- Cart 0
- English
A complete guide to molecular cloning technology
August 11, 2025
Clicks:177
In the early 1970s, the birth of genetic engineering molecular cloning technology pushed life science research into a new era of rapid development, and many biological problems with it as the breakthrough point of research were solved. Genes can be transferred and expressed between species, genetically engineered drugs have been developed, gene therapy has been realized, and new agricultural varieties such as transgenic plants and animals have been cultivated. Since then, biological evolution has entered the historical process of human knowledge intervention. The realization of "human genome sequencing", which is rated as one of the three major scientific achievements of the century, is also a masterpiece of mankind based on molecular cloning technology. The content of life science is no longer a compartmentalized platter, but a unified biology integrating the concepts of molecular biology and cell biology.
Figure 1 Gene editing (picture from the Internet)
01 The concept of molecular cloning
Molecular cloning (gene cloning/DNA recombination/vector construction) techniques provide a method of purifying and amplifying specific DNA fragments at the molecular level. They often contain target genes. They are inserted into cloning vectors by in vitro recombination methods to form recombinant cloning vectors. Through transformation and transduction, they are introduced into a suitable host body for replication and amplification, and then separated and purified from the screened host cells. The required cloning vector can obtain many copies of the inserted DNA, thereby obtaining amplification of the target gene. Its main purpose is to amplify a large number of target genes to prepare for the next step of gene function research. It can be applied to protein expression, virus packaging, gene therapy, cell therapy, mRNA vaccine, RNAi interference, cell function and other studies.
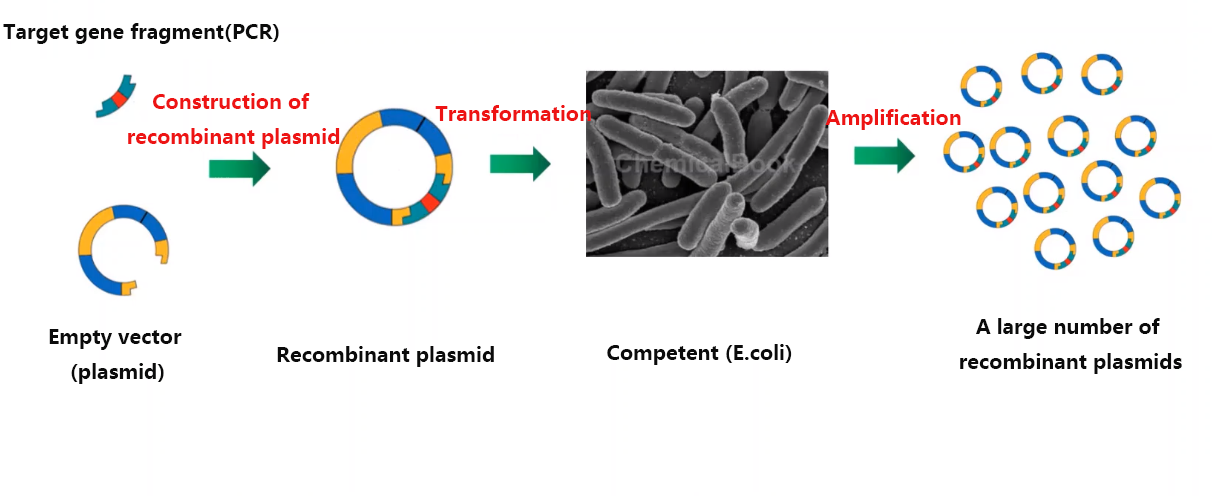
Figure 2 Molecular cloning technology
02 Principle of molecular cloning
Molecular cloning technology can simply be understood as covalently linking DNA fragments (or genes) to vectors, then introducing them into host cells, and then screening to obtain recombinant clones. The first step in the molecular cloning method is to obtain the desired insert (gene of interest), which can be DNA or mRNA from any cell type from eukaryotes, prokaryotes, or it can be synthesized directly in the laboratory. A DNA sequence containing the target gene is isolated from genomic DNA or cDNA (cDNA synthesized by reverse transcription of mRNA in vitro) by PCR, enzyme digestion and other technologies, and then linked to a linearized vector after purification of the product. Regarding vectors, the plasmid vector is commonly used, which is a small circular DNA molecule-as the most commonly used and simplest vector in genetic engineering. Compared with natural plasmids, plasmid vectors usually carry one or more selectable marker genes (such as antibiotic resistance genes) and a synthetic multi-cloning site sequence containing multiple restriction endonuclease recognition sites, and remove most of the non-essential sequences to reduce the molecular weight as much as possible to facilitate genetic engineering operations. By cleaving the vector DNA and the foreign DNA (gene of interest) with the same restriction enzyme (e.g., EcoRI, etc.), the cleaved vector and foreign DNA are brought into an end-compatible configuration. The vector and the prepared target DNA were mixed under the action of DNA ligase to carry out ligation reaction, thus completing the construction of recombinant DNA.
