- Cart 0
- English
Follow-up Research on Immune Cell Culture Strategy (6)
overview
There are six basic processes for immune cell culture: sample preparation, cell sorting, typing identification, expansion & culture, quality optimization, and follow-up studies. Xiaoai has given you a detailed introduction to "Immune Cell Culture Strategy: Sample Preparation (1)", "Immune Cell Culture Strategy: Cell Sorting (2)", "Immune Cell Culture Strategy: Typing and Identification (3)", "Immune Cell Culture Strategy: Expansion & Culture (4)" and "Immune Cell Culture Strategy: Quality Optimization (5)" Let's continue to learn about it todayFollow-up studies.
Follow-up study: use flow cytometry, ELISA, cell co-culture and other experimental techniques to study the function of immune cells (killing ability, secretion of cytokines, phagocytosis function, proliferation ability, etc.). There are too many follow-up studies that can be done on immune cells, such as: CAR-T/NK/M, tumor cells and immune cells co-culture, organoid immune co-culture, cytokine storm, etc., Xiao Ai is here to introduce you to 3 popular ideas for immune cell research: NK cell killing ability identification, mixed lymphocyte response, and Treg in vitro inhibition experiment.
NK cell killing ability identification
As a natural killer cell with its own immune memory, NK is also very hot in research on its killing function.
NK cells mainly kill target cells through the following four pathways:
(1) NK cells are degranulated, releasing perforin and granzyme to kill target cells;
(2) activated NK cells kill target cells by releasing cytokines;
(3) induce apoptosis of target cells through death receptors such as Fas/FasL and TNF-α/TNFR-1 pathways;
and (4) mediate the killing of target cells by ADCC[1].
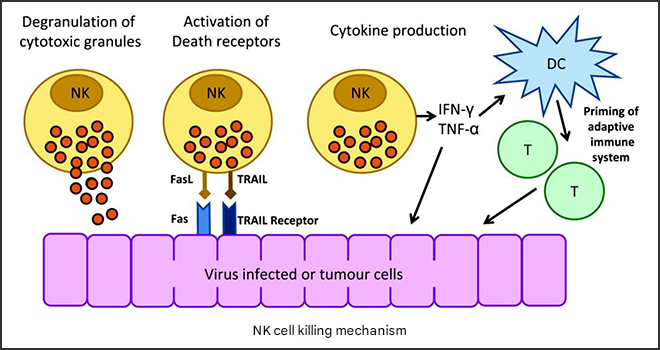
Fig.1 Four pathways by which NK cells kill target cells
In vitro research on the killing function of NK cells is mainly to co-culture NK cells with target cells (usually K562 cells), and then detect the enzymes released by the target cells or label the target cells with CAM and CFSE, and by detecting fluorescence, the number of cells can also be detected by MTT/CCK8, so as to obtain the killing activity of NK cells, and the cytokines secreted by NK cells or the degranulation index CD107a can also be detected. Of course, we can co-culture other immune cells and tumor cells.
Xiao Ai also sorted out the steps for you to refer to:
1. Target cells (generally tumor cells) labeled with fluorescent dyes GFP and CFSE were seeded into 96-well plates, and the seeding density of different tumor cells can be referred to Figure 2;

Fig.2 Seeding density of different tumor cells in NK and tumor cell co-culture
2. On the second day, the medium was changed to the culture system of NK cells, and NK cells were added according to the ratio of target cells and effector cells (NK) 1:3, and fluorescence microscopy was taken at 0-12 hours.
Note: The co-culture ratio of target and effector cells, as well as the timing, need to be determined by pre-experiment.
