- Cart 0
- English
Cell viability detection | Six commonly used methods to reveal cell viability
August 13, 2025
Clicks:827
In the broad field of biomedical research, cell viability detection plays a vital role. It not only helps scientists evaluate the living status of cells, but also provides an in-depth understanding of cells' response to drugs, environmental changes or pathological processes. Cell viability assays typically include measuring aspects such as cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cell death. Today, Xiaoai introduces you to six commonly used methods for cell viability detection: ATP bioluminescence method, LDH detection method, MTT colorimetry method, CCK-8 method, fluorescent dye method and apoptosis detection method, so as to reveal the scientific mystery of cell viability together.
1. ATP bioluminescence method
The content of intracellular ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a direct indicator of cellular energy metabolism. The ATP bioluminescence method evaluates cell activity by measuring the level of intracellular ATP. This method has high sensitivity and wide dynamic range, and is especially suitable for experiments requiring high sensitivity detection.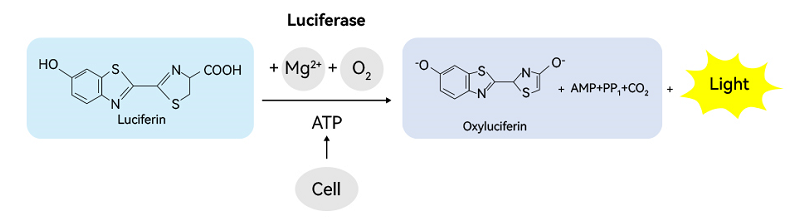
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of ATP detection kit (abs580117) for detecting cell activity
2. LDH detection method
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme widely existing in cells. It plays a key role in the glycolytic pathway and can catalyze the reversible reaction between lactate and pyruvate. LDH catalyzes lactic acid to produce pyruvate, and pyruvate reacts with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine to produce pyruvate dinitrophenylhydrazone. The latter is brown-red in alkaline solution, and the color depth is proportional to the concentration of pyruvate. By measuring the OD value, the activity of LDH can be calculated. In cell viability assays, the release of LDH is commonly used as an indicator of cell membrane integrity. When the cell membrane is damaged, the intracellular LDH will be released into the culture medium. By measuring the activity of LDH in the culture medium, the degree of cell damage or death can be assessed.
3. MTT colorimetric method
MTT (3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) colorimetric assay is a classic method for detecting cell viability. It indirectly reflects the metabolic activity of cells by measuring the activity of dehydrogenase in living cells to reduce MTT to the purple formazane product. This method is simple to operate and low in cost, and it is a common screening tool in laboratories.
4. CCK-8 method
The CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8) method is a colorimetric method based on WST-8 (2-(2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2, 4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazole monosodium salt). It evaluates cellular activity by measuring the activity of cellular mitochondrial dehydrogenase. CCK-8 method has high sensitivity and wide dynamic range, and is suitable for the activity detection of various cell types.
5. Fluorescent dye method
The fluorescent dye method utilizes specific fluorescent dyes, such as Calcein-AM or CFSE, to label living cells. These dyes are metabolized into fluorescent products within living cells, which are detected by flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy. Fluorescent dye method can provide intuitive image of cell viability, which is suitable for cell proliferation and migration research.
6. Apoptosis detection
Apoptosis is a process of programmed cell death, which is closely related to cell activity. By staining with Annexin V and PI (propidium iodide), phosphatidylserine externalization on the cell surface can be detected and thus the extent of apoptosis can be assessed. This approach is of great significance for studying cell death mechanisms and drug toxicity.
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of six commonly used methods for cell viability detection
|
Detection Method |
advantage |
shortcoming |
|
ATP bioluminescence method |
It has high sensitivity, can quickly detect cell activity, is easy to operate, directly reflects the metabolic activity of cells, and is proportional to the number of cells. |
May be interfered by other sources of ATP in the sample, such as microbial contamination. |
|
LDH detection method |
The colorimetric method is simple and fast to operate, the standard curve method is accurate and quantitative, and has high sensitivity. It is suitable for a variety of cell types, reflects the integrity of cell membranes, and can also be used to evaluate cytotoxicity. |
May be interfered by other sources of LDH in the sample, such as microbial contamination. It can only reflect cell death, but cannot directly reflect cell proliferation. |
|
MTT colorimetric method |
Low cost, simple operation, suitable for many cell types. It can reflect the metabolic activity of cells, especially the activity of mitochondria. |
Live cells are required to participate, and dead cells cannot be detected. A longer incubation time is needed and the experimental period is longer. |
|
CCK-8 method |
Easy operation and high sensitivity. Suitable for use with various cell types, including suspension cells. Can reflect cell proliferation and viability. |
The cost of CCK-8 may be higher relative to MTT. There may be toxicity to certain cell types. |
|
Fluorescent dye method |
Cell activity can be monitored in real time, which is suitable for long-term tracking experiments. For example, Calcein-AM can be cleaved by esterases in living cells to produce fluorescence, thereby indicating cell activity. |
Fluorescent dyes may be somewhat toxic to cells, especially when stained at high concentrations or for long periods of time. Furthermore, the fluorescence signal may be affected by photobleaching. |
|
Apoptosis assay |
Apoptosis can be specifically detected, as by Annexin V and PI staining, which can distinguish early and late apoptotic cells. |
Specific reagents and equipment, such as flow cytometers, are required, and the operation is relatively complex and costly. |
Each method has its specific application scenarios and limitations, and the selection of the appropriate detection method needs to be decided according to the specific needs and conditions of the experiment.
