- Cart 0
- English
A comprehensive strategy for organoids & spheroids & cell proliferation, viability, and toxicity detection
July 04, 2025
Clicks:1207
1. Overview
In the vast field of biomedical research, cell viability assays play a crucial role. It not only helps scientists assess the survival of cells, but also provides insight into how cells respond to drugs, environmental changes, or pathological processes. Organoid/spheroid/cell viability assays typically include measures for cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cell death. Today, Xiaoai will introduce to you six commonly used methods for organ/tumor spheroid/cell activity detection: cell metabolism detection method, DNA synthesis detection method, cell ATP detection method, fluorescent dye detection method, cell membrane permeability detection method, and cell LDH detection method.
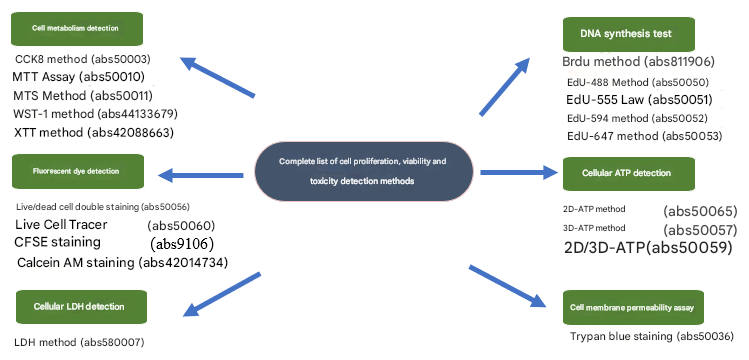
A complete set of methods for detecting cell proliferation, viability, and toxicity
2. Detection methods
1. Cell metabolism detection method
The detection methods based on cellular metabolites include CCK8 method (abs50003), MTT method (abs50010), MTS method (abs50011), WST-1 method (abs44133679) and XTT method (abs42088663). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on comparing the CCK8 method and the MTT method.
Both the CCK-8 method and the MTT method are suitable for large-scale, rapid drug evaluation. Compared with MTT, the CCK-8 method has obvious advantages. In a certain range of cell number, the linear relationship between OD value and viable cell number detected by CCK-8 was more obvious than that of MTT method. Moreover, the MTT method produces blue-purple crystals that are insoluble in water, which requires the dissolution of organic solvent DMSO, and incomplete dissolution or cell loss often occurs during the operation, which affects the accuracy of the results. The CCK-8 method is only a one-step operation of adding dye, which is simple to operate, real-time detection, and eliminates the need to remove the medium, which is the mainstream method of cell proliferation, viability and toxicity. It is more environmentally friendly, does not use the organic solvent DMSO, and requires fewer consumables.
Below is a comparison of the advantages of the two test kits:
|
Detection method |
MTT method |
CCK8 method |
|
The water solubility of the formazan product |
difference |
Very good |
|
Product composition |
MTT, MTT solvent, Formazan dissolved solution |
CCK8 solution |
|
How to use: |
It needs to be prepared into a solution before use |
Ready to use |
|
Detection sensitivity |
So so |
high |
|
The time required for the test |
Longer |
Very short |
|
Detection wavelength |
570-690nm |
430-490nm |
|
Cytotoxicity |
high |
Very low |
|
Batch sample testing |
OK |
It's a perfect fit |
|
The price of the product |
The cost is lower |
The cost is higher |
2. DNA synthesis detection method
The detection methods based on DNA synthesis include Brdu method (abs811906), EdU-488 method (abs50050), EdU-555 method (abs50051), EdU-594 method (abs50052) and EdU-647 method (abs50053). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on introducing the EDU method to you.
EdU (5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine), known in Chinese as 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine, is a thymine nucleoside analogue, whose alkyne hydroxyl group is rare in natural compounds, and can replace thymidine (thymidine) into the replicating DNA molecule during cell proliferation, the acetylene group on EdU can covalently react with fluorescently labeled small molecule azide probes (such as Azide Alexa Fluor 488, etc.) through monovalent copper ions to form a stable triazole ring, which is very rapid, called clickreaction, so that cell proliferation can be detected efficiently and quickly, especially the percentage of cells in S phase. Compared with the traditional immunofluorescence staining (BrdU) detection method, EdU is only 1/500 of the size of the BrdU antibody, which is easier to diffuse in cells, does not require strict sample denaturation (acid hydrolysis, pyrolysis, enzymatic hydrolysis) treatment, effectively avoids sample damage, helps to observe the real situation of cell proliferation at the overall level of tissues and organs, and has higher sensitivity and faster detection speed.
