- Cart 0
- English
A comprehensive guide to apoptosis detection
July 07, 2025
Clicks:1758
1. Overview
Apoptosis is a kind of active and orderly death of cells, which involves the activation, expression and regulation of a series of genes, and it is not a phenomenon of autologous damage under pathological conditions, but a kind of death that is actively fought for in order to better adapt to the living environment. Today, Xiao Ai introduces to you six common methods of apoptosis: cell membrane phosphatidylserine detection, TUNEL nick end labeling method, mitochondrial membrane potential detection, Caspase apoptosis core molecule detection, morphological observation, and mitochondrial membrane potential transition pore detection.
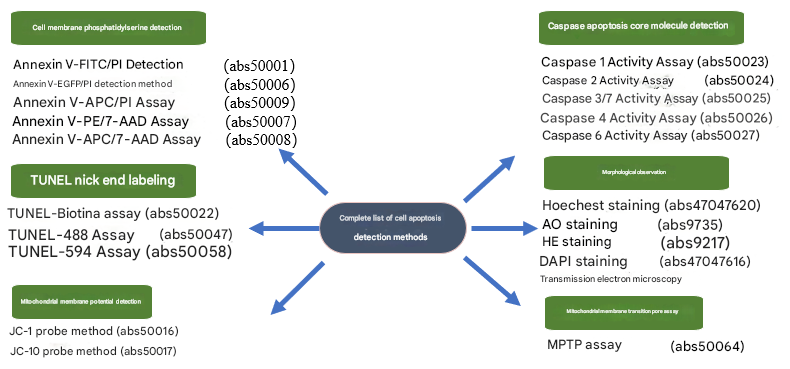
A complete set of apoptosis detection methods
2. Detection methods
1. Detection of phosphatidylserine in cell membrane
The detection methods based on cellular metabolites include Annexin V-FITC/PI assay (abs50001), Annexin V-EGFP/PI assay (abs50006), Annexin V-APC/PI assay (abs50009), and Annexin V-PE/7-AAD assay (). abs50007), Annexin V-APC/7-AAD assay (abs50008). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on the Annexin V-FITC/PI detection method.
(1) Detection principle
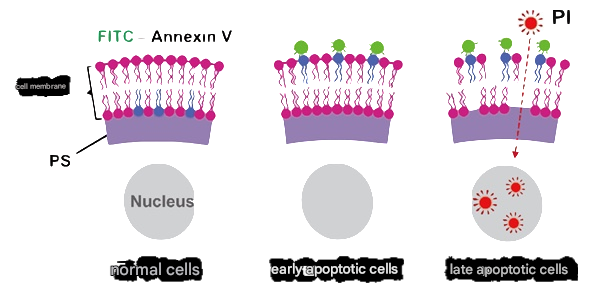
Principle of Annexin V/PI detection
(2) Applicable samples: adherent cells, suspension cells
(3) Equipment: flow cytometer/fluorescence microscope
(4) Advantages: Annexin is one of the most sensitive indicators at present; Qualitative and quantitative
(5)Apoptosis test results of An nexin V cells
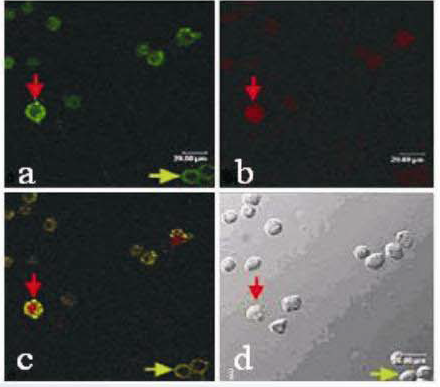
Under fluorescence microscopy, Annexin V-FITC&PI double staining can distinguish between normal cells, early apoptosis, late apoptosis and necrotic cells. As shown in the figure above, a, b, and c are apoptotic cells under fluorescence microscopy, where a and b are single stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, respectively, and c is double stained with Annexin V-FITC&PI. d are apoptotic cells under ordinary light microscopy (red arrows indicate late apoptotic cells, green arrows indicate early apoptotic cells).
