- Cart 0
- English
Complete analysis of tag protein purification fillers: an in-depth guide from principles to applications
September 11, 2025
Clicks:1594
1. Metal chelating filler
Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) is a technology widely used in the purification of proteins, especially recombinant proteins with histidine tags. The core principle is to use the affinity between amino acid residues on the surface of proteins (mainly histidine) and transition metal ions (usually nickel ions, Ni ² ⁺) immobilized on the chromatography medium for selective separation. The following is a brief introduction to three common IMAC chromatography media: Ni-IDA, Ni-NTA, and Ni-TED.
|
Peculiarity |
Ni-IDA Sepharose FF |
Ni-NTA Sepharose FF |
Ni-TED Sepharose FF |
|
Structure and Chelation |
IDA (Iminodiacetic acid) is a tridentate chelating agent that binds to nickel ions through three sites (one nitrogen atom and two carboxyl oxygen atoms). This allows three remaining coordination sites on the nickel ion to bind to the histidine tag of the target protein |
NTA (Nitrilotriacetic acid) is a tetradentate chelating agent that uses four sites (one nitrogen atom and three carboxyl oxygen atoms) to immobilize nickel ions. This leaves two usable binding sites for the histidine tag of the target protein |
TED (Tris (carboxymethyl) ethylenediamine) is a pentadentate chelating agent that firmly chelates nickel ions through five sites, leaving only one coordination site to bind to the target protein |
|
Affinity/Binding Loading |
tall |
tall |
normal |
|
Specificity |
Lower. Ni ions expose more coordination sites, and the possibility of non-specific adsorption increases accordingly |
High. Nickel ions are more tightly encapsulated by NTA, reducing non-specific binding |
High. Minimize non-specific adsorption and obtain high-purity protein |
|
Chelating agent tolerance |
Intolerance |
≤ 1 mM EDTA |
≥ 10 mM EDTA |
|
Ion leakage risk |
Higher |
Low |
Extremely low |
|
Applications |
Suitable for conventional purification with low requirement of purity or high expression of target protein |
The "gold standard" for His tag protein purification, suitable for most scenarios requiring high-purity proteins, is the most widely used IMAC medium |
Suitable for purification tasks where samples contain interfering substances such as EDTA or DTT (such as animal cell expression), or where protein purity is extremely required |
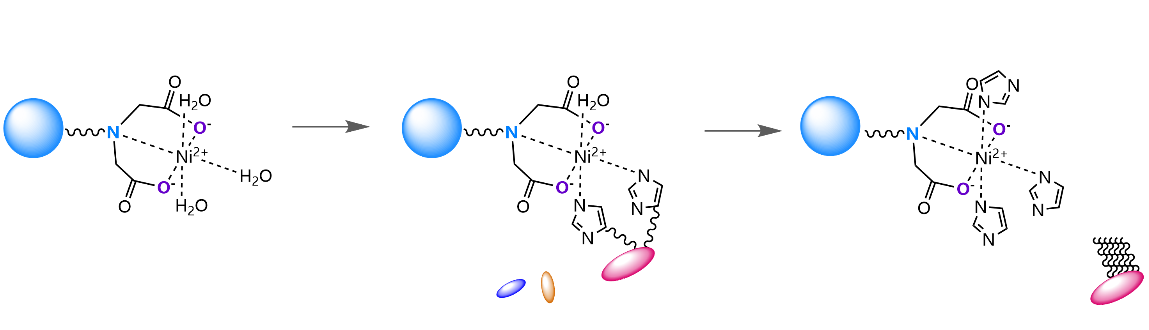
Ni-IDA Sepharose FF Series Use Flow Chart
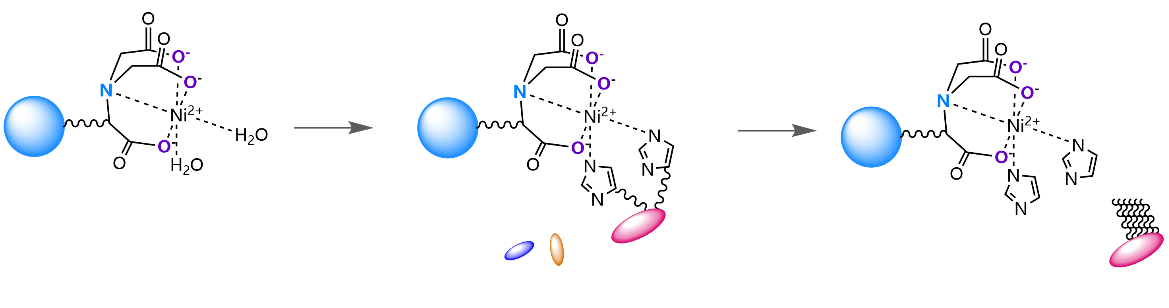
Ni-NTA Sepharose FF Series Use Flow Chart
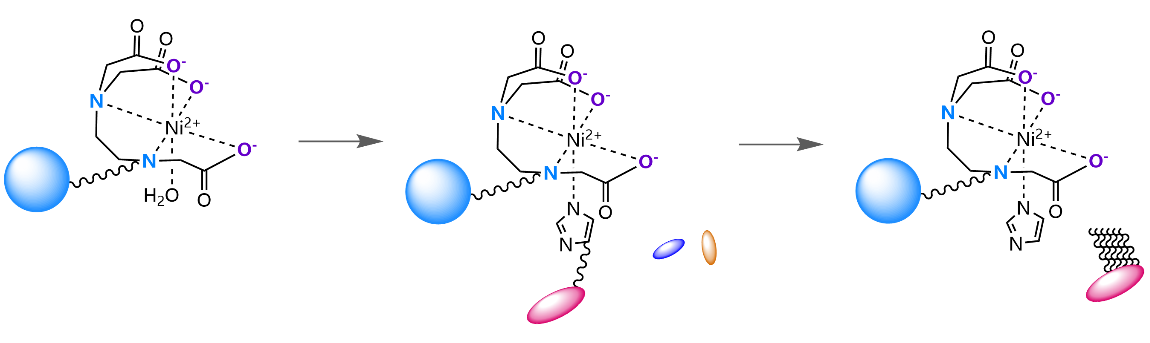
Ni-TED Sepharose FF Series Use Flow Chart
2. His tag protein purification filler parameters:
|
Category |
Ni-IDA Sepharose FF |
Ni-NTA Sepharose FF |
Ni-TED Sepharose FF |
|
Matrix |
6% cross-linked agarose |
||
|
Ligand |
Iminodiacetic acid, ~ 30 μmol Ni2 +/mL |