Below, Xiaoai focuses on introducing the ATP detection method with the advantages of high sensitivity, easy operation and speed.
ATP detection kit (abs580117) method of use
|
Components |
Specifications |
|
ATP Assay Buffer |
50mL |
|
D-luciferin |
120μL |
|
Cofactor |
120μL |
|
Luciferase |
120μL |
|
ATP Standard (100μM) |
200μL |
|
Instructions |
1 serving |
2. How to use
1. Reagents and equipment to be brought by yourself
1) Phosphate buffer solution (PBS) pH 7.4 for cell culture
2) Triton X-100
3) Series of adjustable range pipettes and tips
4) Centrifuge tube and white 96-well plate
5) Chemiluminescence plate reader
2. Preparation before the experiment
1) Sample preparation:
① Preparation of cell culture supernatant: inoculate the cells to be measured into the culture plate. After treatment with intervention factors, directly aspirate the cell supernatant. If it is suspended cells, centrifuge at 4 ℃ and 300g for 5 minutes to collect the supernatant.
② Preparation of cell lysis supernatant: Collect the cells to be measured (1 × 106-1 × 107) into a 5 mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4 °C and 300 g for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, then add 200 μL PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100, lyse in an ice bath for 30 minutes, centrifuge at 4 °C and 10000 g for 10 minutes, and collect the supernatant.
③ Preparation of tissue lysis supernatant: Collect the tissue to be measured (20-50mg) into a glass homogenizer or automatic homogenization tube, then add 500μL PBS containing 1% Triton X-100, homogenize for 1min, centrifuge at 10000g for 10min at 4 ℃, and collect the supernatant.
Note: If various samples are not measured immediately, please freeze at-80 ℃; Before the formal measurement, the sample was appropriately diluted with an ATP Assay Buffer based on the results of the preliminary test, and then measured.
2) Preparation of standard:
In a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 990 μL of ATP Assay Buffer, and then add 10 μL of 100 μM concentration ATP Standard to the centrifuge tube to prepare 1 μM concentration ATP Standard; Then, take another 8 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes, add 200μL ATP Assay Buffer respectively, and then aspirate 200μL of 1μM concentration ATP Standard and dilute it to 0.5, 0.25, 0.125, 0.0625, 0.0312, 0.0156, 0.0078, 0.0039 μM concentrations sequentially.
3) Preparation of test working fluid:
Preparation of ATP testing working solution: According to the number of samples to be tested, refer to the table below to prepare an appropriate amount of ATP testing working solution, and the reagents in the table are mixed according to the proportion to obtain ATP testing working solution.
|
Sample components |
1 sample |
10 samples |
100 samples |
|
ATP Assay Buffer |
47μL |
470μL |
4.7mL |
|
D-luciferin |
1μL |
10μL |
100μL |
|
Cofactor |
1μL |
10μL |
100μL |
|
Luciferase |
1μL |
10μL |
100μL |
3. Operation steps
Operation steps
1) Set up blank control wells, standard wells and sample wells in a white 96-well plate, refer to the table below, add 50μL ATP Assay Buffer to the blank control wells, add 50μL gradient concentration ATP test working solution (0.0039-1 μM) to the standard wells, and add 50μL sample to the sample wells.
|
|
Blank Control Well |
Standard well |
Sample well |
|
ATP Assay Buffer |
50μL |
—— |
—— |
|
ATP Standard |
—— |
50μL |
—— |
|
Sample |
—— |
—— |
50μL |
|
ATP detection working fluid |
50μL |
50μL |
50μL |
2) As shown in the table above, add 50μL of ATP detection working solution to each well, mix well, and incubate at room temperature for 5min.