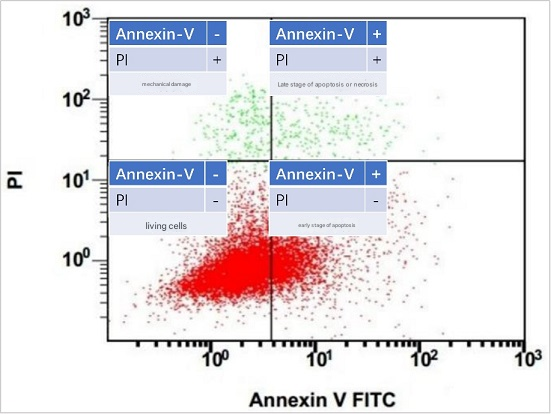
Apoptosis flow cytometry results of Annexin V cells
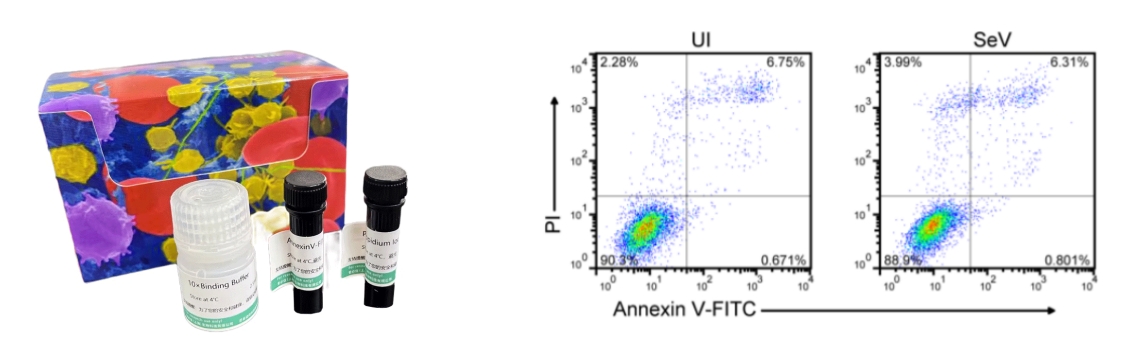
The effect of using the Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Assay Kit (abs50001) is shown in the figure above, the document name: Serine metabolism antagonizes antiviral innate immunity by preventing ATP6V0d2-mediated YAP lysosomal degradation Journal: Cell Metabolism Impact Factor: 27.287
(6) Precautions for apoptosis detection of Annexin V cells
A. It is recommended not to trypsinize adherent cells containing EDTA;
B. It is recommended to collect the cells suspended in the culture medium separately and store them in 2% BSA before trypsin;
C. Centrifuge at low speed before using the reagent to avoid liquid accumulation of the cap and wall of the tube;
D. Annexin V-FITC and PI are photosensitive substances, please pay attention to protect from light during operation. When handling and labeling, do so in the dark as much as possible. During the incubation phase, wrap the container in aluminum foil or place in a drawer. After cell labeling, observe with a microscope in a dark chamber;
E. The whole operation process should be as gentle as possible, do not blow the cells hard, and try to operate at 4 °C so as not to affect the cell state;
F. In the last step of cell washing, please try to discard the supernatant to avoid PBS residue, which may affect the experimental results;
G. In order to prevent fluorescence decay, flow cytometry detection should be carried out within 1 h;
H. PI staining time is too long, which may cause the apoptosis rate of detection to be high, so it is recommended to perform Annexin V-FITC staining first, and then add PI staining at the shortest 5min before the machine.
