- Cart 0
- English
One article explains Native-PAGE
August 14, 2025
Clicks:1195
Non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Native-PAGE), or active electrophoresis, is a polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins that remain active without adding denaturants such as SDS and mercaptoethanol. It is commonly used for enzyme identification, isozyme analysis and purification. The biggest difference from non-denaturing gel electrophoresis is that the protein will not be denatured during and after electrophoresis, ensuring the function of the protein.
Why does SDS-PAGE require denaturation of proteins?
In the natural state, proteins exist in folded form, and have both positive and negative charges in the same molecule. Different charges and folding methods make different proteins with the same molecular weight migrate at different speeds on the gel, which makes it difficult to separate proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Deformation treatment can ensure that the mobility of proteins only depends on the molecular mass of proteins.
What are the roles of SDS and DTT as commonly used reagents for WB?
SDS: It is a detergent that can break intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonds, destroy the secondary and tertiary structures of protein molecules, and denature folded proteins into linear molecules. Furthermore, SDS allows the negative charge to uniformly attach the protein.
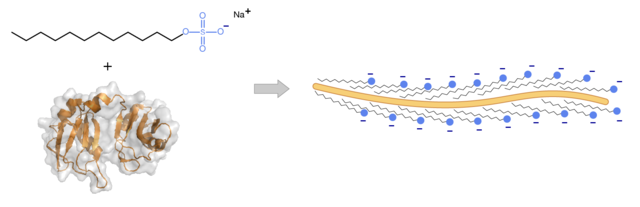
Interactions between proteins and SDS
DTT: dithiothreitol, which breaks the disulfide bonds between cysteine residues and prevents the formation of disulfide bonds between cysteines in proteins. However, it is impossible to reduce the disulfide bonds embedded in the protein structure. The reduction of such disulfide bonds often requires heating or denaturing agents to open the protein structure first.
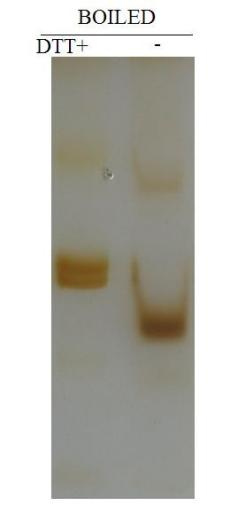
Effect of adding DTT on electrophoresis
Native-PAGE experimental method
The operation of electrophoresis is basically the same as that of SDS-PAGE, except that the preparation of non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel and the electrophoresis buffer cannot contain denaturants such as SDS. Generally, non-denaturing gel electrophoresis of proteins must first distinguish whether they are alkaline or acidic proteins. Acidic proteins usually use a buffer system with a pH of 8.8. The proteins will be negatively charged and the proteins will move to the anode; However, basic protein electrophoresis is usually carried out in a slightly acidic environment, and the protein is positively charged. At this time, the cathode and anode need to be inverted.
1. Sample preparation
The cells can be ultrasonicated. After ultrasonication, centrifuge the supernatant, mix the sample with the sample buffer, and be careful not to heat the sample to avoid protein denaturation. The loading buffer (abs9830) should not contain denaturants such as SDS.
2. Electrophoresis
Under non-denaturing conditions, protein migration is related to protein charge, protein shape and protein molecular weight. The molecular weight of protein should be determined by determining the Rf value of protein at different gel concentrations, and drawing the curve of gel concentration versus Rf to determine the molecular weight of protein.
During the electrophoresis process, too high voltage may cause fever and lead to protein denaturation, so it is best to place ice cubes outside the electrophoresis tank to lower the temperature; If the molecular weight of the protein is large, the electrophoresis time can be extended, so that the target protein has sufficient mobility to separate from other proteins.
3. Staining and analysis
After electrophoresis, the gel was peeled off and protein bands were observed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining (abs964) or silver staining (abs50085).
Silver staining operation steps (abs50085) (you need to bring your own ethanol, acetic acid and deionized water)
1) Take an appropriate amount of sample and carry out SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis;
2) Fixation: Peel off the gel after electrophoresis from the glass plate, rinse it clean with clean water, put it in a clean glass dish with a diameter of 12cm, add the ionized water without the glue, cover it, and shake it at room temperature on the decolorizing shaker for 5 minutes, discard the ionized water, add the fixative without the glue, cover it, and shake it on the decolorizing shaker for 30 minutes at room temperature.
Preparation of fixative solution: Add 17.5 mL of ethanol, 3.5 mL of ethanol and 14mL of deionized water in sequence, mix well to form 35mL of fixative solution.
3) Sensitization: Discard the fixative solution, add the removed water without the glue, cover the lid, shake on the decolorizing shaker at room temperature for 5 minutes, repeat the wash with water once, a total of 2 times, add the sensitizing solution without the glue, cover the lid, and shake on the decolorizing shaker at room temperature for 30 minutes.
Preparation of sensitizing solution: Add 3.5 mL of sensitizing solution I, 70 μL of sensitizing solution II, and 100 μL of sensitizing solution III to 31.5 mL of deionized water, mix well and use, and prepare now.
4) Dyeing: Discard the allergenic solution, add the allergenic solution without the glue, cover the lid, shake on the decolorizing shaker at room temperature for 2 minutes, repeat the wash with water once, a total of 2 times, add the dyeing solution without the glue, cover the lid, and shake on the decolorizing shaker at room temperature for 20 minutes.
Dyeing solution: Add 0.35 mL silver solution to 35 mL of pure water, and mix 30 μL of color development solution II well, and prepare it now.
5) Color development: Discard the dyeing solution, add the decolorizing water without the glue, cover the lid, shake on the decolorizing shaker at room temperature for 1 min, repeat the water wash once, a total of 2 times, add the colorizing solution without the glue, shake it on the decolorizing shaker at room temperature for about 2 minutes, the solution becomes turbid, discard the liquid, add a new colorizing solution and continue to develop color until the desired band is clear, and take photos.
Color development solution: Add 3.5 mL of color development solution I and 15μL of color development solution II to 31.5 mL of dissolved water, mix well, and prepare now.
4. Protein recovery
According to the dyeing results, cut the tape containing protein, chop it with a scalpel, put it into the treated dialysis bag, add an appropriate amount of buffer (which can maintain protein activity, usually the same as Native PAGE electrophoresis solution), finally put the dialysis bag into an ordinary nucleic acid electrophoresis tank, add an appropriate amount of buffer (the same as the buffer in the dialysis bag) into the electrophoresis tank, and electrophoresis at low temperature for 2-3h.
The above is the basic guideline, and the specific operation needs to be adjusted according to the experimental conditions and the characteristics of the target protein.
Related reagents
|
Item number |
Product Name |
Specifications |
|
abs9830 |
Non-denaturing protein loading buffer (5 ×) |
10mL |
|
abs9164 |
30% acrylamide/methylidene bisacrylamide (29: 1) |
500mL |
|
abs9360 |
Tris-Glycine Electrophoresis Buffer (10 ×) |
500mL |
|
abs9614 |
Glass gel Tris-Gly 10%, 10wells, 1.5 mm |
10 tablets/box |
|
abs964 |
Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining Kit (Conventional Type) |
1kit |
|
abs50085 |
Silver staining kit |
20T |
|
abs9232 |
BCA Protein Quantification Kit |
500T/2500T |
|
abs9162 |
Broad Spectrum Phosphatase Inhibitor Mixture (100 × Stock) |
1 mL/1 mL × 5 |
|
abs9161 |
Broad-spectrum protease inhibitor cocktail (EDTA-free, 100 × DMSO stock) |
1 mL/1 mL × 5 |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