It's not finished after the recombination of the target gene and the vector is completed! Recombinant DNA is to be introduced into a host organism (generally E. coli is selected) for mass replication. As the host, the engineered bacteria will change the permeability of its cell membrane under certain chemical conditions or physical stimuli, so that it is easy to absorb foreign genes attached to the cell surface into the cell, and this process is transformation. Selection markers can be used to easily identify engineered bacteria that have successfully introduced the target gene, such as antibiotic resistance screening-all engineered bacteria that have successfully introduced the recombinant vector have obtained a certain antibiotic resistance, while engineered bacteria that have not been introduced cannot grow in a medium containing the antibiotic, which is the screening of preliminary positive strains. Subsequently, the corresponding positive monoclonal identification and plasmid sequencing were carried out to successfully complete the molecular cloning experiment.
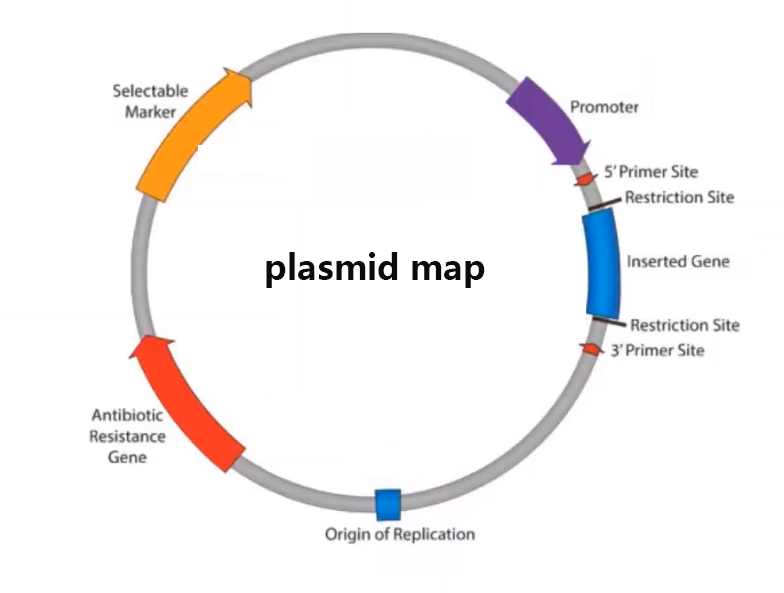
Figure 3 Plasmid map
03 Experimental process
The whole molecular cloning begins with the design of primers, and according to the corresponding nucleic acid sequence of the target protein, the specific primer molecule containing the cleavage site and the required Tag is designed. The rest is to obtain the target gene, enzyme digestion, ligation, transformation and screening, bacterial solution PCR or enzyme digestion identification and sequencing comparison. The main experimental process is shown in the figure below. Different cloning methods (which we will continue to introduce in the next issue) will have different steps in enzyme digestion and ligation, and the overall process is basically the same.
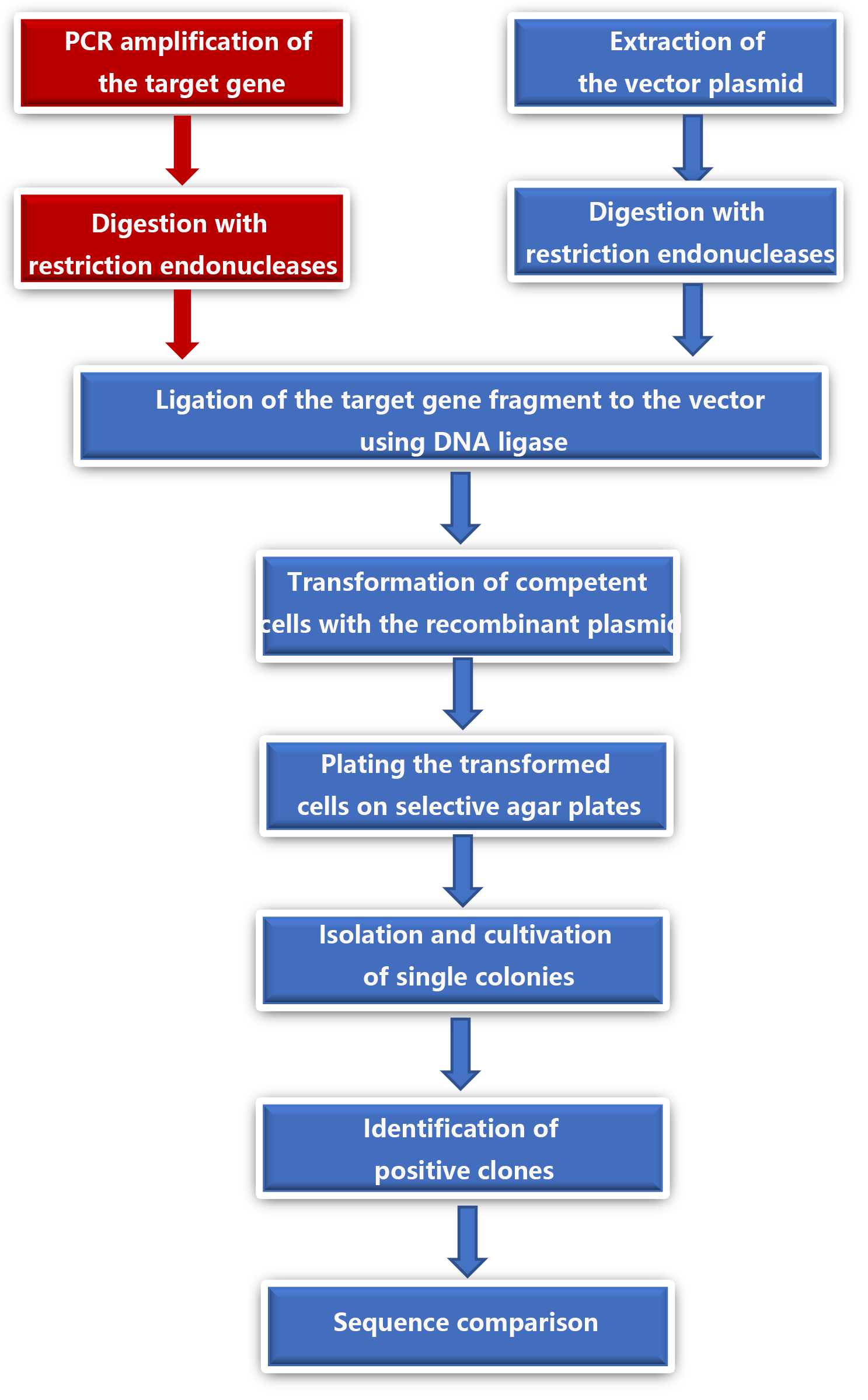
Fig. 4 General flow chart of molecular cloning technology
Molecular cloning related product recommendations
|
Item number |
