- Cart 0
- English
Sample preparation of immune cell culture strategy (1)
September 22, 2025
Clicks:159
immune cells refer to cells involved in or related to immune responses, including lymphocytes, dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages, granulocytes, mast cells, etc., which play a vital role in immune cell therapy. Immune cell therapy enhances the body's resistance to diseases by collecting immune cells in the body, culturing them in vitro, expanding them, and finally infusing them back into the body. Therefore, immune cell culture is crucial.
To this end, Xiaoai created the "Collection of Immune Cell Culture Strategies", which will introduce six basic processes of immune cell culture in detail: sample preparation, cell sorting, typing identification, expansion & culture, quality optimization, follow-up research. Today, let's learn sample preparation together first!
In addition, we also need to understand the distribution and proportion of immune cells in blood and various immune organs, so that we can select samples with relatively enriched immune cells for the preparation of single cell suspension. The following lists the proportions of immune cells in human peripheral blood, mouse spleen, peripheral blood and lymph nodes for your reference (Table 1 and Table 2).
Table 1 Proportion of human peripheral blood immune cells
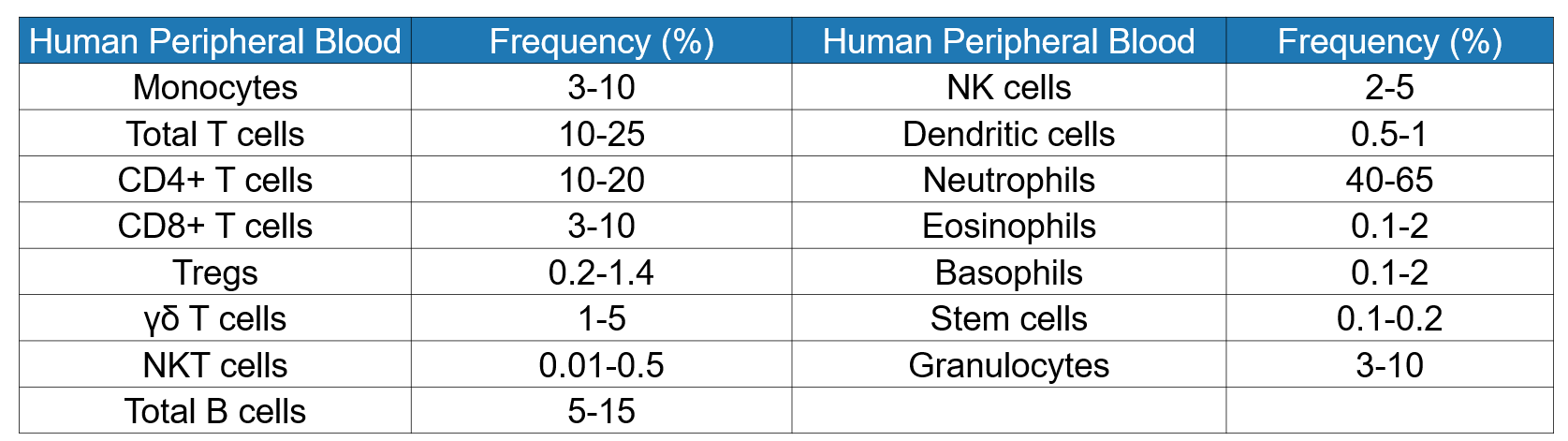
Table 2 Proportion of immune cells in spleen, peripheral blood and lymph nodes of mice
Experimental procedure
1、Sample preparation pretreatment
Before formal sample preparation, we also need to collect and preprocess samples. According to the differentiation of target immune cells and the distribution of blood and immune organs, appropriate samples are selected, fresh materials are taken, and relevant pretreatment is carried out.