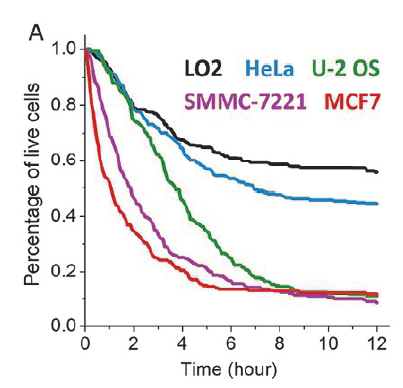
Fig.3 Cumulative survival curves of different epithelial cell lines co-cultured with NK
Table 1 Tumor immunology co-culture table
|
name |
Catalog number |
apply |
|
Human Natural Killer Cell (NK) Amplification Kit |
NK cell culture |
|
|
Recombinant Human IL-15 Protein |
Cytokines (domestic cost-effective) |
|
|
Recombinant Human IL-2 Protein |
Mixed Lymphocyte Response (MLR)
Mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR), also known as mixed lymphocyte culture, refers to the proliferation and activation of T cells stimulated by antigen-presenting cells, and the histocompatibility of antigen differences and the ability to respond to allogeneic cells are evaluated according to the intensity of the lymphocyte response. It can be divided into two-way mixed lymphocyte culture and one-way mixed lymphocyte culture. In vitro studies, cytokines secreted by T cells, such as IFN-γ and T cell proliferation antigen CD107a, are also commonly measured.
Bidirectional mixed lymphocyte culture: PBMCs from two different donors are co-cultured to enable bidirectional activation of T cells from both donors.
Unidirectional mixed lymphocyte culture: CD4+ T cells isolated from one donor are combined with DCs isolated from another donor, resulting in unidirectional activation of T cells.
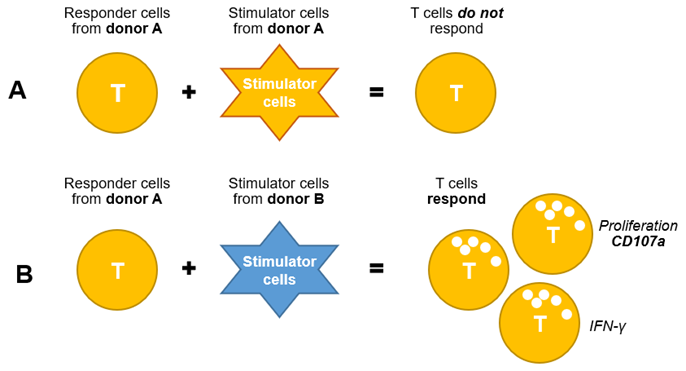
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of in vitro study of unidirectional mixed lymphocyte culture
Xiaoai takes unidirectional mixed lymphocyte culture as an example to introduce the experimental procedures:
1. PBMCs from donor B were treated with 50 μg/mL mitomycin at 37°C for 30 min, and these cells were used as stimulated cells;
2. Centrifuge at 300×g for 5min to remove mitomycin, according to 2x106PBMCs/mL (or magnetic beads to sort DC cells) into 24-well plates (250 uL);
3. Add another 250uL PBMCs (2x10) from A6cells/mL) (or magnetic beads to sort out T cells) as response cells;
4. Place the MLR composed of stimulated cells and responding cells at 37°C, 5% CO2Incubated in the incubator for seven days;
After 5 or 7 days, the proliferation of response cells and the secretion of cytokines can be detected.
Table 2 Tumor immunology co-culture table
|
name |
Catalog number |
apply |
|
Human lymphocyte isolate |
Obtain PBMCs |
|
|
CD3/CD28 magnetic beads |
Sort T cells |
CD4+CD25+Treg and CD8+T inhibition assays in vitro
The advantage of in vitro inhibition assays is that because only Tresp cells (CD4+CD25-) or Treg cells are co-cultured with immune cells, the inhibitory effect of Treg cells on CD8+ T cell responses can be directly assessed. In addition to CD8+ T cells, the effects of Treg cells on other immune cells, such as dendritic cells or natural killer cells, can also be assessed by changing experimental conditions.
