- Cart 0
- English
Efficient screening of PROTAC star target VAV1 ligand molecules
August 21, 2025
Clicks:477
In recent years, PROTAC has risen rapidly in the field of drug research and development and has become one of the important models of drug development. As an emerging target, VAV1 is a key signaling protein downstream of T cell and B cell receptors. The degradation of VAV1 leads to a significant reduction in cytokines related to immune-mediated diseases, and its potential therapeutic value in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases has attracted much attention.
VAV1 basic information
VAV1 (Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1) is an important signal transduction protein, which belongs to one of the members of the Vav family. VAV1 is mainly expressed in hematopoietic cells, including T cells, B cells, monocytes, natural killer cells, granulocytes and dendritic cells. The VAV1 gene is located to human chromosome 7p15 and contains 21 exons. The VAV1 protein has multiple domains.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of VAV1 domain
Calmodulin homology (CH) domain: This domain is involved in the mobilization of calcium ions (Ca ² ⁺). Calcium ions play an important regulatory role in cell signal transduction. For example, during immune cell activation, the release of calcium ions can trigger a series of downstream signaling pathways.
Acidic (Ac) motifs: The mammalian Vav protein contains three tyrosine-regulating motifs, while the DroVav protein in Drosophila contains one. These tyrosine residues can regulate the activity of VAV1 through phosphorylation, and the phosphorylation state affects its interaction and function with other proteins.
Dbl homology (DH) domain: This is a highly conserved region that is a key functional domain for VAV1 as a phosphorylation-dependent GDP/GTP exchange factor (GEF) for Rho GTPase. It is able to facilitate the exchange of Rac/Rho GTPase from GDP (inactive state) to GTP (active state), thus activating Rho GTPase.
Plekstrin homology (PH) domain: Typically the PH domain is involved in phospholipid binding and cell membrane localization, helping to localize VAV1 onto the cell membrane, thus participating in signal transduction more effectively.
VAV1 Function
VAV1 is a multifunctional domain protein that not only functions as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), but also participates in GEF-independent signaling pathways as a scaffold protein
GEF-dependent function
Activation of Rac/Rho family GTPases: The primary GEF-dependent function of VAV1 is the activation of Rac/Rho family GTPases. When VAV1 is phosphorylated by tyrosine, its GEF activity is activated, catalyzing the replacement of GDP on Rho GTPase by GTP, thereby causing the Rho GTPase to transition from an inactive state to an active state.
Cytoskeletal recombination: Activated Rac/Rho family GTPases trigger actin recombination and F-actin polymerization, which in turn affect cell morphology and motility. For example, in T cells, VAV1 promotes actin polymerization by activating Rac1, which contributes to the formation of immune synapses between T cells and antigen presenting cells (APCs).
Cell migration and adhesion: VAV1 regulates integrin-mediated cell adhesion activation by activating Rho GTPase and is involved in chemokine-mediated cell migration. In macrophages, VAV1 activity is required for CSF-1-mediated chemotaxis and phagocytosis.
Receptor aggregation and signaling: The GEF activity of VAV1 contributes to the aggregation of T cell receptors (TCR) and B cell receptors (BCR), thereby enhancing receptor-mediated signaling.