Blood: Preparation of PBMCs from blood is a common method for isolating specific immune cell subsets. After the blood sample is collected, it should be filled into a container containing an appropriate anticoagulant to prevent agglutination, and the blood should be thoroughly and gently mixed with the anticoagulant. Different anticoagulants have slightly different anticoagulant principles. Xiaoai also compiled the principles, advantages and disadvantages of common anticoagulants for everyone (Table 3). At present, the anticoagulant suitable for subsequent immune cell culture is heparin anticoagulant.
Table 3 Summary of commonly used anticoagulants
|
Anticoagulant |
Mode of action |
advantage |
shortcoming |
|
Heparin |
Strengthen antithrombin III, inactivate serine protease, and prevent the formation of thrombin to achieve the purpose of anticoagulation. |
Reversible, non-toxic. |
It can only delay the coagulation process but not prevent coagulation; Price is expensive. |
|
EDTA |
It combines with calcium ions in the blood to form chelates, which makes calcium ions inactive and interrupts the coagulation process, thus achieving the purpose of anticoagulation. |
Does not affect white blood cell count and size. |
Affects many cellular processes, including energy metabolism, DNA and RNA synthesis, etc. |
|
Sodium citrate |
It combines with calcium ions in the blood to form chelates, which makes calcium ions inactive and interrupts the coagulation process, thus achieving the purpose of anticoagulation. |
Less cytotoxic. |
It has an inhibitory effect on acid and alkaline phosphatase. |
Entity tissue: The pretreatment of entity tissue is relatively simple, mainly cleaning the tissue. Use culture medium or PBS to clean the residual blood on the tissue, and remove the related connective tissue. Sterility must also be ensured during the integration process.
Precautions:
1) The sample must be fresh and sterile, so as to ensure the state of the cells;
2) The blood should be gently mixed with anticoagulant, and violent shaking can cause hemolysis;
3) After blood collection, testing is required to ensure quality and sterility.
2. Sample preparation
Sample Preparation: The source of immune cells can be divided into blood and various solid tissues. Therefore, the method of Sample Preparation can be divided into PBMC preparation and solid tissue preparation into single cell suspension.
The preparation method of mononuclear cells (PBMC) is mainly density gradient centrifugation. The principle is that the specific gravity of each cell component in blood is different. When centrifuging, the components will aggregate according to the density gradient.
The specific steps are as follows:
1) Prepare sterile 15mL centrifuge tubes or conical tubes;
2) Add 5 mL of human lymphocyte separation solution (abs930). (Note: The lymphocyte separation solution needs to be restored to room temperature, 18-25 ℃ before use);
3) Hank's solution (abs9257) or PBS (abs962) buffer 1: 1 ratio (if the whole blood sample is viscous, the ratio can be appropriately increased) to dilute the anticoagulated whole blood sample;
4) Carefully along the wall tube, close to the separation solution level, add a fresh diluted 4mL whole blood sample very slowly on top of the lymphocyte separation solution (note: remember not to muddy the lymphocyte separation solution);
5) Carefully put it into the centrifuge (horizontal rotor), centrifuge at 4 °C for 25min, and the speed is 500g. During this process, the lifting speed is reduced to 1 to avoid cell fusion;
6) Carefully take out the centrifuge tube (remember not to vibrate), discard the yellow liquid on the upper layer, and suck the white film layer in the middle layer, which is PMBC (as shown in Figure 2);
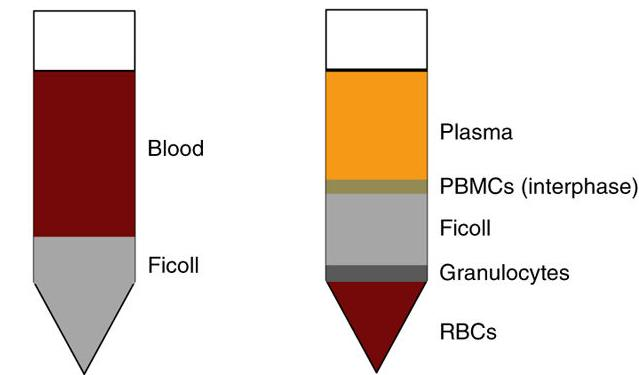
Figure 2 Illustration after adding Ficoll to anticoagulant blood (left); Illustration after centrifugation stratification (right panel)
7) Wash the obtained PBMC with 10mL of PBS, centrifuge for 10min, and rotate at a speed of 250g. During this process, the lifting speed is reduced to 1 to avoid cell fusion, and the supernatant is discarded;
8) Repeat the wash once and resuspend the cells for later use.