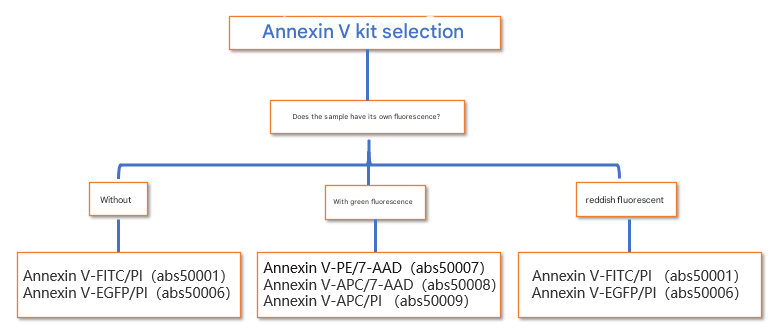
(7) Annexin V kit selection guide
2. TUNEL notched end marking
The detection methods based on TUNEL nick include TUNEL-Biotin assay (abs50022), TUNEL-488 assay (abs50047), and TUNEL-594 assay (abs50058). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on the TUNEL-488 detection method.
(1) Detection principle
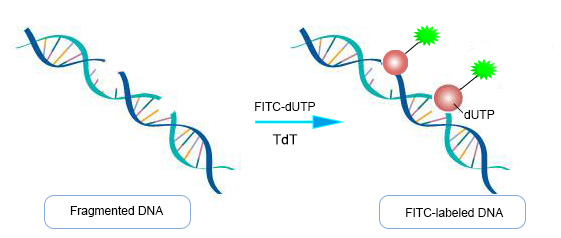
Detection principle of TUNEL notched end marker
Double- or single-strand breaks in genomic DNA produce a large number of sticky 3'-OH ends, which can be catalyzed by deoxyribonucleotide terminal transferase (TdT) and bind to 488/Cy-dUTP, allowing direct detection of apoptotic cells by fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry.
(2) Applicable samples: adherent cells, suspension cells, cell smears, paraffin sections, frozen sections
(3) Equipment: flow cytometer, optical/confocal/fluorescence microscope, fluorescence microplate reader, etc
(4) Advantages: simple operation, qualitative and accurate
(5) TUNEL apoptosis detection AQ
A. What is the difference between the red fluorescent and green fluorescent kits and the biotinylated kits?
The biggest difference is that the adapted instruments are different, the biotin-labeled kit is adapted to the light microscope, so when the nucleus is stained, the biotin-labeled kit is generally adapted to hematoxylin or methyl green, and the fluorescein-labeled kit is generally adapted to DAPI, but the fluorescein-labeled kit has a short experimental time, simple operation, and easy to observe the results.
B. What is the role of positive and negative controls?
The positive control is used to verify whether there is any problem with the experimental operation and the kit, and the negative control is also used to adjust the shooting exposure intensity in order to rule out non-specific staining caused by apoptosis, operation process, or dyes. In general, only one positive control and one negative control are required, and multiple negative controls can be set up for multiple tissues.
C. Non-specific markers (false positives)?
a. The nuclease or polymerase activity level of cells or tissues is high (such as smooth muscle), and the DNA is cut off, which can easily lead to false positives. Suggestion: Immediately and sufficiently fix the cells or tissues after removal to prevent the activity of these enzymes, and setting a negative control is helpful to judge;
b. Influence of endogenous peroxidase, it is recommended that for tissues with a lot of blood cells such as liver and kidney, appropriately prolong the blocking time and increase the concentration of hydrogen peroxide;
c. The concentration of the fixative solution is too high or too low, resulting in poor fixation effect in the center of the tissue, resulting in autolysis of the central cell and irregular breakage of the DNA strand, resulting in false positives. Recommendation: 4% paraformaldehyde is recommended;
d. The TdT enzyme reaction time is too long or the reaction solution evaporates or leaks during the Tunel reaction, and the surface of the cell or tissue cannot be kept wet. Suggestion: Take care to control the reaction time and ensure that the TdT enzyme reaction solution can cover the sample;
e. Paraffin, fat, blood, body fluids, etc. are easy to combine with dyes, so tissue sections should be kept clean and dewaxed thoroughly;
f. Some reagents or cells have autofluorescence, and the color of autofluorescence should be avoided when choosing dyes.