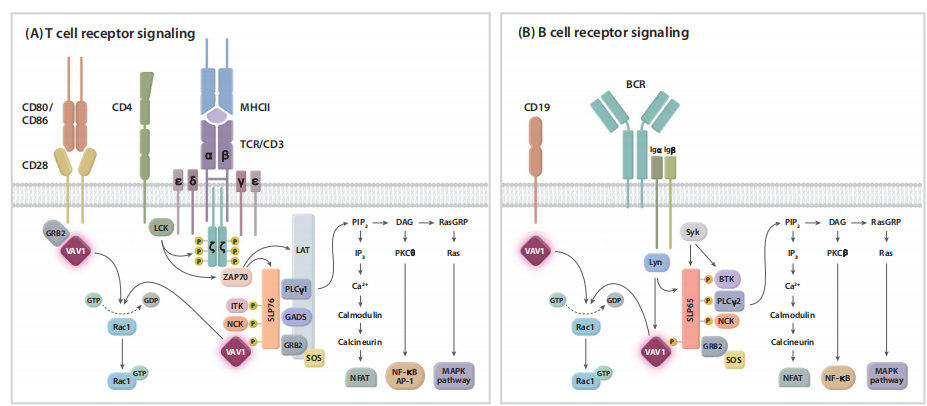
Figure 2 The role of VAV1 in antigen receptor signaling
VAV1 is a key component of the antigen receptor signaling complex and is associated with (A) T cell receptor (TCR)/CD3 and (B) B cell receptors. In T cells, SLP76 is recruited through its SH2 domain to T cell transmembrane activated connexin (LAT), and the resulting LAT/SLP76 complex acts as a key scaffold for other proteins, including VAV1, in the proximal TCR signaling complex. VAV1 interacts with other proteins through the SH2 domain and the proline-rich region/SH3 domain. In B cells, the signaling complex involved in VAV1 includes the scaffold protein SLP65 (also known as B cell connexin) homologous to SLP76, Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), growth factor receptor binding protein 2 (Grb2), and phospholipase γ (PLCγ) 2. The assembly of these protein complexes activates downstream events. The primary function of VAV1 dependent on GEF is to activate the Rac/Rho family GTPases. In T cells and B cells, co-stimulation via CD28 and CD19, respectively, is essential for optimal phosphorylation of VAV1 and activation of downstream signaling pathways.
GEF-independent function
As a scaffold protein: VAV1 functions primarily as a scaffold protein in the GEF-independent pathway. It binds to other proteins through various linker domains and participates in the formation of antigen receptor-proximal signaling complexes. For example, VAV1 interacts with phospholipase C-γ (PLCγ) 1 and is essential for TCR-mediated calcium ion release and activation of the NFAT pathway.
Promotes cell survival and cell cycle progression: VAV1 promotes cell survival and cell cycle progression in a GEF-independent manner, thereby promoting DNA damage responses.
Modulation of oxidative stress responses: VAV1 is also involved in the regulation of oxidative stress responses, affecting the redox balance within cells through its independent functions.
Relationship between VAV1 and disease
Autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases: Abnormal expression or dysfunction of VAV1 is related to a variety of autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis. Therefore, VAV1 is considered as a potential target for the treatment of these diseases.
Tumor: In malignant tumors, such as breast cancer and lung cancer, the overexpression of VAV1 is usually closely related to the malignant degree, metastasis and prognosis of the tumor.
With the development of drug research and development technologies such as new molecular gels, interventions against VAV1 have shown potential to treat autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. For example, MRT-6160, as a VAV1-targeted molecular gel degrader, has shown significant efficacy in preclinical and early clinical studies.
TR-FRET-based rapid detection of small molecules mediating the interaction between the DDB1/CRBN complex and VAV1
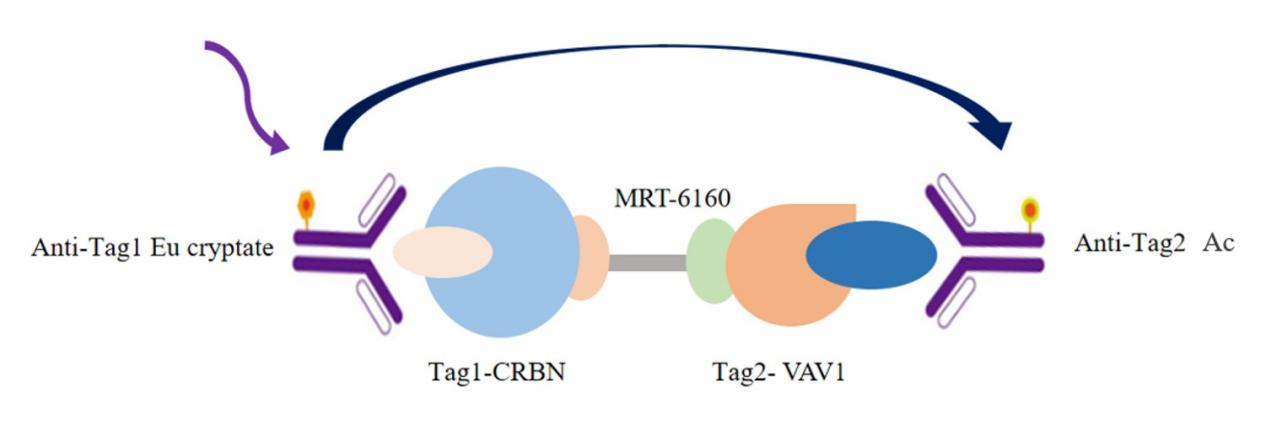
The interaction between DDB1/CRBN and VAV1 was detected by using Eu-labeled anti-Tag1 antibody (TR-FRET donor) and Accepter-labeled anti-Tag2 antibody (TR-FRET acceptor). Because the molecular glue MRT-6160 mediates the interaction between DDB1/CRBN and VAV1, the donor antibody is close to the acceptor antibody, and the excitation of the donor antibody will trigger fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to the acceptor antibody, which makes the acceptor antibody specifically emit a signal with a wavelength of 665nm. This specific signal is directly proportional to the degree of interaction between MRT-6160 and DDB1/CRBN, VAV1. The homogeneous experiment is simple to operate and does not require a washing step.

