marker |
|
T cells |
CD3, CD4, CD8 |
|
B cells |
CD19, CD20 |
|
DC cells |
CD11c, CD123 |
|
NK cells |
CD56 |
|
Hematopoietic stem cells |
CD34 |
|
Macrophages/monocytes |
CD14, CD33 |
|
Granulocyte |
CD66b |
At present, there are four conventional methods of cell sorting: Magnetic Cell Separation (Magnetic Cell Separation), Fluorescence-activated Cell Sorting (Fluorescence-activated Cell Sorting), Immunodensity Cell Isolation (Immunodensity Cell Isolation) and Microfluidic Cell Sorting (Microfluidic Cell Sorting). Xiao Ai also summarizes the principles, advantages and disadvantages of the four methods here.
Table 2 Comparison of four cell sorting methods
|
Method |
Principle |
advantage |
shortcoming |
|
Magnetic bead sorting |
Based on the ability of cell surface antigens to bind to specific monoclonal antibodies (mAb) coupled magnetic beads, the target cells are adsorbed for specific immune binding under the action of external magnetic field. |
Applicable to a wide range of sample types, simple operation and high purity of cells obtained by sorting |
It is difficult to sort multiple cell populations labeled with multiple antigens at the same time. |
|
Flow sorting FACS |
The different cells are separated by labeling one or more cells in the sample with different fluorescein, and then distinguishing the light scattering and fluorescence characteristics of the different cells by flow cytometry. |
High sensitivity, high throughput and high purity of cells obtained by sorting |
The requirements for equipment and operators are high, and the cell viability is easily affected by shear forces. |
|
Immune density gradient cell sorting |
The antigen-antibody reaction is combined with density gradient centrifugation technology, and the antibody is used to cross-link the non-target cells with the red blood cells in the sample to form an immune rosette structure, and then the target cells and the non-target cells are separated by density gradient centrifugation |
The operation is simple and quick, no magnetic poles or special instruments are needed, the purity of separated cells is high, and it can be directly applied to downstream experiments. |
It is only suitable for samples such as peripheral blood and umbilical cord blood and can only be negatively selected and cannot be widely used. |
|
Microfluidic cell sorting |
Based on the principles of fluid mechanics, cells are separated by microfluidic micron-scale chips or microfluidic droplet systems |
Commonly used for clinical isolation of cells or single cell sequencing; High efficiency, high integration and fast analysis speed |
Expensive instruments |
Since magnetic bead sorting and flow sorting are the most commonly used for cell sorting now, I will introduce the sorting strategies of these two methods in detail.
Magnetic bead sorting strategy
Sorting strategies for magnetic bead sorting: positive sorting, negative sorting, multiple sorting, whole blood sorting.
Positive sorting: After the target cells are labeled by magnetic beads, they are directly sorted as positive components. The sorted cells do not need to be removed from the MACS microbeads and can be used immediately for culture or subsequent manipulation. This method can enrich magnetically labeled target cells 10,000-fold. The purity of positive sorting is better, especially for some rare cells that need to be enriched, and the recovery rate is higher;
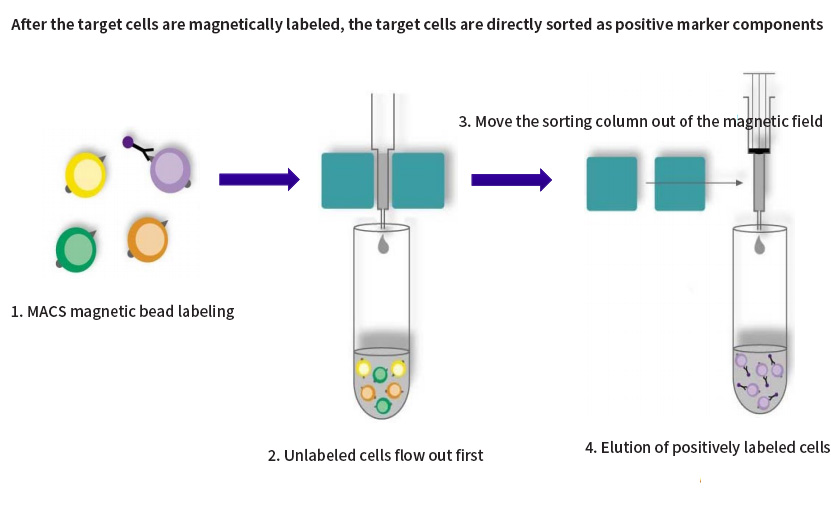
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of positive sorting of magnetic bead sorting
Negative sorting: magnetically label non-target cells and remove them from the cell mixture, that is, the magnetically labeled cells are the target cells. Negative sorting is also called removal sorting;
Scope of application: Remove unwanted cells; Lack of specific antibodies against cells of interest (e.g. tumor cells); There is no need for the antibody to bind to the cell of interest, i.e., the cell is not activated (e.g., T cell, B cell, NK cell function analysis).