D. Not fluorescent?
a. Insufficient fixation. The first choice for fixative solution is 4% paraformaldehyde, which is now used and prepared. The use of ethanol is not recommended, as the penetration of ethanol fixative solution to tissues is weak, which affects the efficiency of TUNEL labeling;
b. The permeability of the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane is insufficient, and the TdT enzyme fails to reach the nucleus. Cells and frozen sections can be permeabilized with 2% Triton X-100 solution for 5-30 min, and proteinase K is recommended for paraffin sections, permeabilized at 37°C for 30 min; Different cells and tissues require slightly different permeabilization time, and it is easy to detach if the time is too long, so adjust appropriately;
c. Extend the labeling time to 2h, and appropriately increase the amount of TdT enzyme and dUTP;
d. Confirm that the cells of the experimental subjects have apoptosis. Prepare a DNase I-treated positive control to verify that the TdT reaction is performed correctly.
E. High fluorescence background?
a. Mycoplasma contamination: Mycoplasma staining detection kit can be used for verification;
b. If the reaction time of TdT enzyme is too long, you can dilute TdT enzyme 2-5 times with the TdT enzyme dilution provided by the kit and then operate according to the instructions, and the diluted TdT enzyme is only for use on the same day;
c. The DAB incubation time is too long, which reduces the DAB staining time;
d. Cells in a state of rapid division and proliferation sometimes have DNA breaks in the nucleus. Recommendation: Sampling and testing during non-proliferative periods;
e. Some reagents or cells have autofluorescence, and the color of autofluorescence should be avoided when choosing dyes;
f. Non-specific binding of Biotin-X-dUTP, after the TdT enzyme reaction, wash three times with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and 1 mg/mL BSA.
F. Low marking rate?
a. Ethanol, methanol or formaldehyde (most of the formaldehyde purchased on the market contains methanol) fixed samples with low labeling efficiency (because chromatin fails to cross-link with the protein during fixation and is lost during operation), the recommended fixative solution is used;
b. The fixation time is too long, resulting in a high degree of cross-linking, and the fixation time is reduced;
c. If adherent cells are induced by drugs to induce apoptosis, the cells will shrink and the adhesion of the adhesion will be reduced, resulting in the easy shedding of apoptotic cells. Recommendation: Be gentle to prevent apoptotic cells from being washed away during washing. The whole operation also needs to be gentle.
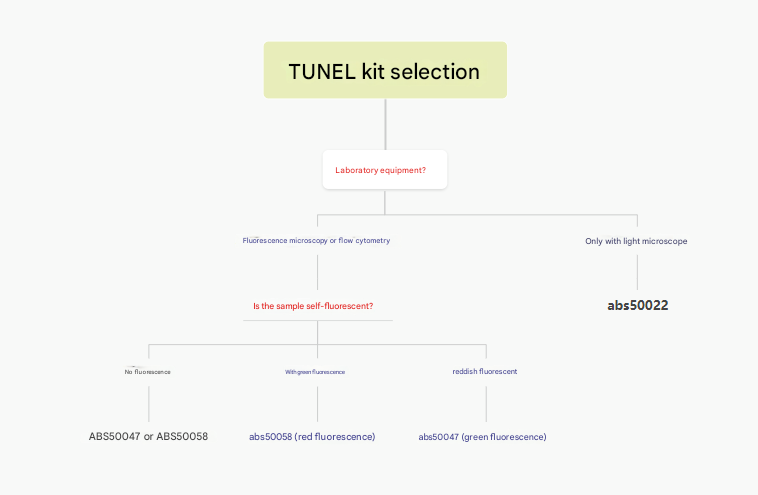
(6) TUNEL kit selection guide
TUNEL Apoptosis Kit (green fluorescence) (abs50047)
3. Detection of core molecules of caspase apoptosis
The detection methods based on the core molecule of Caspase apoptosis include Caspase 1 activity detection (abs50023), Caspase 2 activity detection (abs50024), Caspase 3/7 activity detection (abs50025), Caspase 4 activity detection (abs50026), Caspase 6 activity assay (abs50027). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on the Caspase 3/7 activity detection method.