The following data is not a substitute for the data obtained in the experiment and is only an example and the results may vary depending on the TR-FRET compatible instrument.
VAV1 antibody
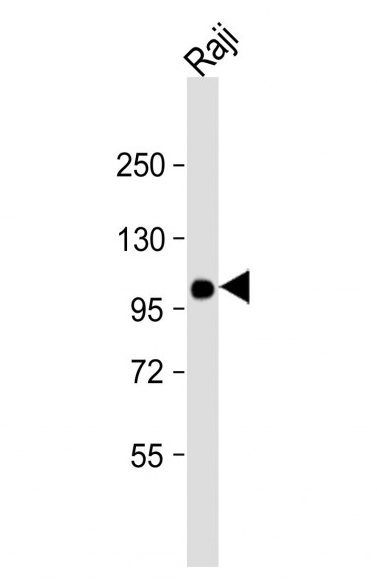
abs100534 Mouse anti-VAV1 Monoclonal Antibody(1582CT802.383.58)
References
[1]Neurath MF, Berg LJ. VAV1 as a putative therapeutic target in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. Trends Immunol. 2024 Aug;45(8):580-596. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2024.06.004. Epub 2024 Jul 26. PMID: 39060140.
Product recommendation
|
Item number |
Product Name |
Specifications |
|
Human VAV1/CRBN PROTAC Binding KIT |
500T/2500T/10000T |
|
|
Human CRBN Ligand Screening Assay Kit |
500T/2500T/10000T |
|
|
Mouse anti-VAV1 Monoclonal Antibody(1582CT802.383.58) |
50uL |
|
|
Microplate (384-well plate, white, shallow well) |
40 pieces/box |
|
|
Microplate (96-well plate, white, shallow well) |
50 pieces/box |
Other related products
|
Item number |
Product Name |
Applications |
|
Human Total IgG Kit (Assay Pro) |
Detection of Human IgG antibody in cell culture supernatant |
|
|
Human IgG Sandwich Assay Kit |
Concentration of human IgG antibody or hFc-tagged protein in cell culture supernatant |
|
|
TR-FRET Kinase-TK Assay Kit |
Activity detection of various tyrosine kinases and screening of inhibitors |
|
|
Human KRAS WT&cRAF Binding Kit |
Rapid detection of small molecule inhibitors of KRAS-cRAF interaction |
|
|
Human DDB1-CRBN&GSPT1 Binding Kit |
Detection of small molecules capable of mediating the interaction between the DDB1/CRBN complex and GSPT1 |
|
|
Human TNF-α/TNFR1 Binding Kit |
Determining the interaction between TNF-α and TNFR1 |
|
|
Human IL4/IL4R Binding Kit |
Determination of the interaction between interleukins and their receptors, as well as their inhibitors and antibody blockers |
|
|
Human BCL-XL/CRBN PROTAC Binding Kit |
Detection of small molecules capable of mediating the interaction between the DDB1/CRBN complex and BCL-XL |
|
|
Human BCL-XL/VHL PROTAC Binding Kit |
Detection of small molecules capable of mediating the interaction between the VHL complex and BCL-XL |
|
|
Human BRD4/CRBN PROTAC Binding Kit |
Detection of small molecules capable of mediating the interaction between the DDB1/CRBN complex and BRD4 |
|
|
Human Epigeneous Bromodomain Binding Kit |
To determine the interaction between BRD4 and [LYS (5, 8, 12, 16) AC] H4 (1-21) peptide, as well as its inhibitors and antibody blockers |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