3. Cellular ATP detection method
The detection methods based on cellular ATP include 2D-ATP method (abs50065) (suitable for cells); 3D-ATP method (abs50057) (applicable to organoids and spheroids); 2D/3D-ATP method (abs50059) (applicable to cells, organoids, and spheroids). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on comparing the similarities and differences between these three methods.
Similarities: The above three methods are based on the ATP-dependent luciferase-catalyzed fluorescein luminescence reaction, and the intracellular ATP content is determined by chemiluminescence signal, so as to detect cell viability or quantitatively detect the number of viable cells, with a wide linear range, high sensitivity and good stability。 There is a good linear relationship between 100 and 100,000 cells in a 96-well plate, but the upper limit of the assay will vary from cell to cell. In addition, the operation is simple, the assay reagent provided in the kit is ready-to-use, the readability is stable, the detection speed is fast, and the assay is completed in about 10 minutes, without the need to wash cells, and there is no need to change or remove the culture medium.
Differences: The 2D-ATP method (abs50065) is suitable for 2D cell culture systems; However, structures between cells and tissues, such as organoids/spheroids, require ATP detection kits with stronger lysis ability, so the 3D-ATP method (abs50057) uses a reagent with stronger lysis ability, which is suitable for ATP detection of organoids and tumor spheroids. The 2D/3D-ATP method (abs50059) is a general-purpose reagent, which has the functions of cell, organoid, and tumor spheroid detection, and is more versatile. For ATP detection strategies for organoids and tumor spheroids, please refer to the link 3D tumor spheroids & organoid drug susceptibility activity detection strategy.
4. Fluorescent dye detection
The detection methods based on fluorescent dyes include live cell tracer (abs50060), live/dead cell double staining (abs50056) (commonly used in organoids and tumor spheroids), CFSE staining (abs9106), and Calcein AM staining (abs42014734). Today, Xiao Ai will focus on introducing the live cell tracer method and the live/dead cell double staining method.
(1) Live-cell tracing
Studying cell motility and localization requires specific probes that are non-toxic to living cells. The Live Cell Tracking Kit provides a versatile and well-preserved cell tracking reagent (Cell Tracker Green) for monitoring cell motility, localization, proliferation, migration, chemotaxis, and invasiveness。 Cell Tracker Green is a live-cell fluorescent tracer probe that can be entered into cells by passive diffusion, covalently binds to intracellular proteins, and is a long-acting cell tracking dye. Once inside the cell, the non-fluorescent Cell Tracker Green is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases to produce green fluorescence (Ex/Em=494/521nm). These fluorescent products can only accumulate in cells with intact cell membranes, so dead cells and unintact cell membranes cannot be stained. Cell Tracker Green is not sensitive to pH changes and can be fixed by formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde. The Cell Tracker Green probe can remain in live cells for several generations and can display fluorescence for at least a week. Probes can be transferred to daughter cells, but not to neighboring cells in the population.
(2) Live/dead cell double staining method
In the process of organoid culture, if we want to understand the proliferation and apoptosis status of organoids, we can fluorescently stain live and dead cells and take photos through fluorescence microscopy.
Calcein-AM is a cell staining reagent that fluorescently labels live cells and fluoresces green (Ex=490 nm, Em=515 nm). The introduction of an acetylmethoxymethyl ester (AM) group on top of the traditional Calcein (calcein) adds hydrophobicity and allows it to easily penetrate living cell membranes. Once inside the cell, Calcein-AM (which is not fluorescent by itself) is cleaved by intracellular esterases to form the membrane-impermeable polar molecule Calcein, which is trapped within the cell and emits a strong green fluorescence. Calcein-AM is the most suitable fluorescent probe for live-cell staining due to its very low cytotoxicity compared to other similar reagents (e.g., BCECF-AM and CFDA) and does not inhibit any cellular functions such as proliferation and lymphocyte chemotaxis.
Due to the lack of esterases in dead cells, Calcein-AM is only used for cell viability testing and short-term labeling of live cells. Therefore, Calcein-AM is often used in combination with dead cell fluorescent probes such as propidium iodide (PI) to perform fluorescent double staining of live and dead cells at the same time. Propidium iodide (PI) cannot cross the cell membrane of living cells, but can only pass through the disordered region of the dead cell membrane to reach the nucleus, and intervene in the DNA double helix of the cell to produce red fluorescence (Ex=535 nm, Em=617 nm), so PI only stains dead cells. Since both Calcein and PI-DNA can be excited at 490 nm, both live and dead cells can be visualized with fluorescence microscopy. With 545 nm excitation, only dead cells can be observed.