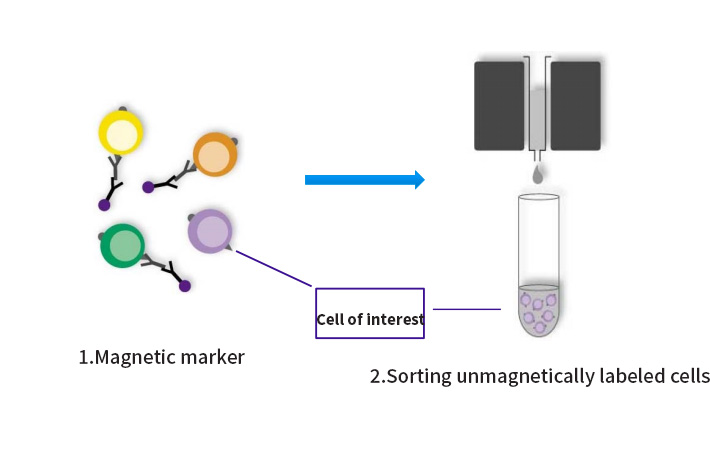
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of negative sorting of magnetic bead sorting
Multiple sorting: There are two schemes: scheme 1: negative sorting + positive sorting, that is, some non-target cells are removed first, and then positive sorting is carried out; Scheme 2: Multi-selection magnetic beads + positive/negative sorting, that is, first use multi-selection magnetic beads to positive sort cells, shearing and removing the magnetic beads, and then perform secondary sorting on the sorted cells;
Scope of application: In the cell suspension, the non-target cells also express the antigen used to positively select the target cells. It is necessary to remove this group of non-target cells first, or select multiple magnetic beads/REAlease magnetic beads to dissociate the magnetic beads on the cell surface. After the beads, the sorted cells are sorted for a second time; If very rare cells are to be sorted, the non-target cells are first removed from the cell suspension, and on the basis of enriching cells, positive sorting can be carried out to obtain high-purity target cells.
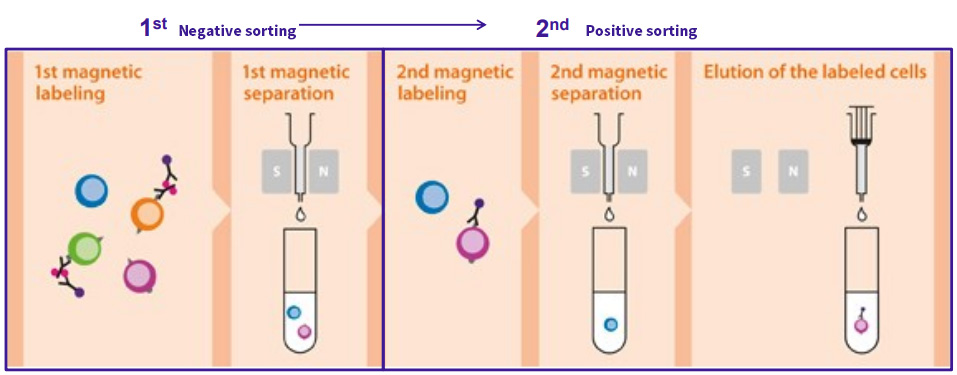
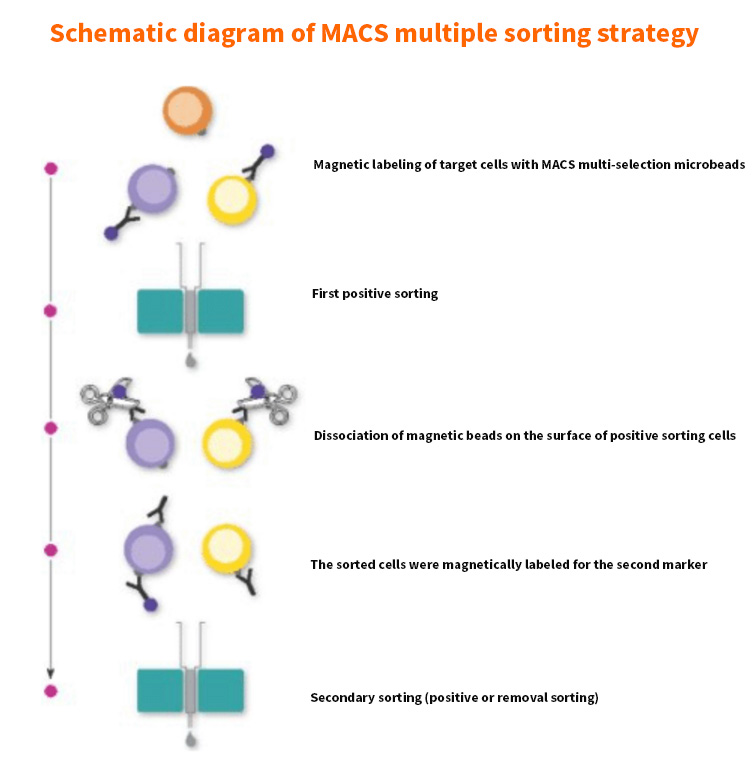
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of multiple sorting of magnetic bead sorting (top: negative sorting + positive sorting; bottom: multiple magnetic beads + positive/negative sorting)
Whole blood sorting: The traditional method of sorting cells from peripheral blood requires the preparation of PBMC first, and then the subsequent magnetic bead sorting or flow sorting. The operation time is up to 2 hours. Miltenyi contains a whole blood magnetic bead, which does not need to lyse red blood cells or density gradient centrifugation, and the target cells with good activity and high yield can be obtained within 30 minutes.
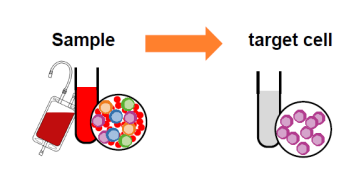
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of whole blood sorting by magnetic bead sorting
Streaming sorting strategy
Streaming sorting strategy: The steps of streaming sorting are relatively fixed:
1. Prepare a single cell suspension;
2. Cell staining;
3. Cell sorting;
