- Cart 0
- English
CTB Labeled Lipid Raft (LR) Solution
August 20, 2025
Clicks:1034
lipid raft microdomains (LR) are tiny domains rich in cholesterol and sphingolipids on the cell membrane (Figure 1). They have unique physicochemical properties and can be used as key biological processes such as signal transduction, cell adhesion and protein transport. Regulatory hub. In recent years, it has been found that the dysfunction of LR is closely related to many diseases, including tumors, neurodegenerative diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Due to its important pathophysiological role, the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting LR has become a current research hotspot.
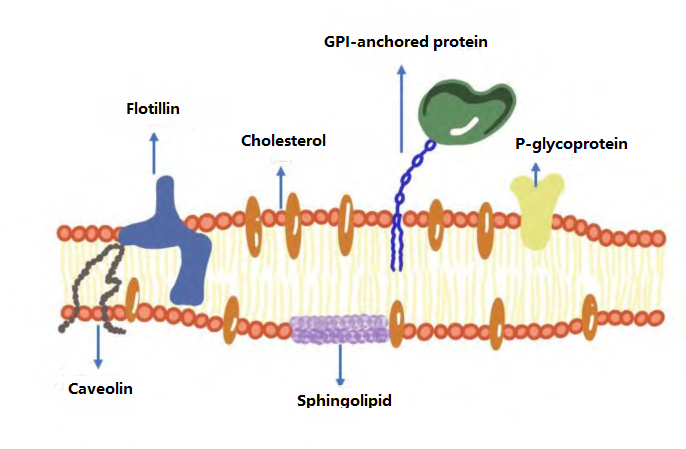 Fig. 1 Structure and composition of LR [1]
Fig. 1 Structure and composition of LR [1]
Cholera toxin B subunit
Cholera Toxin B subunit (CTB/CTxb) is a classic tool widely used in Lipid Rafts labeling, endocytosis research and neuroscience. The CTB provided by Aibixin can be used as neuronal tracer, cell membrane marker, immune adjuvant, etc. Products are strictly optimized for high-resolution imaging, flow analysis and functional studies.
Product core advantages:
1. Thirteen years of profound R&D accumulation and practical verification, the technology is mature and reliable;2. It has been cited by 68 high-scoring documents, providing strong support for scientific research;
3. Conventional CTB and FITC-marked CTB are available from stock;
4. More fluorescein-labeled CTBs can be customized, such as AF488/AF555/AF594;
5. The effect is comparable to imported brands, high quality and cost performance.
Featured application cases
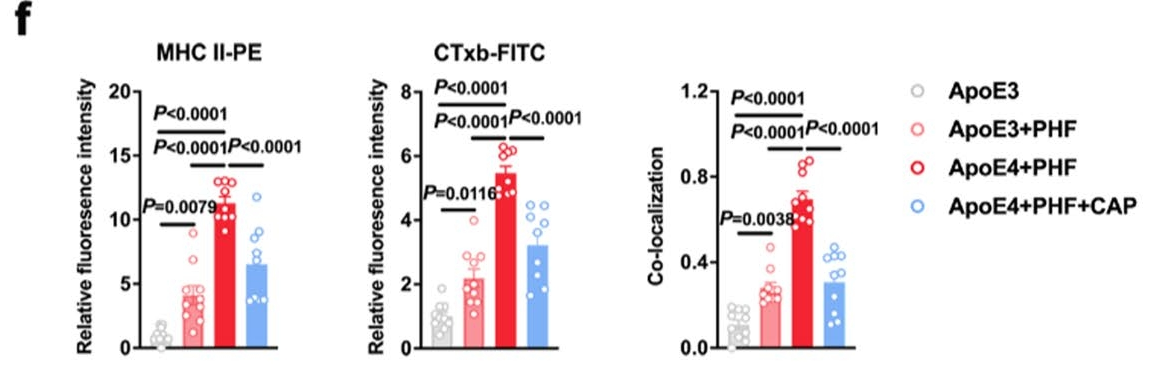
In October 2024, Yu Zhihua's research team from the Department of Pharmacology and Chemical Biology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine published an article titled at Translational Neurodegeneration (IF = 10.8) "TRPV1 alleviates APOE4-dependent microglial antigen presentation and T cell infiltration in Alzheimer's disease" Research paper, in which CTxb-FITC (abs80003, cholera toxin B subunit coupled FITC) was used as a lipid raft marker to study the effect of APOE4 on microglial lipid raft structure and antigen presentation function, as well as TRPV1 channel regulation.
CTxb-FITC was used in this study to label lipid rafts on cell membranes. Specific functions include:
Lipid raft localization: CTB binds to GM1 gangliosides on the cell membrane, a hallmark component of lipid rafts, and the distribution of lipid rafts is visualized by FITC fluorescent labeling.
Colocalization analysis: Colocalization experiments with MHC II molecules (PE markers) to verify how APOE4 promotes MHC II aggregation in lipid rafts through cholesterol accumulation, thereby enhancing antigen presentation function.

Experimental Methods [2]
1. CTxb-FITC Staining Step
Cell treatment: BV2 microglia were treated with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes at room temperature.
Blocking and staining:
Blocking solution: Incubate with PBS containing 5% BSA to block non-specific sites.
Staining: CTxb-FITC (8 μg/mL) and MHC II-PE (2 μg/mL) were added and incubated at 4 °C for 30 min. The nuclei were then stained with DAPI.
Imaging: TCS SP8 confocal microscope photography, ImageJ analysis of colocalization signal.
2. Key experimental procedures
Cell model: BV2 mouse microglia cell line, treated with ApoE3/ApoE4 (4 μg/mL) and tau protein fibers (PHF).