The Live/Dead Cell Double Stain Kit (abs50056) works by using a dual dye of Calcein-AM and PI to perform a double stain label of live and dead cells for analysis at the live and dead cell levels. According to the optimized experimental system of our company, a 24-well plate with 25uL of organoid matrigel gel aggregate per well was taken as an example, and 500uL of staining solution was added to each well for staining. For specific experimental procedures, please refer to the link organoid in situ live-dead staining experiment.
5. Cell membrane permeability detection
The detection methods based on cell membrane permeability include trypan blue staining cell viability detection kit (ABS50036), eosin staining solution (ABS9222), neutral red staining solution (0.33%, for live cell staining) (ABS42154867).
Trypan blue or eosin staining is a method that uses normal healthy cells to reject trypan blue or eosin, while cells that have lost the integrity of their cell membrane can be stained with trypan blue or eosin. Trypan blue or eosin staining measures the integrity of the cell membrane, which is generally considered to have lost its integrity and is considered dead. After trypan blue or eosin staining, cell viability can be quantified more accurately by counting directly under the microscope or counting after taking pictures under the microscope.
Neutral red is a weakly basic dye and a pH indicator with a discoloration range of 6.4 to 8.0 (from red to yellow). Neutral red staining is often used to identify the dead or alive of animal cells. Live cells are stained red, while dead cells do not change color, in contrast to trypan blue staining. By measuring the cell's intake of neutral red, the proliferation or toxicity of the cells can be assessed.
6. Cell LDH detection
The cell-based LDH assay is the LDH method (abs580007). The principle of LDH detection is based on the properties of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). The following is the detailed principle of the LDH test kit (abs580007):
(1) Distribution and release of LDHLDH is a stable cytoplasmic enzyme that is widely present in various organisms and cannot normally pass through cell membranes. When cells are damaged or die, the integrity of the cell membrane is disrupted and LDH is released into the extracellular medium.
(2) Determination of LDH activity:LDH catalyzes the formation of pyruvate from lactic acid, and in this process, NAD+ is reduced to NADH. NADH and tetrazolium salt INT (2-p-iodophenyl-3-nitrophenyl tetrazolium chloride) reacted to form red formazan under the catalysis of diphorase.
(3) The relationship between color change and cell damage: the amount of formazan is directly proportional to the number of lysed (dead) cells. At the wavelength of 490 nm, formazan produces an absorption peak, which can be used to detect the activity of LDH in samples such as cell culture medium and cell lysate by colorimetry. Absorbance is linearly positively correlated with LDH activity, i.e., positively correlated with the number of lysed (dead) cells.
(4) Experimental operation: In the experiment, the cell culture medium of different treatment groups was centrifuged, the supernatant was moved to a 96-well plate, and the LDH detection reagent was added, and the released LDH activity could be measured by microplate reader or spectrophotometer after a certain period of time. By comparing the LDH activity released by different groups of cells, the magnitude of cell damage can be determined.
(5) Application:LDH release assays are mainly used to assess cytotoxicity and cell death, and are widely used in drug screening, toxicology studies, and cell culture. At the same time, it also has certain reference value in the diagnosis and treatment of some diseases, such as myocardial infarction, hepatitis, cancer, etc.
In summary, LDH assay is a method to assess the degree of cell damage by measuring LDH activity in cell culture supernatants, and its sensitivity, convenience, and precision make it an important tool in cytotoxicity analysis.
That's all for today's explanation, if you have any questions about cell and organoid experiments, welcome to join the group to communicate!
This issue is recommended by Xiaoai
|
Catalog number |
name of article |
specification |
|
CCK-8 kit |
500T |
|
|
MTT cell proliferation and cytotoxicity detection kit |
500T |
|
|
2D Luminescent Cell Viability Assay |
50mL×2 |
|
|
3D Luminescent Cell Viability Assay |
50mL×2 |
|
|
2D/3D/Organoid ATP Viability Assay Kit |
100mL |
|
|
Live/dead cell double staining kit |
500T |
|
|
Live Cell Tracing Kit (Green Fluorescence) |
500T |
|
|
EdU-488 Cell Proliferation Assay Kit (6-well plate) |
200T |
|
|
EdU-555 Cell Proliferation Assay Kit |
200T |
|
|
Trypan blue stained cell viability assay kit |
500T |
|
|
CFSE |
10mg |
|
|
Lactate Dehydrogenase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
