- Cart 0
- English
TUNEL Apoptosis Kit Selection & FAQs
Principle of Detection:
During apoptosis, cells activate certain endonucleases that cleave genomic DNA between nucleosomes, producing DNA fragments of approximately 180-200 bp. When genomic DNA undergoes double-strand or single-strand breaks, a large number of sticky 3'-OH ends are generated. These ends can be labeled with derivatives of fluorescent dyes, peroxidases, alkaline phosphatases, or biotin under the catalysis of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT). This allows direct detection of apoptotic cells using optical microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, or flow cytometry. This method is known as Terminal-deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL).
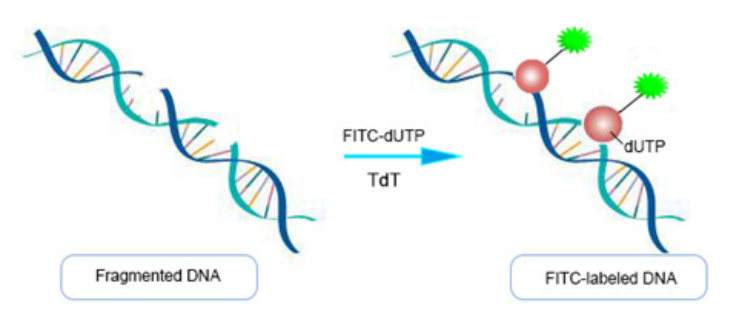
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the principle of the TUNEL assay kit
Applications:
This assay can be used to detect apoptosis in frozen or paraffin sections and cultured adherent or suspension cells. It selectively detects apoptotic cells, rather than necrotic cells or cells with DNA strand breaks caused by irradiation or drug treatment.
Product Advantages:
1. Broad Application: Suitable for adherent cells, suspension cells, frozen sections, and paraffin sections;
2. High Sensitivity: Allows in situ staining of intact individual apoptotic cell nuclei or apoptotic bodies;
3. Simple and Rapid: The entire procedure can be completed in 1.5-3 hours;
4. High Signal-to-Noise Ratio: Low background staining with bright positive staining;
5. Diverse Detection Methods: Fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, optical microscopy.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the differences between red fluorescence, green fluorescence, and biotin-labeled TUNEL assay kits?
The main difference lies in the compatibility with different instruments. Biotin-labeled kits are suitable for optical microscopy, and are often used with hematoxylin or methyl green for nuclear staining. Fluorescent-labeled kits are generally used with DAPI. Fluorescent-labeled kits offer shorter experimental times, simpler operations, and easier observation of results.
2. What are the roles of positive and negative controls?
Positive controls are used to verify the validity of the experimental procedure and the assay kit, while negative controls help exclude nonspecific staining caused by cell intrinsic apoptosis, procedural factors, or dye-related issues. They are also used to adjust exposure intensity for imaging. Typically, one positive control and one negative control are sufficient, although multiple negative controls can be set for different tissues.
3. Non-specific labeling (false positives)?
1) High levels of nuclease or polymerase activity in cells or tissues (e.g., smooth muscle) can lead to DNA fragmentation and false positives. Immediate and thorough fixation is recommended to inhibit enzymatic activity. Negative controls can help determine the source of the issue;
2) Endogenous peroxidase activity can interfere with the assay. For tissues with high blood cell content, such as liver or kidney, extend the blocking time and increase the concentration of hydrogen peroxide;
3) Inadequate fixation due to improper concentration of fixative can cause incomplete fixation in the tissue center, leading to autolysis of cells and irregular DNA strand breaks. A 4% paraformaldehyde solution is recommended;
4) Prolonged TdT enzyme reaction time or evaporation/leakage of the reaction mixture can cause the surface of cells or tissues to dry out. Ensure proper reaction time and coverage of the TdT enzyme reaction mixture;
5) Paraffin, fat, blood, and other body fluids can easily bind to dyes. Ensure clean tissue sectioning and complete dewaxing;
6) Some reagents or cells exhibit autofluorescence. Avoid using dyes that overlap with the autofluorescence spectrum.
4. No fluorescence detected?
1) Inadequate fixation. Paraformaldehyde (4%) is the preferred fixative. Ethanol is not recommended as it has weak penetration and can affect TUNEL labeling efficiency;
2) Insufficient permeabilization of cell membranes and nuclear membranes, preventing TdT enzyme access to the nucleus. For cells and frozen sections, use 2% Triton X-100 solution for 5-30 min. For paraffin sections, proteinase K is recommended at 37°C for 30 min. Adjust permeabilization time according to cell or tissue type, as excessive time can lead to section detachment;
3) Extend labeling time to 2 hours and increase the amount of TdT enzyme and dUTP;
4) Confirm apoptosis in the experimental cells. Prepare a DNase I-treated positive control to verify proper TdT enzyme activity.

Figure 2 TUNEL and HE staining images
5. High fluorescence background?
1) Mycoplasma contamination: Use a mycoplasma staining detection kit to verify;
2) Prolonged TdT enzyme reaction time. Dilute the TdT enzyme 2-5 times with the diluent provided in the kit before proceeding according to the instructions. Diluted TdT enzyme is for single-day use only;
3) Excessive DAB incubation time: Reduce DAB staining time;
4) Cells in high proliferation and division phases may exhibit DNA breaks in the nucleus. Sample during non-proliferative phases;
5) Avoid dyes that overlap with cellular autofluorescence;
6) Non-specific binding of Biotin-X-dUTP: After TdT enzyme reaction, wash three times with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and 1 mg/mL BSA.
6. Low labeling efficiency?
1) Samples fixed with ethanol, methanol, or formaldehyde (commercial formaldehyde often contains methanol) have low labeling efficiency due to poor chromatin-protein cross-linking and loss during processing. Use recommended fixatives;
2) Excessive fixation time leading to high cross-linking. Reduce fixation time;
3) For adherent cells induced to apoptosis by drugs, cell shrinkage and reduced adhesion can cause apoptotic cells to detach. Handle gently during washing to prevent loss of apoptotic cells. Subsequent steps should also be performed carefully.
|
Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Specifications |
|
Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection Kit |
100T |
|
|
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Analysis Kit |
100T |
|
|
Annexin V-APC/PI Apoptosis Analysis Kit |
100T |
|
|
Annexin V-EGFP/PI Apoptosis Analysis Kit |
50T |
|
|
Caspase 3 / 7 Activity Assay Kit |
20T |
|
|
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit (JC-1) |
100T |
|
|
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit (JC-10) |
100T |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
April 02, 2025
Clicks:706