3) After the reaction is completed, measure the relative luminescence intensity (RLU) with a chemiluminescence microplate reader.
4) Calculation results: Use the standard concentration as the abscissa and the RLU value as the ordinate to make a standard curve, and obtain the functional relationship between the horizontal and vertical coordinates, and then use the RLU value of each sample to calculate the ATP concentration in the sample. The ATP curve determination is shown in the figure below:
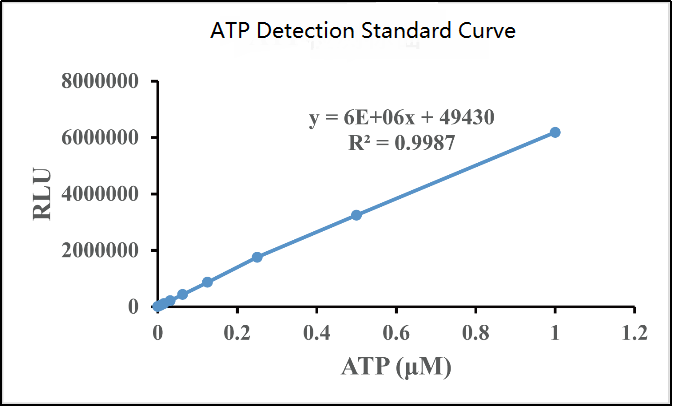
Cell viability detection is a bridge between basic research and clinical application. Through the above six commonly used methods, researchers can more accurately assess the survival status of cells and provide important information for disease treatment and drug development. With the continuous advancement of biotechnology, more innovative detection methods may come out in the future, revealing more mysteries of cell vitality for us.
Product recommendations in this issue:
|
Item number |
Product Name |
Specifications |
|
ATP Assay Kit |
96T |
|
|
Lactate dehydrogenase detection kit |
96T |
|
|
MTT cell proliferation and cytotoxicity detection kit |
500T |
|
|
CCK-8 kit |
500T |
|
|
abs42014734 |
Calcein-AM |
1mg |
|
abs9106 |
CFSE |
50mg |
|
Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection Kit |
100T |
Recommended cell staining products:
|
Item number |
Product Name |
λEx/λEm (nm) |
Product Description |
|
DiO perchlorate (green) |
484/501 |
Viable cell tracing, cell membrane staining |
|
|
DiD p-chlorobenzene sulfonate (red) |
644/663 |
Viable cell tracing, cell membrane staining |
|
|
Cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) |
— |
Neurotracer |
|
|
Cholera toxin B subunit-FITC |
494/520 |
Neurotracer |
|
|
DiR iodide (dark red) |
748/780 |
Animal in vivo imaging |
|
|
D-fluorescein potassium salt |
— |
Animal in vivo imaging |
|
|
Rhodamine labeled phalloidin (orange red) |
540/565 |
Cytoskeleton staining (F-action) |
|
|
Phalloidin-Fluor 488 (green) |
493/517 |
Cytoskeleton staining (F-action) |
|
|
Phalloidin-Fluor 555 (orange red) |
556/574 |
Cytoskeleton staining (F-action) |
|
|
Calcein red (red) |
560/574 |
Cytoplasmic staining |
|
|
CFSE (green) |
492/517 |
Cytoplasmic staining |
|
|
DASPEI |
550/573 |
Mitochondrial staining |
|
|
JC-1 |
585/590 |
Mitochondrial membrane potential detection |
|
|
Lysosomal green fluorescent probe |
504/511 |
Lysosomal staining |
|
|
Lysosomal red fluorescent probe |
577/590 |
Lysosomal staining |
|
|
PKH26 Red Fluorescent Cell Ligation Kit |
551/567 |
Exosome staining |
|
|
PKH67 Green Fluorescent Cell Ligation Kit |
490/502 |
Exosome staining |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum green fluorescent probe |
489/520 |
Endoplasmic reticulum staining |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum red fluorescent probe |
587/615 |
Endoplasmic reticulum staining |
|
|
DAPI staining solution (blue) |
364/454 |
Nuclear staining |
|
|
Hoechst 33342 (blue) |
350/461 |
Nuclear staining |
|
|
7-AAD (red) |
545/650 |
Nuclear staining |
|
|
PI staining solution (red) |
535/617 |
Nuclear staining |
|
|
Fluo 3-AM |
506/526 |
Calcium ion (Ca2 +) probe |
|
|
DCFH-DA |
502/523 |
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) probes |
|
|
DAF-2 DA |
491/513 |
Nitric oxide (NO) probe |
|
|
WSP-1 |
465/515 |
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) probe |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
