- Cart 0
- English
RCR, RT-PCR, qPCR, RT-qRCR learned?
July 01, 2025
Clicks:680
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was developed by Dr. Kary Mullis in the 80s of the 20th century. The technology has been likened to a "molecular copier" for its ability to recognize specific DNA sequences and synthesize large numbers of copies quickly and accurately. Various derivatization techniques based on the original PCR method have been developed. Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qPCR), combines PCR amplification and detection in a single step. Another technique called reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) uses RNA as a nucleic acid starting template.
● PCR: Repeated heating and cooling cycles of a reaction mixture containing DNA template, DNA polymerase, primers, and dNTPs. [1] Each cycle doubles or so the amount of DNA, as a new strand of DNA becomes a template for replication in the next cycle. This results in an exponential increase in the amount of DNA.
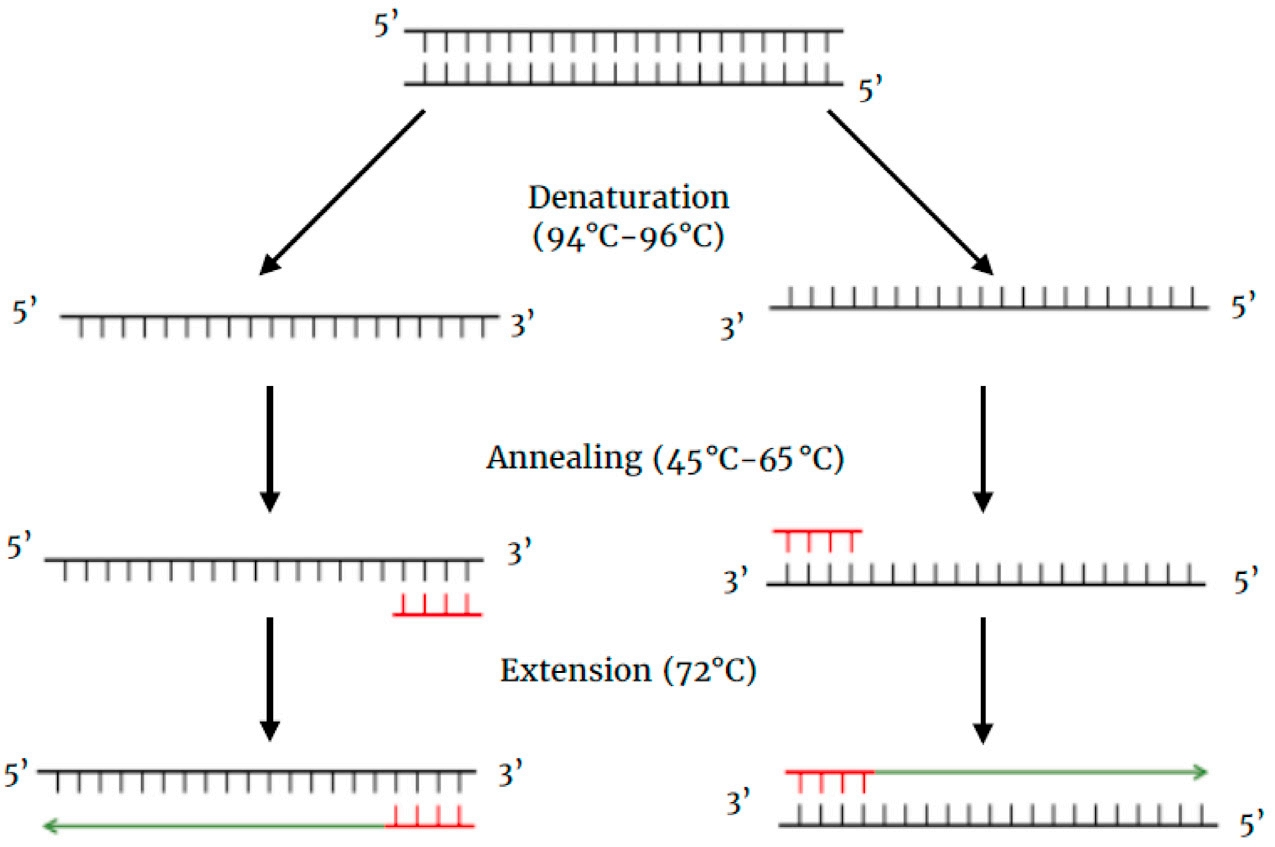
Fig.1 First cycle of PCR[1]
● RT-PCR (Reverse transcription PCR): Reverse transcription PCR can use RNA as a template to generate complementary DNA (cDNA). Reverse transcriptase is used to generate single-stranded copies of cDNA. This can be done using oligomeric (dT) primers that bind to the PolyA tail of the RNA, or using random hexamers (primers six to nine bases long that bind at multiple points in the RNA transcript). In general, a mix of the two primers is considered best because of its ability to amplify PolyA-tailed RNAs (mostly mRNAs) and PolyA-free RNAs (tRNA, rRNA, etc.). DNA polymerase is then amplified to generate double-stranded cDNA that is fed into a standard PCR-based amplification process.