(1) Detection principle
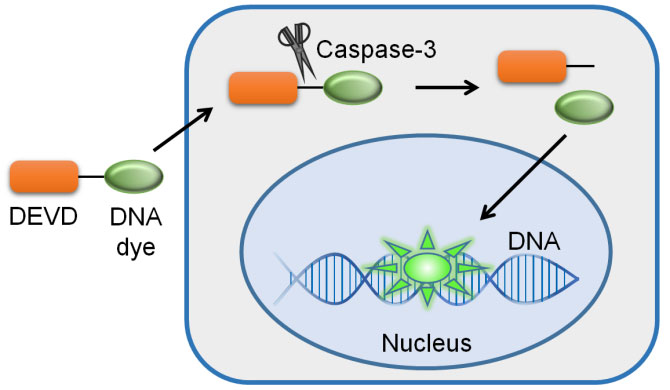
Schematic diagram of the Caspase-3 Activity Assay Kit
Based on caspase 3/7, the substrate Ac-DEVD-pNA can be catalyzed to produce yellow pNA (p-nitroaniline), so that the activity of caspase 3/7 can be detected by measuring the absorbance. pNA has strong absorption around 405 nm.
(2) Applicable samples: adherent cells, suspension cells, and tissue samples
(3) Equipment: flow cytometer, confocal/fluorescence microscope, fluorescence microplate reader, etc
(4) Advantages: high sensitivity, strong specificity, no cross-reactivity with other known caspases
4. Mitochondrial membrane potential detection
The detection methods based on mitochondrial membrane potential include mitochondrial membrane potential detection kit (JC-10) (abs50017) and mitochondrial membrane potential detection kit (JC-1) (abs50016).
(1) Detection principle
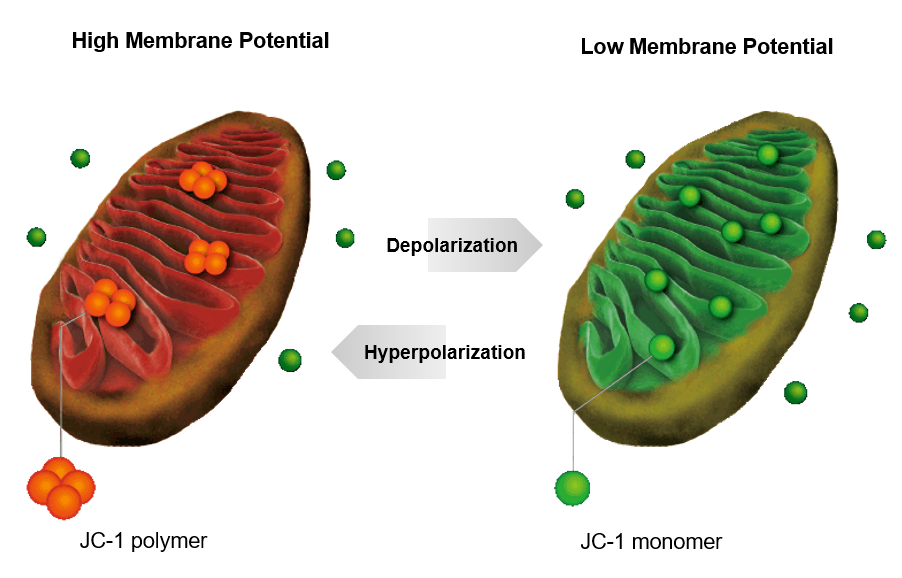
Schematic diagram of the mitochondrial membrane potential detection kit (JC-10).
The decrease in mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Δψm) is the earliest event in the apoptosis cascade, and the mitochondrial membrane potential is measured by dye tracking.
(2) Applicable samples: adherent cells, suspension cells, purified mitochondria
(3) Equipment: flow cytometer, confocal/fluorescence microscope, fluorescence microplate reader, etc
(4) Apoptosis detection results of JC-1 cells

Fluorescence images of JC-1-stained chondrocytes
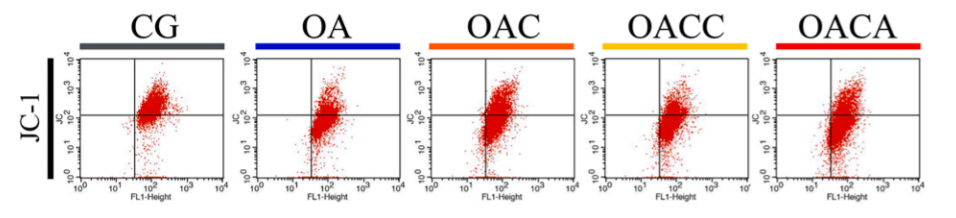
Flow cytometry results of JC-1-stained chondrocytes
The results of the customer's use of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection Kit (JC-1) (ABS50016) are shown in the figure above, and the article name: Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy Journal: Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy Key Factor: 7.18
5. Mitochondrial membrane transition pore detection
The mitochondrial membrane transition pore-based detection method includes the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore (MPTP) Assay Kit (ABS50064).