Nitrilotriacetic acid, ~ 17 μmol Ni2 +/mL |
Tricarboxymethylethylenediamine, ~ 60 μmol Ni2 +/mL |
|
Particle size range a |
45-165 μm |
||
|
Average particle size |
~ 90 μm |
||
|
Dynamic binding loadingb |
≥ 40 mg/mL |
≥ 20 mg/mL |
|
|
Recommended working flow rate |
60 ~ 300 cm/h |
||
|
Use pH |
4 ~ 8.5 (recommended working pH), 3 ~ 12 (long-term stability); 2 ~ 14 (short-term stable) |
||
|
Chemical stability |
Stable in the following solutions: commonly used aqueous phase buffer, 1 mol/L sodium hydroxide, 8 mol/L urea, 6 mol/L guanidine hydrochloride, 70% ethanol, etc. |
||
Note:
A: More than 90% by volume of the microspheres are in this particle size range;
B: DBC 10% test conditions were: 10% flow-through, E. coli expression of histidine-tagged recombinant protein, 6min residence time.
3. Application data:
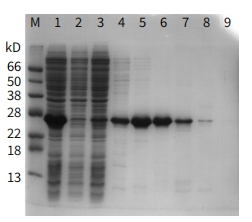
Figure 4
Lane M: Marker
Lane 1 :Start material
Lane 2: Flowthrough 1
Lane 3: Flowthrough 2
Lane 4: Elution (20 mM Imidazole)
Lane 5: Elution (50 mM Imidazole)
Lane 6: Elution (100 mM Imidazole)
Lane 7: Elution (200 mM Imidazole)
Lane 8: Elution (300 mM Imidazole)
Lane 9: Elution (500 mM Imidazole)
Packing: Ni-IDA Sepharose FF (Gravity Preloaded Column) (Cat: abs91007-G), 1 mL
Sample: his6-tagged recombinant Streptococcus Protein G produced in E. coli
Binding Buffer : 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4
Elution Buffer : 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, 20-500 mM Imidazole, pH 7.4
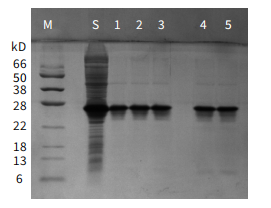
Figure 5
Packing: Ni-NTA Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Preloaded Column) (Cat: abs91008-M), 1 mL
Sample: his6-tagged recombinant Streptococcus Protein G produced in E. coli
Binding Buffer : 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4
Elution Buffer : 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, 20-500 mM Imidazole, pH 7.4
Affinity Purification of Other Tag Proteins
|
Peculiarity |
GST Sepharose FF |
MBP Sepharose FF |
Biotin Sepharose FF |
Strep II Sepharose FF |
|
Filler ligand |
Glutathione |
Dextrin |
Streptavidin |
Streptavidin mutant |
|
Label of action |
GST (Glutathione S-transferase), ~ 26 kDa |
MBP (Maltose-Binding Protein), ~ 42 kDa Protein of |
Biotin labels (site-directed ligation by biotin ligase (BirA) to specific sequences of the target protein (e.g. AviTag), can also be non-specifically ligated by chemical methods |
Strep II, a short peptide of 8 amino acids (WSHPQFEK) |
|
Purification principle |
GST tag can specifically and reversibly bind to glutathione immobilized on medium |
The MBP tag is able to specifically recognize and bind dextrin on the medium |
There is one of the strongest non-covalent interactions in nature between biotin and streptavidin |
The Strep II tag enables high-affinity, high-specificity reversible binding to the biotin-binding pocket of the streptavidin mutant |