● qPCR (Quantitative PCR): refers to quantitative real-time PCR, that is, PCR amplification of DNA in real time, and measurement by fluorescent probes (most commonly intercalation dyes or hydrolysis probes) to quantify PCR products. It is used to detect the presence of pathogens and to determine the copy number of the DNA sequence of interest. SYBR Green I is the most commonly used DNA-binding fluorescent dye that fluoresces when bound to double-stranded DNA, and the fluorescence intensity increases in proportion to the concentration of the PCR product.
The advantage of quantitative PCR over standard PCR is that it is possible to observe in real time which reactions are working without the need for an agarose gel. It also enables true quantification.
● RT-qPCR (Reverse Transcription Quantitative real-time PCR): This is a technique that combines RT-PCR with qPCR for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR. Rapid detection of changes in gene expression by using cDNA in qPCR reactions to measure RNA levels.
RT-qPCR can be used to study changes in gene expression when a model system is treated with inhibitors, stimulators, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), or knockout models. This technique is also frequently used to detect expression changes before (as quality control) and after (confirmation of changes) in RNA-Seq experiments.
The final step in RT-qPCR sample preparation is to generate cDNA. In addition to considering primers, cDNA generation can be generated as part of a qPCR experiment (referred to as one-step RT-qPCR) or separately from qPCR (two-step RT-qPCR) (Figure 3).