4. Subsequent cell culture and analysis.
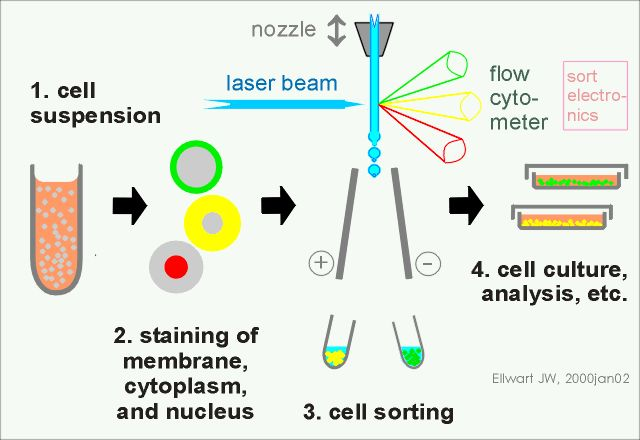
Figure 5 Basic steps of flow sorting
One of the more difficult things is the choice of antibody-conjugated fluorescein. Many teachers will encounter this situation and determine the marker of the cells to be sorted, but they don't know how to choose the conjugated fluorescein. Generally speaking, three principles need to be followed:
1. Select fluorescein according to the instrument configuration: When matching multi-color labeled fluorescein, only one fluorescein should be selected for each channel; The fluorescein between the channels can be matched with each other;
2. Reasonably allocate fluorescein according to the intensity of antigen expression: that is, if the antigen is highly expressed, it can be combined with fluorescein antibody with low fluorescence intensity;
3. Choose fluorescein with small spectral overlap: Due to the wide emission spectrum of fluorescein, there is spectral overlap between fluorescence channels, so the possibility of spectral superposition should be minimized when selecting fluorescein combination. In multicolor flow experiments, it is often necessary to eliminate the influence of spectral overlap through compensation adjustment.
Here are some tips for streaming sorting:
1. Because the cells obtained by sorting will continue to be cultured, it is necessary to ensure the sterility of the samples;
2. Cells cannot be fixed with fixative, because living cells die after being treated with fixative;
3. Add PH regulator HEPES (final concentration 25mM, PH adjustment range 6.8-8.2) to the cell resuspension to reduce the change of PH caused by high pressure;
4. Avoid containing bacteriostatic agents, such as ethanolamines, in the sheath fluid, so as not to affect cell activity;
5. If the cells need to be cultured again after sorting, a collection tube containing serum needs to be prepared; Ensure that the serum concentration is greater than 5% when sorting is completed;
6. If you want to remove dead cells, you can add 7-AAD, PI or DAPI without affecting subsequent experiments;
After understanding the two commonly used cell sorting methods, how should we choose?