Xiao Ai also sorted out the experimental steps in the literature, which can be used as a reference:
1. Cleaning of CD3/CD28 magnetic beads:
1) Resuspend the beads in a centrifuge tube (vortex for more than 30s, or reverse and mix well for 5min);
2) Transfer the determined volume of beads to a centrifuge tube;
3) Add an equal volume of PBS buffer containing 1% HSA, or at least a volume of 1 ml, to resuspend;
4) Place the centrifuge tube on the magnetic rack (special for magnetic beads) for 1min, and then discard the supernatant;
5) Transfer the centrifuge tube off the magnetic stand (for magnetic beads) and resuspend the beads with the same volume of PBS buffer containing 1% HSA (the initial volume of beads in step 2).
2. Take 50 μL of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells (1×105cells/wells). Add 50 μL of CD8+ T cells per well as Response T (Tresp) cells (1×10).5cells/wells). Add already washed CD3/CD28 beads to each well, adjusting the bead-to-cell ratio to 1:1.
Note: In this step, control wells are labeled and established as follows: unstimulated CD8+T (without anti-CD3/CD28); stimulated CD8+ T cells (containing anti-CD3/CD28); Stimulated Treg cells (containing anti-CD3/CD28). Treg cells can be diluted with complete medium and co-cultured with Treg cells (1:0.25-1:1) in different ratios;
3. Add 50 μL or an appropriate volume of medium to each well, for a total volume of 200 μL. Cover the plate with aluminum foil and place it in a carbon dioxide incubator at 37 °C for 72 h;
4. After 72 hours of incubation, cytokine production analysis was carried out, and the supernatant of each well was separated to another plate, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed to detect the level of IFN-γ;
5. After separating the supernatant of each well, wash the Petri dish containing cells with FACS buffer, centrifuge at 4°C, 300g for 2min, and wash 3 times;
6. After washing, discard the supernatant. Resuspend the cells with 50 μL of antibody buffer (anti-CD4, anti-CD8, and cell viability assay reagents) and stain the proliferating CD8+ T cells (when CD8+ T cells are obtained, they can be labeled with dyes that track cell proliferation). Incubate at 4°C in the dark for 20min;
7. Centrifuge at 4 °C, 300g for 2min, wash twice. After washing, the supernatant was discarded and fixed with 100 μL of fixation buffer at 4°C for 20 min.
8. Centrifuge at 4°C, 300g for 2min, and wash twice. The cells were resuspended in 200 μL FACS buffer, and the proliferation of labeled CD8+ T cells was detected by flow cytometry.
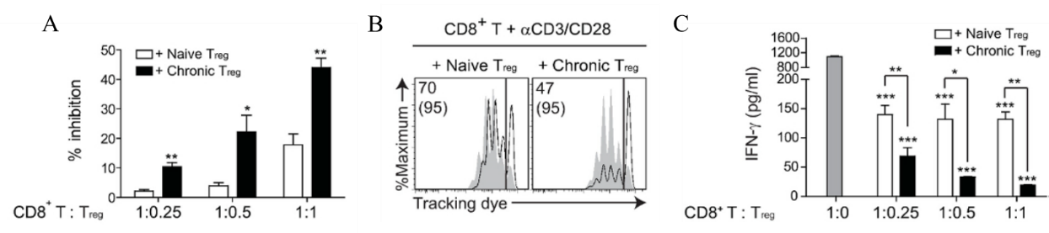
Fig.6 Activated Treg cells inhibit the proliferation of CD8+ T cells and secrete IFN-γ
|
name |
Catalog number |
apply |
|
Human T cell expansion medium |
Human T Cell Activation Amplification Kit (Micron Magnetic Beads) |
That's all for today's explanation, if you have any cell culture questions, welcome to join the group to communicate!
This issue is recommended by Xiaoai
|
Catalog number |
name of article |
specification |
|
Human Natural Killer Cell (NK) Amplification Kit |
1kit |
|
|
Recombinant Human IL-15 Protein |
10ug/50ug/100ug/500ug |
|
|
Recombinant Human IL-2 Protein |
10ug/500ug |
|
|
Human lymphocyte isolate |
200mL/200mL×10 |
|
|
CD3/CD28 magnetic beads |
1mL |
|
|
Human T cell expansion medium |
1kit |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
July 10, 2025
Clicks:90