|
method |
One-step RT-qPCR |
Two-step RT-qPCR |
|
merit |
Experiments have less variability, less risk of contamination, and enable high-throughput screening |
More reactions and flexible priming options for each sample |
|
shortcoming |
The number of sample uses is limited |
More optimization is needed |
|
apply |
Clinical screening |
Large-scale gene expression analysis |
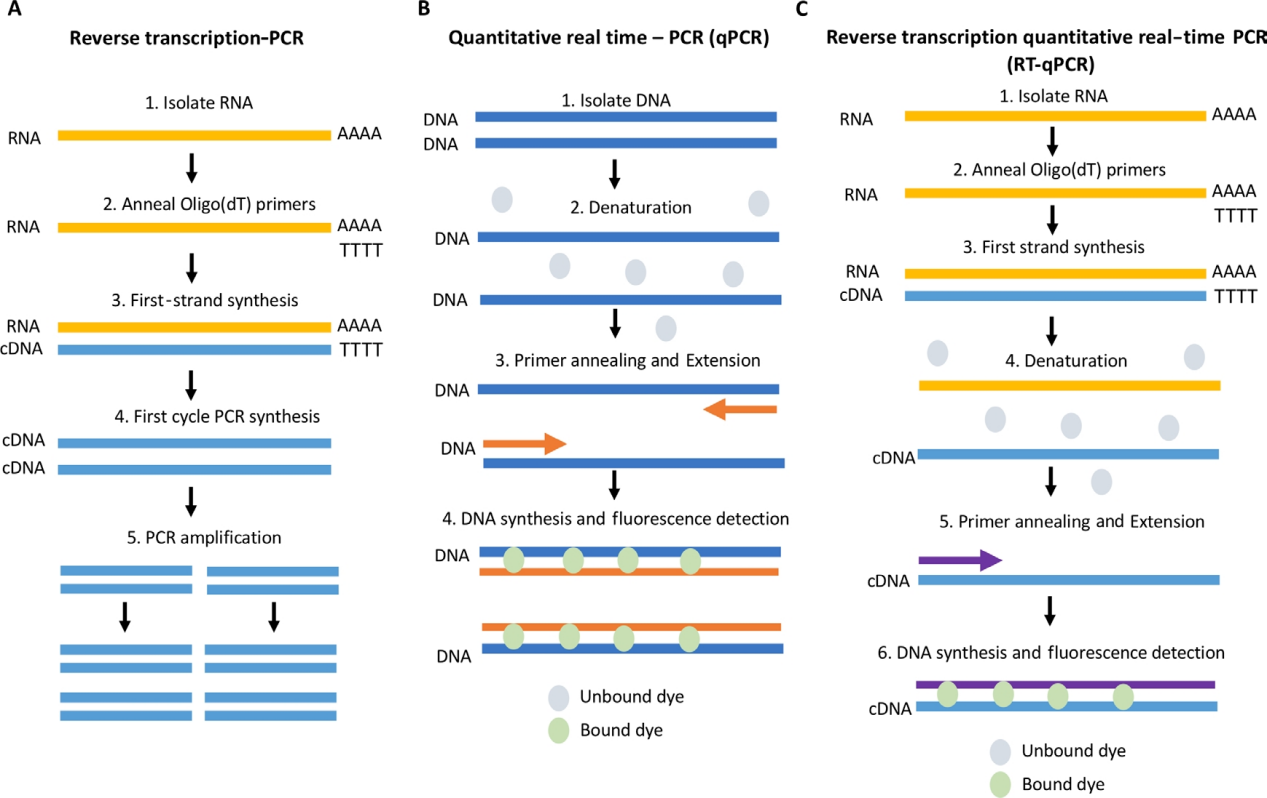
Fig.2. Schematic diagram of RT-PCR, qPCR and RT-qPCR [2]
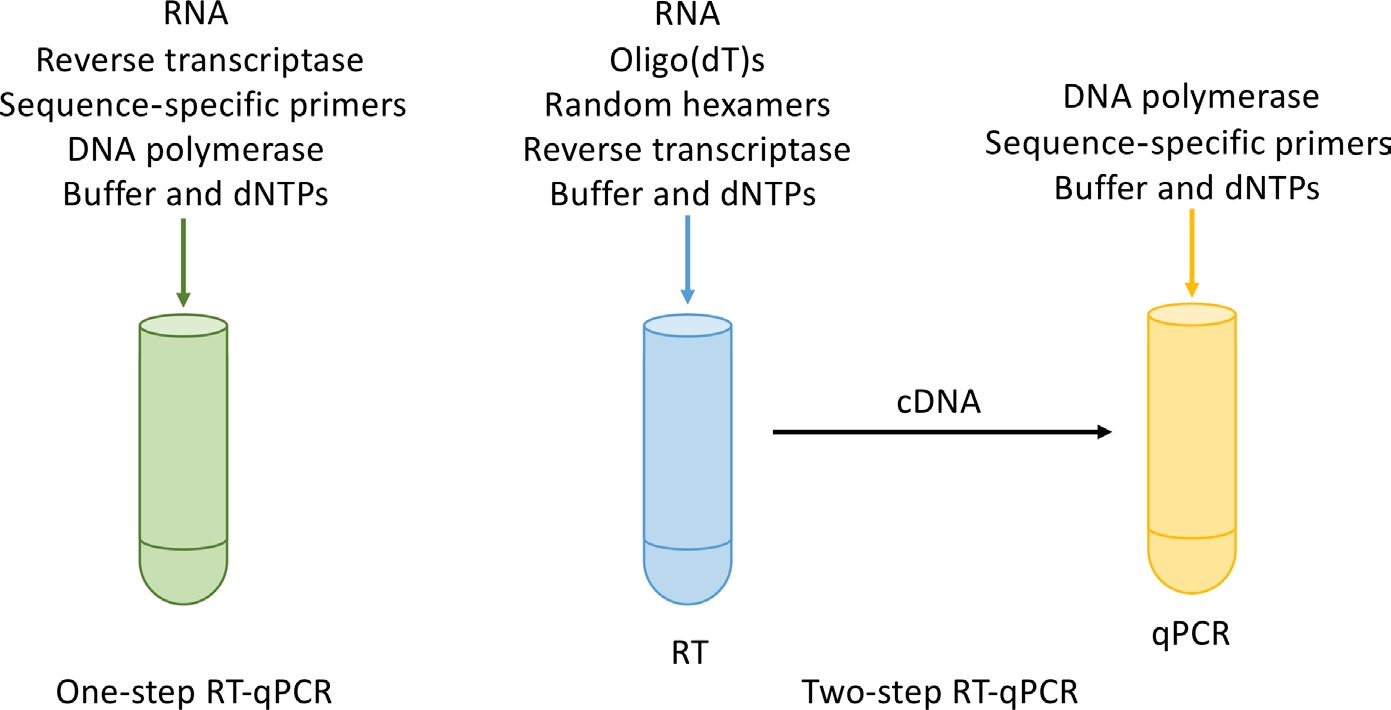
Fig.3. One-step RT-qPC and two-step RT-qPCR[2]
● ddPCR (Droplet-based Digital PCR): The sample passes through a microfluidic chip to form a segmented stream in which the sample is split into tens of thousands of droplets that act as a PCR chamber and are separated by immiscible liquids (e.g., mineral oil) to form an emulsion [3]. The emulsion is collected in vials, subjected to PCR, and the samples are subsequently processed by flow cytometry to count the number of PCR-positive droplets. or the emulsion is fed into a plastic chip to form a monolayer of droplets, which are thermally cycled and fluorescence images of the droplets are captured and evaluated [4]. Compared with qPCR, ddPCR has the advantage of higher accuracy and lower coefficient of variation for absolute quantification [5]. PCR multiplexing is typically performed by probe-based fluorescence, with a different excitation color for each DNA/RNA. It is also used to generate libraries for single-cell RNA sequencing.