Precautions:
1) Human lymphocyte separation solution (Ficoll) and blood (available now) are restored to room temperature (18-25 ℃ is appropriate) before the experiment and mixed upside down to prevent the density of lymphocyte separation solution from increasing at low temperature and red blood cells from aggregating at low temperature, so as to reduce PBMC contamination by red blood cells;
2) In order to maintain the activity of lymphocytes, it is best to select fresh anticoagulated blood within 2 hours of blood collection; If further culture and testing of isolated lymphocytes is required, please pay attention to aseptic operation during blood collection and separation;
3) Dilute or wash buffers, do not use buffers containing calcium and magnesium ions to avoid blood cell aggregation;
4) Before centrifugation and dumping to harvest cells, the top plasma layer can also be aspirated to collect or discard, which helps to reduce the contamination of cells by platelets;
5) Excessive absorption of components other than the white membrane layer of lymphocytes will cause some granulocytes or platelets at the junction to be mixed in;
6) Due to the differences between different blood samples, the separation effect may be affected. The centrifugal force and time can be appropriately adjusted according to the actual situation. The reference centrifugal force and time range are: 400-1000g, 20-30min;
7) After mixing blood and lymphocyte separation solution for a certain period of time, it is normal for red blood cell sedimentation to occur.
Preparation of solid tissue into single cell suspension: Traditional methods for dissociating solid tissue into single cell suspension include mechanical methods, enzymatic hydrolysis methods and chemical methods. Xiaoai also compiled the principles, scope of application, advantages and disadvantages of these three methods for everyone (Table 4).
Table 4 Differences between traditional methods of tissue preparation of single cell suspension
|
Method |
Principle |
Type |
Scope of application |
advantage |
shortcoming |
|
Mechanical method |
Physical methods such as cutting, squeezing, or scraping break down tissue |
Net rubbing method |
1. Soft tissues with less fibrous components: thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, etc. |
1. Low cost |
1. It is easy to cause mechanical damage to tissue cells and produce cell debris |
|
Enzymolysis method |
The interstitial cells (interstitial fibers, interstitial proteins, etc.) are removed by enzymes to shed and disperse cells |
Trypsin |
1. Relatively compact tissues: epithelium, liver, kidney, etc. |
1. Maintain cell integrity and activity |
1. The operation steps are cumbersome, the digestion time is long and difficult to control |
|
Chemical method |
The addition of a compound having an affinity for cations, such as Ca2 and Mg2 +, causes chemical bonds within tissues to dissolve to loosen intercellular binding |
EDTA |
Embryonic cell isolation |
1. Safe and gentle |
1. Time-consuming |
The combination of mechanical and enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain single cell suspension is the most commonly used method, and the steps are as follows:
Reagents, consumables, devices and instruments required:
Reagents: DMEM medium (abs9483), red blood cell lysate (abs9101)
Consumables: 1.5 mL centrifuge tube (abs7119), 15mL centrifuge tube (abs7120), 50mL centrifuge tube (abs7121), disposable sterile filter (70 µ m) (abs7306)
Instruments: ophthalmic scissors, ophthalmic forceps
Instruments: constant temperature shaker, centrifuge
Operation steps:
1) Take about 100mg of fresh tissue and add it to a sterile centrifuge tube, thoroughly cut the tissue to 1-2mm3 with ophthalmic scissors, and add 1mL of tissue dissociation solution (abs9482);
2) Place that centrifuge tube on a constant temperature shaker, shake and incubate at 37 ℃/180rpm for 60min to digest the tissue, and the digestion time can be appropriately extended according to the different tissues;
3) After incubation, filter the tissue homogenate in the centrifuge tube through a 70 µ m sterile filter, then add cell culture medium to rinse the sterile filter, and collect the filtrate with a 50 mL centrifuge tube;
4) Centrifuge that cell suspension at 1200 rpm for 5 min, and discard the supernatant;
5) Add appropriate amount of culture medium, centrifuge at 1200rpm for 5min, and discard the supernatant;
6) Resuspend the cells with cell culture medium, take a small amount of cells to observe the digestion under a microscope;
7) Use cells for subsequent experiments as needed;
8) (Optionally, red blood cell lysate may be used to remove red blood cells during tissue dissociation.