(1) Detection principle
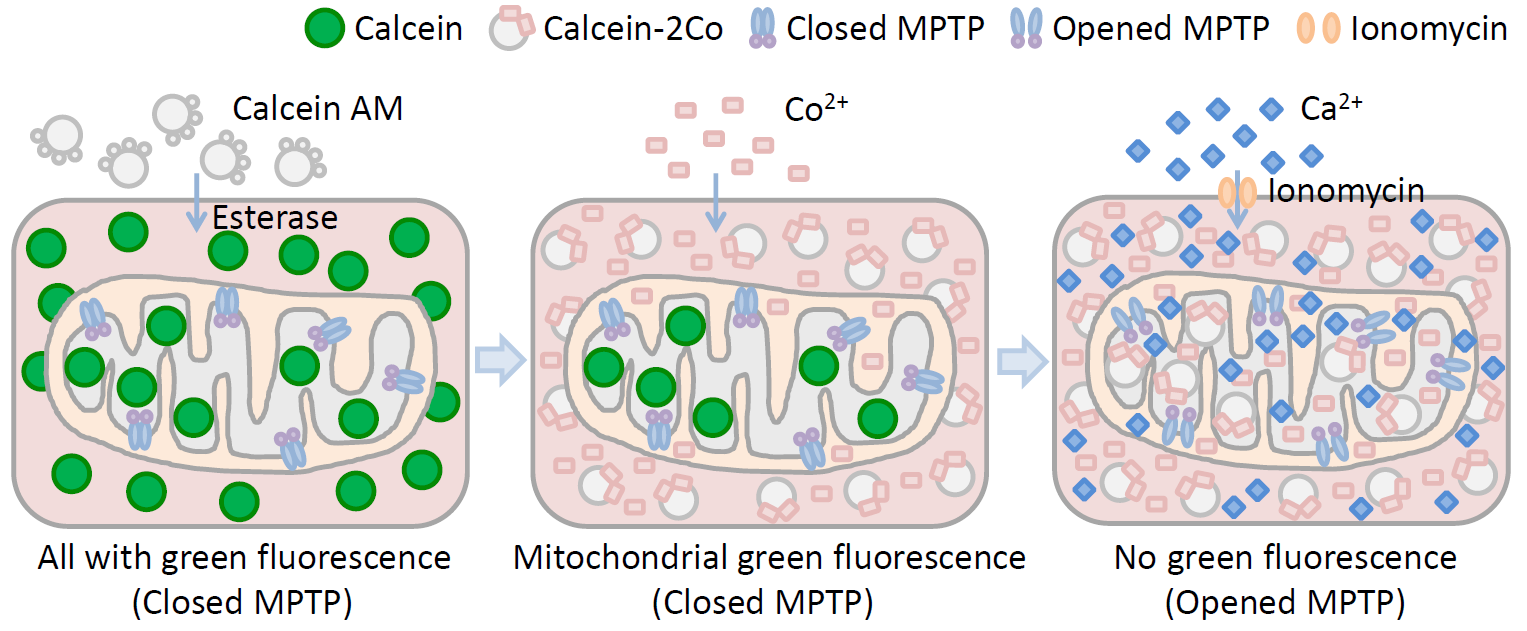
Schematic diagram of mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) detection
When cells undergo apoptosis and pathologic death, the permeability of mitochondrial membrane potential transition pore is altered, Ca2+Overload, oxidation of mitochondrial glutathione, elevation of reactive oxygen species levels, including the release of subsequent cytochrome C, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, etc., all lead to the activation of mitochondrial permeable transition pores.