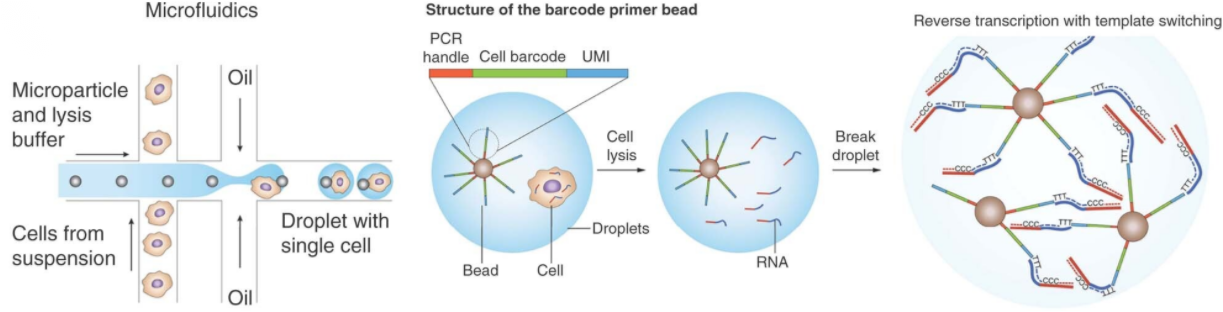
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of ddPCR[6]
References:
[1] Jalali M, Zaborowska J, Jalali M. The polymerase chain reaction: PCR, qPCR, and RT-PCR[M]//Basic science methods for clinical researchers. Academic Press, 2017: 1-18.
[2] Zhang H, Tang K, Wang B, Duan CG, Lang Z, Zhu JK. Protocol: a beginner's guide to the analysis of RNA-directed DNA methylation in plants. Plant Methods. 2014 Jun 14; 10:18. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-10-18. PMID: 24955108; PMCID: PMC4065543.
[3] Schiffman M, Bauer H, Lorincz A et al. Comparison of Southern blot hybridization and polymerase chain reaction methods for the detection of human papillomavirus DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol.29(3), 573–577 (1991).
[4] Madic J, Zocevic A, Senlis V et al. Three-color crystal digital PCR. Biomol. Detect. Quant. 10, 34–46 (2016).
[5] Hindson CM, Chevillet JR, Briggs HA et al. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 10, 1003 (2013).
[6] Hwang B, Lee JH, Bang D. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Exp Mol Med. 2018 Aug 7; 50(8):1-14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0071-8. Erratum in: Exp Mol Med. 2021 May; 53(5):1005. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00615-w. PMID: 30089861; PMCID: PMC6082860.
|
Catalog number |
name |
specification |
|
2×Taq PCR Mix |
1mL×5 |
|
|
2×Taq PCR Master Mix(for PAGE) |
1mL×5 |
|
|
2× Xerox PCR Master Mix |
1mL×5 |
|
|
2×HotStart Taq plus Master Mix(Quick Load) |
1mL×5 |
|
|
2×Pfu Master Mix |
1mL×5 |
|
|
2×Long Taq PCR Master Mix |
1mL×5 |
|
|
Whole Genome Amplification Kit |
50T |
|
|
Reverse transcription is a tube of three generations of master mix |
100T |
|
|
First-strand cDNA Synthesis Mix With gDNA Remover |
100T |
|
|
One-Step RT-PCR Kit |
200T |
|
|
miRNA probe reverse transcription kit |
40T |
|
|
Degenomic and reverse transcription in one tube of three generations of master mix |
100T |
|
|
miRNA tailing reverse transcription kit |
40T |
|
|
Plasma miRNA tailing reverse transcription kit |
50T |
|
|
miRNA stem-loop reverse transcription kit |
50T |
|
|
RNase inhibitors |
1mL |
|
|
Two-Step RT-PCR Kit |
1kit |
|
|
2× Premixed real-time PCR reaction system |
1.7mL×3 |
|
|
SYBR One-Step qRT-PCR Kit |
100T |
|
|
Antibody Dye Quantitative PCR Master Mix (Universal ROX) |
1mL×5 |
|
|
2× Mixed Real-Time PCR Reaction System (High Concentration ROX) |
1.7mL×3 |
|
|
SYBR High-Sensitivity qPCR SuperMix |
1mL×5 |
|
|
miRNA stem-loop dye PCR kit |
200T |
|
|
2× Premixed Real-Time PCR Reaction System (Low Concentration ROX) |
1.7mL×3 |
|
|
miRNA probe-based real-time PCR reagents |
200T |
|
|
miRNA plus tail dye method real-time PCR kit |
200T |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.cn |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