Product Name |
Specifications |
|
abs60036 |
2×Taq PCR Mix |
1ml*5/1ml*20/1ml*50 |
|
abs60034 |
2×Xerox PCR Master Mix |
1ml/1ml*5 |
|
abs60167 |
PCR & DNA Fragment Purification Kit |
50T/200T |
|
abs7991 |
PCR product purification kit (magnetic bead method) |
5ml/60ml |
|
abs60023 |
High purity plasmid rapid extraction kit |
50T |
|
abs60171 |
Bsa Ⅰ restriction endonuclease |
1KU/5KU/10KU |
|
abs60209 |
Rapid endonuclease ClaI |
50T |
|
abs60213 |
Rapid endonuclease EcoRI |
600T |
|
abs60230 |
Fast endonuclease PstI |
500T |
|
abs60217 |
Rapid endonuclease HindIII |
500T |
|
abs60084 |
T4 DNA Ligase |
500U/500U×10 |
|
abs60097 |
Site-directed Mutagenesis Kit |
10T |
|
abs60099 |
XL Site-directed Mutagenesis Kit |
10T |
|
abs60100 |
Multi Site-directed Mutagenesis Kit |
10T |
|
abs60104 |
Random Mutagenesis Kit |
20T |
|
abs60085 |
T-Vector Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T |
|
abs60089 |
pBM21 Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T/3×20T |
|
abs60090 |
pBM22 Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T/3×20T |
|
abs60091 |
T-Vector pTOPO Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T/100T |
|
abs60094 |
Blunt pTOPO Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T/100T |
|
abs60095 |
pBM16A Toposmart Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T/3 × 20T |
|
abs60096 |
pBM27 Toposmart Rapid Cloning Kit |
20T/3 × 20T |
|
abs60250 |
Rapid Multi-Fragment DNA Assembly Premix |
50T |
|
abs9314 |
Nucleic acid non-denaturing preform 5%, 10wells |
10 tablets/box |
|
abs9315 |
Nucleic acid non-denaturing preform 10%, 10wells |
10 tablets/box |
|
abs9316 |
Nucleic acid non-denaturing preform 15%, 10wells |
10 tablets/box |
|
abs9317 |
Nucleic acid non-denaturing preform 5%, 15wells |
10 tablets/box |
|
abs9318 |
Nucleic acid non-denaturing preform 10%, 15wells |
10 tablets/box |
|
abs9319 |
Nucleic acid non-denaturing preform 15%, 15wells |
10 tablets/box |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