TRPV1 activation: capsaicin (1 μM, abs817025) pretreatment for 30 min.
Colocalization of lipid rafts with MHC II: Translocation of MHC II from lipid rafts after TRPV1 activation was verified by CTxb-FITC (abs80003) and MHC II-PE double labeling.
3. Other relevant methods
Flow cytometry: MHC II expression was analyzed.
Calcium imaging: Fluo-4 AM detects intracellular calcium signal (abs47014952).
Immunofluorescence: Confocal microscope observation of lipid rafts, MHC II, lysosomes (LysoTracker, abs47038871), etc.
Notes
1. Sample handling and fixationAvoid over-fixation: Use 4% paraformaldehyde (abs9179) for fixation for 10-15 minutes (room temperature) to avoid over-cross-linking of aldehydes to destroy the lipid raft structure. Fixation with organic solvents such as methanol/acetone will dissolve lipid rafts and cannot be used.
Washing: After fixation, gently wash 3 times with PBS (no detergent) to prevent the lipid raft from being destroyed.
2. Blocking and non-specific binding control
The blocking solution is recommended as PBS containing 5% BSA or 1-5% serum (homologous serum is the best), and it is blocked at room temperature for 30 minutes. Avoid the use of blocking solutions containing detergents (e.g. Triton X-100) to avoid dissolving the lipid rafts.
3. CTB Incubation conditions
Concentration optimization: The recommended working concentration of CTB-FITC is 1-10μg/mL (it needs to be determined by pre-experiment, too high concentration will increase the background), and dilute with PBS at pH 7.4.
Incubation time vs. temperature: 4 °C incubation for 30 min (reducing endocytosis, maintaining membrane surface GM1 labeling). If you want to label internalized GM1, incubate at 37 ° C. for 15-30 minutes instead.
Light-protected operation: CTB-FITC is sensitive to light and protects from light throughout the process.
4. Co-location experimental design
Multicolor labeling sequence: CTB-FITC (lipid raft) is stained first, and other antibodies (such as MHC II) are stained after fixation. If intracellular antigens (e.g. lysosomal proteins) are required, they are permeabilized after CTB staining (0.1% Saponin, abs815978).
Control Settings:
Negative control: Pretreatment of cells with methyl-β-cyclodextrin (Me-β-CD, 2-5 mM, abs47047467) depleted cholesterol and CTB signal should disappear.
Positive control: cholesterol enrichment treatment (e.g., LDL loading).
Frequently Asked Problems & Solutions
|
Questions |
Possible cause |
Solutions |
|
CTB signal weak |
Low or over-fixed GM1 expression |
Switch to viable cell labeling or increase CTB concentration (≤ 10 μg/mL) |
|
High background noise |
Non-specific binding or residual detergent |
Increase blocking time (1 hour), wash thoroughly |
|
Lipid raft aggregation abnormal |
Temperature or pH fluctuations |
Operate at 4 °C throughout, PBS pH adjusted to 7.4 |
|
The colocalization results were not significant |
Insufficient antibody penetration or lipid raft disruption |
Optimized permeabilization conditions (0.1% Saponin, 5 minutes) |
References
[1] Yang Ruihong, Yang Shuaihu, Ma Yuxue, Fang Shijian, Xiao Hongbin & Niu Wenying. (2024). Research progress of lipid rafts-based treatment of related diseases. Journal of Hainan Medical College, 30 (15), 1187-1193. doi: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20240424. 001.
[2] Lu J, Wu K, Sha X, Lin J, Chen H, Yu Z. TRPV1 alleviates APOE4-dependent microglial antigen presentation and T cell infiltration in Alzheimer's disease. Transl Neurodegener. 2024;13(1):52. Published 2024 Oct 29. doi:10.1186/s40035-024-00445-6
Related Products:
|
Item No. |
Name |
|
Fluo-4, AM, Cell Permeant |
|
|
Lysosomal Red Fluorescent Probe (FluoLyso Red) |
|
|
Methyl-β-cyclotrine |
|
|
Cholera toxin B subunit |
|
|
Cholera toxin B subunit (FITC conjugated) |
|
|
Saponin |
|
|
4% paraformaldehyde (universal tissue fixative) |
Dye/Probe Recommendations:
|
Item No. |
Name |
|
DASPEI |
|
|
Philepine |
|
|
Oil Red O |
|
|
D-fluorescein potassium salt |
|
|
2, 7-dichlorodihydrofluorescent yellow diacetic acid |
|
|
Calcium fluorescent probe Fluo 3-AM |
|
|
DiO perchlorate |
|
|
DiR iodide |
|
|
Calcein Red, AM |
|
|
Lysosomal Green Fluorescent Probe (FluoLyso Green) |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum green fluorescent probe |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum red fluorescent probe |
|
|
WSP-1 |
|
|
DAPI staining solution |
|
|
DiD p-chlorobenzene sulfonate |
|
|
Rhodamine labeled phalloidin (orange red) |
|
|
Phalloidin-Fluor 488 label (green) |
|
|
Phalloidin-Fluor 555 labeling (orange red) |
|
|
Cell microtubule staining kit (red fluorescence) |
|
|
Hoechst 33342 |
|
|
Tubulin-Tracker Red (antibody microtubule red fluorescent probe) |
|
|
JC-1 iodide |
|
|
7-AAD |
|
|
CFSE |
|
|
PI staining solution |
|
|
PKH26 Red Fluorescent Cell Ligation Kit |
|
|
PKH67 Green Fluorescent Cell Ligation Kit |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