Precautions:
1) The tissue dissociation solution can be packaged according to the actual amount used, stored at-20 °C, and taken at any time to avoid repeated freezing and thawing;
2) The tissue dissociation solution should be stored at 2-8 ℃ for no more than 48 hours. Long-term storage at 2-8 ℃ will reduce the dissociation effect of the product;
3) If cells obtained from tissue dissociation are used for cell culture, ensure that all operations are completed under aseptic conditions.
Plot of experimental results
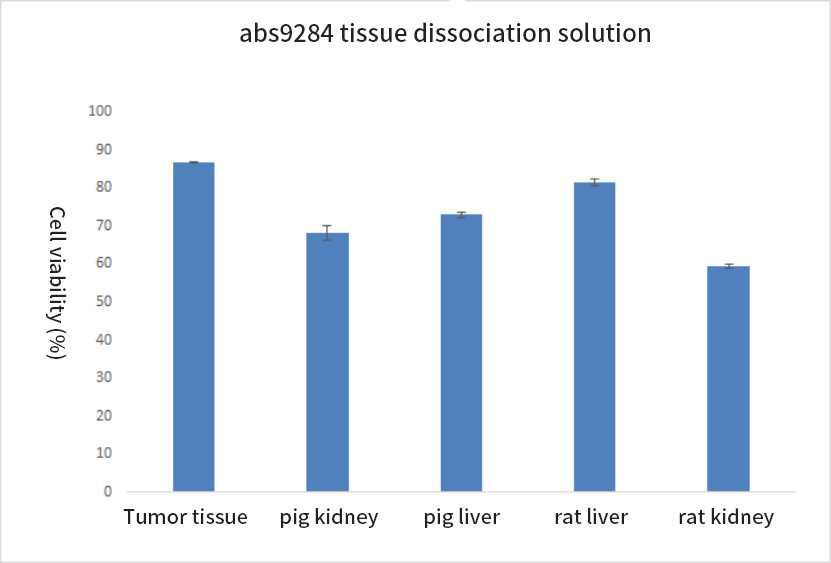
It is suitable for the dissociation of various tissues, and the cell viability after dissociation is high.