(2) Applicable samples: adherent cells, suspension cells
(3) Equipment: flow cytometer, confocal/fluorescence microscope, fluorescence microplate reader, etc
(4) Dye: Calcein AM
6. Morphological observation
The detection methods based on cell morphological observation include fluorescence microscopy/light microscopy {DAPI staining (abs47047616), Hoechest staining (abs47047620), AO staining (abs9735), HE staining (abs9217)}, and transmission electron microscopy.
(1) Fluorescence microscopy/optical microscopy observation method
A. Detection principle
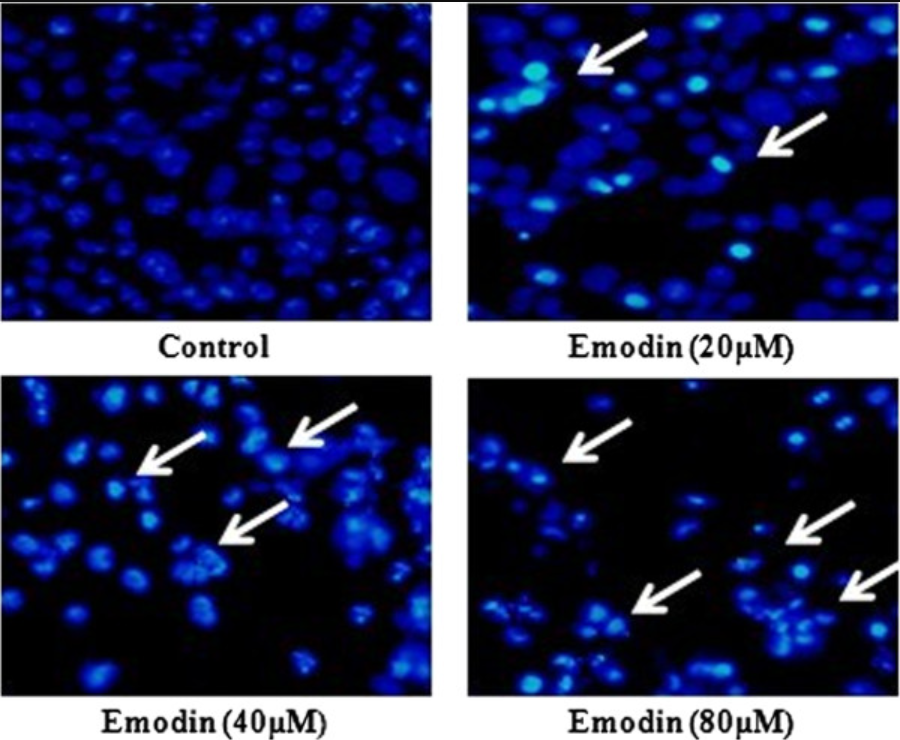
Emodin induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer hela cells via intrinsic mitochondrial and extrinsic death receptor pathway. Cancer cell international. 13. 71. 10.1186/1475-2867-13-71.