Flow sorting can perform multi-parameter sorting and sorting with different fluorescence intensities, but it requires higher equipment, greater cell stimulation, but flexible sorting can meet various sorting requirements; Magnetic bead sorting has simple operation, fast sorting speed, good cell activity, and low requirements for equipment and technicians. However, it can only be sorted according to one parameter, and it cannot be screened for intracellular markers. Here Xiaoyou also gives you a detailed comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of flow sorting and magnetic bead sorting:
Table 3 Comparison of flow sorting and magnetic bead sorting
|
FACS flow sorting |
MACS magnetic bead sorting |
|
|
Sorting speed |
An average of 70,000 cells per second |
Average of 10 ⁷ cells processed per second |
|
Sorting purity |
≈95% |
≈90% |
|
Cell recovery rate |
≈80% |
≈90% |
|
Operational aspects |
Experienced operators required |
No special training required, ready to use |
|
Sterility of cells after sorting |
If the machine is not thoroughly disinfected, it is easy to get |
The instrument is compact and can be placed in the sterile operation table, which can better ensure sterility |
|
Post-sorting result reliability |
Flow sorting and flow cytometry analysis of subsequent cells are the same conditions |
After MACS sorting, it was detected by flow cytometry, which was double-blind with the subsequent test results |
|
Multi-parameter sorting |
Three or more color sorting can be performed simultaneously |
Need to be done step by step |
|
Intracellular fluorescence sorting |
Yes, such as 7-AAD |
Can't |
|
Cell sorting of low expression population |
can |
Pre-enrichment required |
|
Stimulation of cells |
tall |
Low |
Generally speaking, if magnetic bead sorting can meet the research requirements, magnetic bead sorting is generally the first choice. If magnetic bead sorting fails to meet the requirements, flow sorting will be considered.
Take the magnetic bead sorting of human Tregs cells in PBMCs samples as an example to help everyone better get the key points:
Tregs are a subset of CD4 + T cells. Its most specific tag is the nuclear transcription factor Foxp3. In addition, it also highly expresses IL-2α receptor (IL2Rα)-CD25. Therefore, the classic Treg marker is CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + T. If we detect Tregs cells, we can choose membrane markers and nuclear markers for simultaneous identification, but if we need to sort Tregs cells and perform subsequent culture, we cannot use the nuclear transcription factor Foxp3, because magnetic bead sorting can only perform membrane protein labeling. When labeling Foxp3 by flow sorting, fixation and permeabilization steps are required, which will lead to cell death. Therefore, the markers selected for sorting Tregs cells are generally: surface proteins CD4 and CD25.
Its sorting strategy is negative sorting first, then positive sorting.
1. First, all CD4-cells are labeled with biotin-conjugated mixed antibodies (CD8, CD14, CD15, CD16, CD19, CD36, CD56, CD123, TCRγ/δ, and CD235a), and then Anti-Biotin MicroBeads are added, then CD4 + cells flow out first through the magnetic field;
2. Add CD25 magnetic beads to the pre-enriched CD4 + cells for positive labeling, and then elute the unlabeled components to obtain high-purity CD4+CD25 + regulatory T cells.
That's all for today's explanation. In the next issue, we will explain typing and identification!
Recommended by Xiaoai in this issue
|
Item number |
Product name |
Specifications |
|
abs930 |
Human lymphocyte isolate |
200mL |
|
abs9772 |
Serum-free medium for immune cells |
1L |
|
abs160019 |
Anti-Human CD3/CD28 Monoclonal Antibody Beads |
1mL |
|
abs7995 |
Anti-FITC Micro Beads |
2mL |
|
abs7984 |
24-well magnetic plate |
1 |
|
abs7985 |
96-well magnetic plate |
1 |
|
abs7997 |
Sorting column set |
1kit |
|
abs7054 |
25mL disposable serum pipette |
200 pcs/box |
|
abs7033 |
Cell culture plate (standard clear 6-well plate) |
50 pcs/box |
|
abs7011 |
25 cm ² cell culture flask (50 mL, air permeable cap) |
200 pcs/box |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