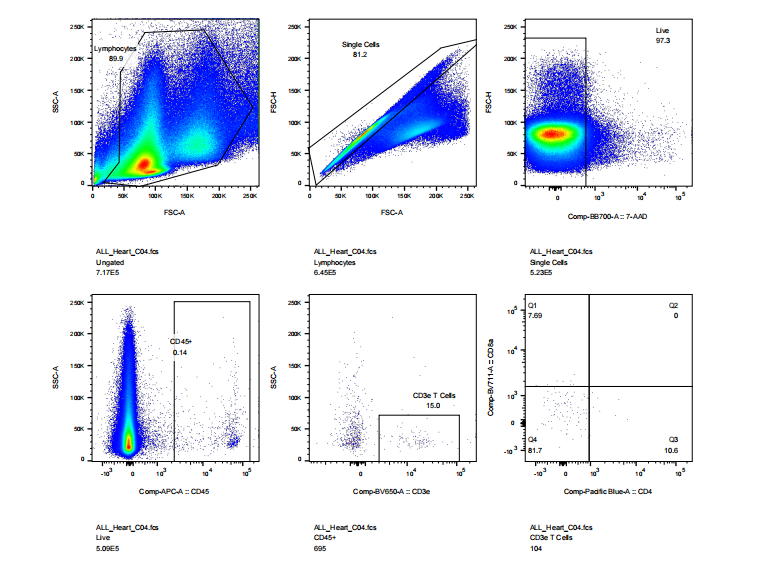
abs9482 treated mouse heart tissue into single cell suspension and performed flow cytometry: cell viability, CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8 staining results
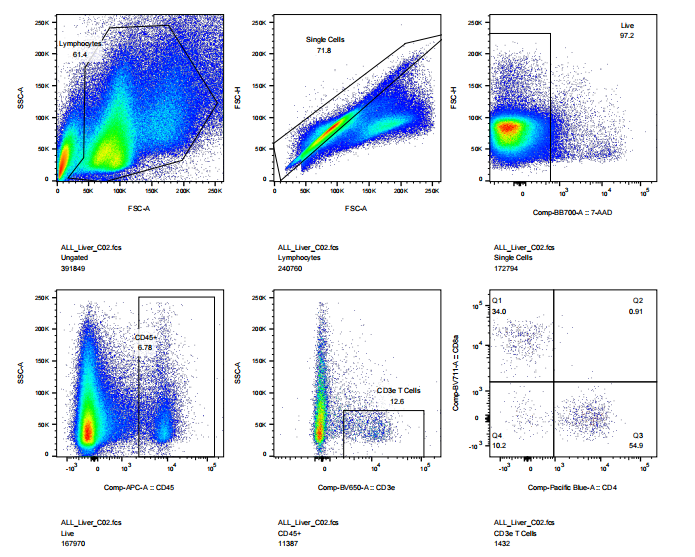
abs9482 treated mouse liver into single cell suspension and performed flow cytometry: cell viability, CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8 staining results
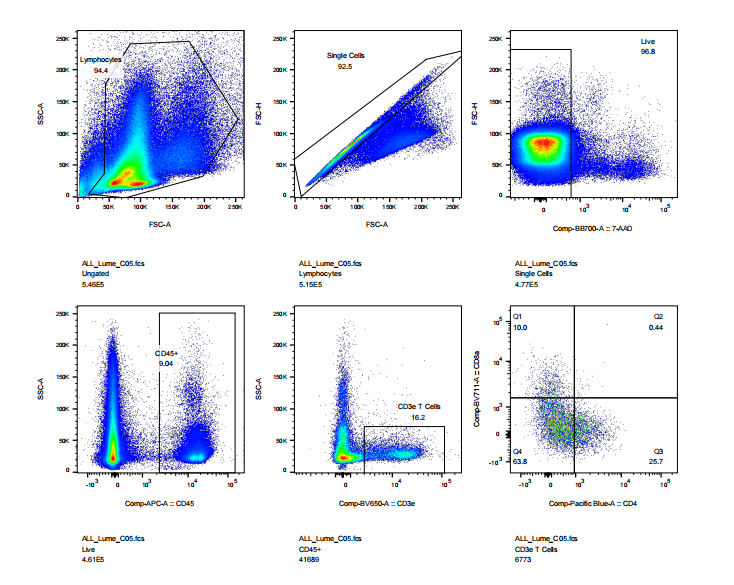
abs9482 treated mouse intestinal tissue into single cell suspension and performed flow cytometry: cell viability, CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8 staining results
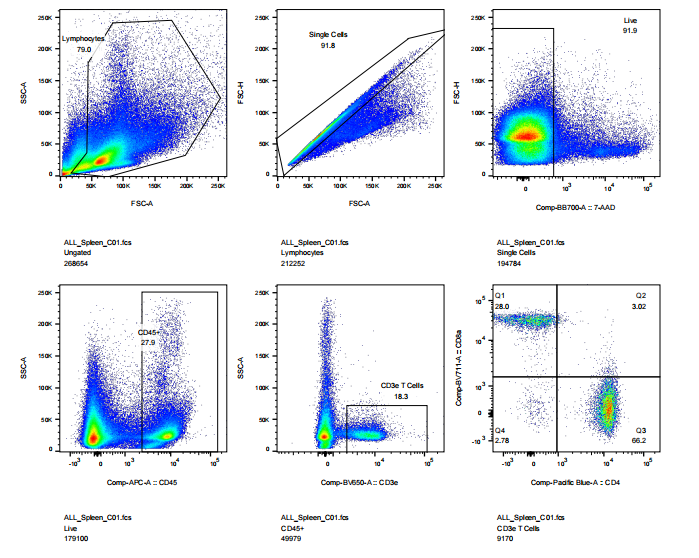
abs9482 mouse spleen was treated into single cell suspension and then performed flow cytometry: cell viability, CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8 staining results
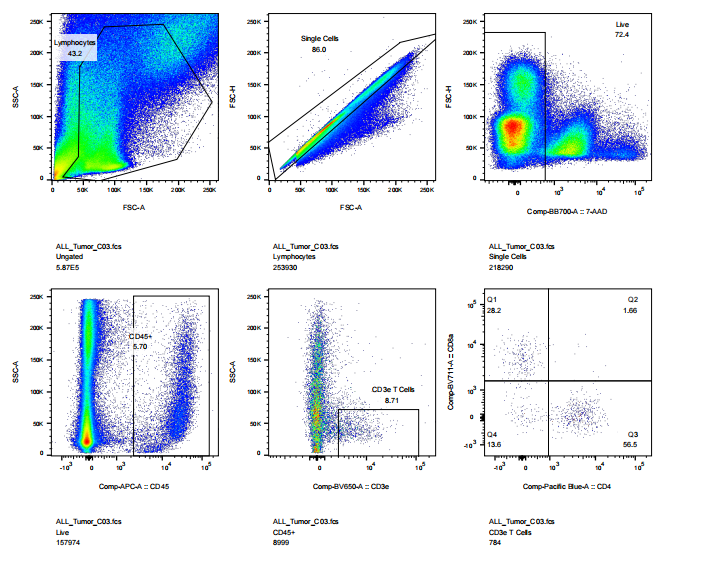
abs9482 treated mouse tumor tissue into single cell suspension and performed flow cytometry: cell viability, CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8 staining results