With the help of the corresponding staining method, the changes in cell morphology can be directly observed. Commonly used fluorescent dyes include Hoechest 33342, acridine orange (AO), DAPI, etc.; Chemical dyes are hematoxylin-eosin (HE), Giemsa, or Wright
B. Sample type: adherent cells, suspension cells, cell smears, paraffin sections, frozen sections
C. Advantages: simple operation and low cost
D. Disadvantages: Subjectivity is large, qualitative and quantitative are poor, and it is rarely used alone
(2) Fluorescence microscopy/optical microscopy observation method
A. Detection principle
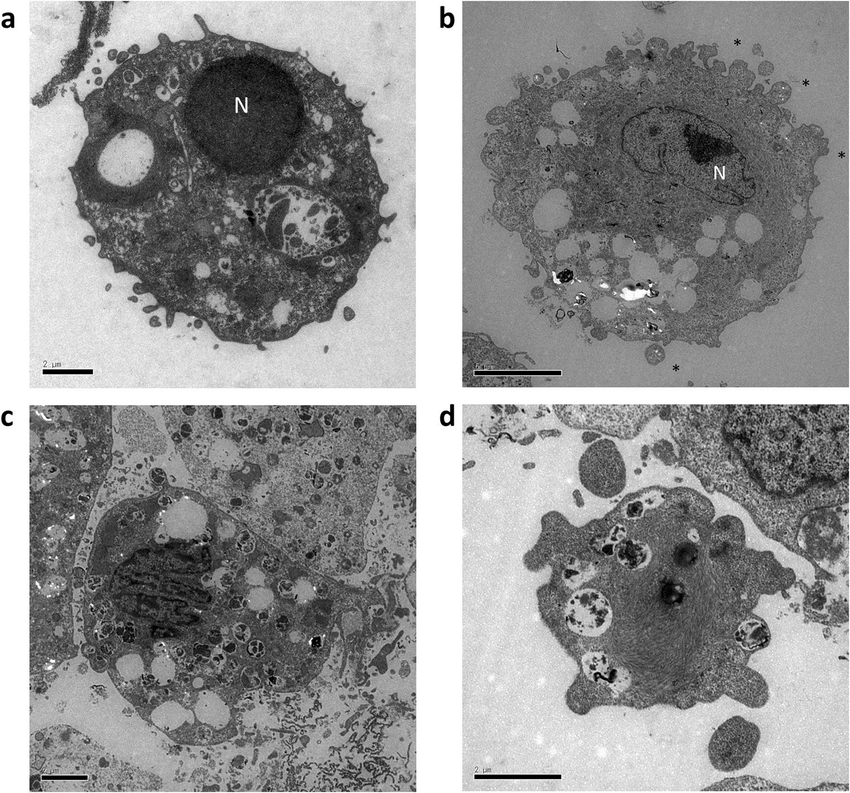
Hydrostatic pressure can induce apoptosis of the skin. Scientific Reports. 10. 10.1038/s41598-020-74695-5.
Apoptotic cells exhibit certain morphological characteristics when apoptosis occurs, and the apoptotic cells show chromatin agglutination, nuclear concentration, nuclear lysis, cytoplasmic contraction, foaming of the cell membrane and the appearance of apoptotic bodies.
B. Sample type: adherent cells, suspension cells, cell smears, paraffin sections, frozen sections
C. Advantages: classic, reliable, gold standard
D. Disadvantages: high cost, long time-consuming, cumbersome steps, cannot be quantified, subjectivity in judgment, and only a small area can be observed at a time.
That's all for today's explanation, if you have any cell culture questions, welcome to join the group to communicate!
This issue is recommended by Xiaoai
|
Catalog number |
name of article |
specification |
|
Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Assay Kit |
25T/50T/100T |
|
|
Annexin V-EGFP/PI Apoptosis Assay Kit |
20T/50T |
|
|
Annexin V-APC/PI apoptosis assay kit |
25T/100T |
|
|
Annexin V-PE/7-AAD Apoptosis Assay Kit |
25T/100T |
|
|
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Assay Kit |
25T/100T |
|
|
Biotin TUNEL Apoptosis Kit |
50T |
|
|
TUNEL Apoptosis Kit (green fluorescence) |
20T/50T |
|
|
TUNEL Apoptosis Kit (red fluorescence) |
20T/50T |
|
|
Caspase 1 Activity Assay Kit |
20T/100T |
|
|
Caspase 2 Activity Assay Kit |
20T/100T |
|
|
Caspase 3/7 Activity Assay Kit |
20T/100T |
|
|
Caspase 4 Activity Assay Kit |
20T/100T |
|
|
Caspase 6 Activity Assay Kit |
20T/100T |
|
|
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit (JC-1) |
100T |
|
|
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection Kit (JC-10) |
100T |
|
|
Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore (MPTP) Assay Kit |
50T/100T |
|
|
AO staining solution (1 mg/mL) |
10mL(1mg/mL) |
|
|
Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining kit |
100mL |
|
|
Hoechst 33342 stain |
10ml/50mL |
|
|
DAPI staining solution |
10ml/50mL |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