|
Elution Method |
Competitive washing using Reduced Glutathione |
Competitive elution using a high concentration of Maltose solution |
Denaturing elution |
Competitive elution using D-biotin solution |
GST Sepharose FF Application:
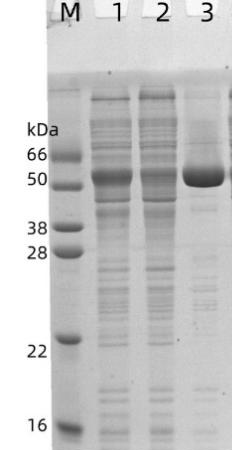
Figure 6
Lane M: Marker
Lane 1: Start material
Lane 2: Flowthrough
Lane 3: Elution
Packing: GST Sepharose FF (Gravity Pre-Packed Column) (Cat: abs91010-G), 1 mL
Sample: GST-SUMO produced in E. coli
Binding Buffer : 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4
Elution Buffer : 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM glutathione, pH 7.4
MBP Sepharose FF Application:
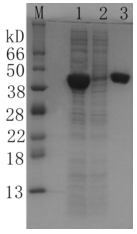
Figure 7
Lane M: Marker
Lane 1: Start material
Lane 2: Flowthrough
Lane 3: Elution
Packing: MBP Sepharose FF (Gravity Pre-Packed Column) (Cat: abs91011-G), 1 mL
Sample: MBP produced in E. coli
Binding Buffer : 20 mM Tris-HCl, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, pH 7.4
Elution Buffer : 20 mM Tris-HCl, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 10 mM D-maltose, pH7.4
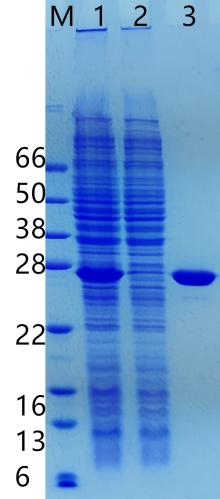
Figure 8
Lane M: Marker
Lane 1: Start material
Lane 2: Flowthrough
Lane 3: Elution
Packing: Strep II Sepharose FF (Gravity Preloaded Column) (Cat: abs91013-G), 1 mL
Sample: Strep II-tagged EGF produced in E. coli
Binding Buffer : 20 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0
Elution Buffer : 20 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM D-Biotin, pH 8.0
4. Absin label protein purification filler product information
|
Item Number |
Trade Name |
|
abs91008-G |
Ni-NTA Sepharose FF (Gravity Pre-Packed Column) |
|
abs91008-M |
Ni-NTA Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
|
abs91008-F |
Ni-NTA Sepharose FF |
|
abs91007-G |
Ni-IDA Sepharose FF (Gravity Preloaded Column) |
|
abs91007-M |
Ni-IDA Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
|
abs91007-F |
Ni-IDA Sepharose FF |
|
abs91009-F |
Ni-TED Sepharose FF |
|
abs91009-G |
Ni-TED Sepharose FF (Gravity Preloaded Column) |
|
abs91009-M |
Ni-TED Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
|
abs91010-F |
GST Sepharose FF |
|
abs91010-G |
GST Sepharose FF (Gravity Pre-Packed Column) |
|
abs91010-M |
GST Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
|
abs91011-F |
MBP Sepharose FF |
|
abs91011-G |
MBP Sepharose FF (Gravity Pre-Packed Column) |
|
abs91011-M |
MBP Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
|
abs91012-F |
Biotin Sepharose FF |
|
abs91012-G |
Biotin Sepharose FF (Gravity Pre-Packed Column) |
|
abs91012-M |
Biotin Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
|
abs91013-F |
Strep II Sepharose FF |
|
abs91013-G |
Strep II Sepharose FF (Gravity Preloaded Column) |
|
abs91013-M |
Strep II Sepharose FF (Medium Pressure Pre-loaded Column) |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