That's all for today's explanation. In the next issue, we will explain cell sorting!
Recommended by Xiaoai in this issue
|
Item number |
Product Name |
Specifications |
|
abs930 |
Human lymphocyte isolate |
200mL |
|
abs9482 |
Tissue dissociation fluid |
10mL |
|
abs910 |
Erythrocyte lysate |
100mL |
|
abs9241 |
Erythrocyte lysate (10 ×) |
100mL |
|
abs9483 |
DMEM medium |
500mL |
|
abs962 |
PBS buffer (1 ×) |
500mL |
|
abs9257 |
Hanks Balanced Salt Solution (Ca2 +, Mg2 + free, phenol red free) |
500mL |
|
abs7306 |
70um cell screen (200 mesh, white) |
100 pcs/box |
|
abs7119 |
1.5 mL centrifuge tube (sterile and enzyme-free) |
5000 pcs/box |
|
abs7120 |
15 mL centrifuge tube (pointed bottom, sterile and enzyme-free) |
1200 pcs/box |
|
abs7121 |
50mL centrifuge tube (sharp bottom, sterile and enzyme-free) |
400 pieces/box |
|
abs7054 |
25mL disposable serum pipette |
200 pcs/box |
|
abs7033 |
Cell culture plate (standard clear 6-well plate) |
50 pcs/box |
|
abs7011 |
25 cm ² cell culture flask (50 mL, air permeable cap) |
200 pcs/box |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
