- Cart 0
- English
293T Cell Culture Guide
January 07, 2025
Clicks:3254
293 [HEK-293] Cells are an immortalized human embryonic kidney cell line formed by transfection with human adenovirus 5 (Ad5). These cells contain and express the transfected Ad5 genes. 293T Cells are a high-transfection derivative of the 293 [HEK-293] cell line, which has been inserted with the temperature-sensitive gene of SV40 T-antigen. They are widely used for viruses packaging, exhibit an epithelial morphology, adhere to surfaces, and their nutritional system is DMEM + 10% FBS.
Table 1 Basic Information of 293T Cells
|
Name |
293T [HEK-293T] (Human Embryonic Kidney Cells) |
|
Morphology |
Epithelial-like |
|
Growth Characteristics |
Adherent |
|
Nutritional System |
DMEM (abs9483) + 10% FBS (abs972) + 1% Antibiotics (abs9478) |

Figure 1 293T [HEK-293T] (Human Embryonic Kidney Cells)
First, we discuss why do 293T cells aggregate severely after passaging? As shown in Figure 2, the background adherent cells adhere well and have a normal morphology, while the yellow clumps are formed due to improper digestion, resulting in cell clusters that are difficult to adhere and exhibit clonal proliferation.
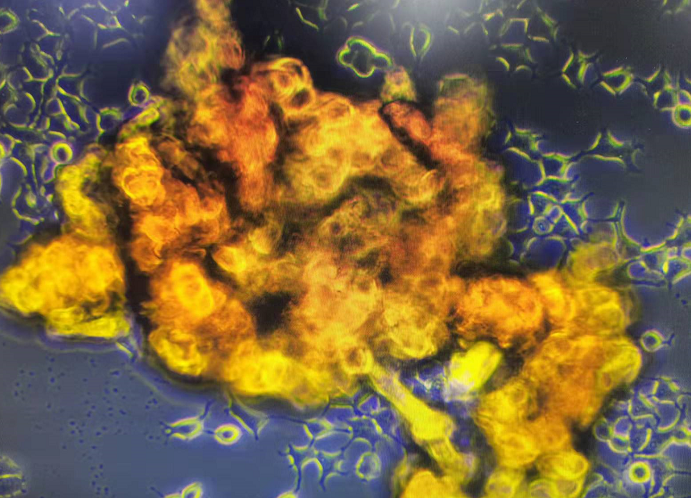
Figure 2 293T [HEK-293T] (Human Embryonic Kidney Cells)
This situation is mostly caused by improper trypsin digestion leading to cell aggregation:
1) Over-digestion or vigorous pipetting causes severe cell damage, and damaged cell debris easily adhere and aggregate;
2) High cell confluence during digestion leads to large areas of cells detaching, which are difficult to disperse and prone to aggregation.
To address improper cell digestion, consider the growth characteristics of the cells. Given that these cells adhere loosely, the digestion time with 0.25% trypsin should be controlled between 15-30 seconds; pipetting should be gentle, limited to 10-20 times; and the cells can be passaged when the confluence reaches 80%.
Second, we discuss why do 293T cells aggregate severely after changing serum batches? As shown in Figure 3, 293T cells that aggregate severely after changing serum batches have indistinguishable cell morphology and adhere together.
There are many factors that can cause cell aggregation, one of which is batch variation in serum leading to cell aggregation.
Serum is derived from animals, and its composition consists of approximately 1000 different components, which can vary with the age, physiological condition, and nutritional status of the donor animal. The percentage content of each batch's components is not fixed, so batch variation exists. 293T cells inherently have a clustering growth characteristic, but severe aggregation may be stimulated by certain factors in the serum.

Figure 3 293T cells aggregating severely after changing serum batches
How can we effectively prevent batch variation in serum? This can be achieved by first using a serum trial pack. If the trial results are satisfactory, purchase the same batch of the main product and stock up for half a year or a year to effectively avoid the impact of batch variation on cells (fetal bovine serum can be stored at -20°C for up to 5 years).
Third, we discuss adhesion issues of 293T cells. There are usually two situations,
The first situation is why do cells adhere poorly after using a new batch of serum? As shown in Figure 4, 293T cells with loose adhesion.

Figure 4 293T cells with loose adhesion
This situation is likely due to batch variation in serum, and the inherent characteristic of 293T cells is poor adhesion. They have different adaptabilities to different batches of serum, which can easily lead to loose adhesion. The serum ratio can be appropriately increased (up to a maximum of 20%); it is recommended to stock up on a good serum batch to avoid the impact of batch variation on cells.
The second situation is why do 293T cells adhere poorly when transferred from a flask (e.g., T25) to a plate (96-well plate)? Excluding factors such as the material of the flask and plate or TC (hydrophilic treatment) processing, the poor adhesion of 293T cells is likely due to isolation of space causing the concentration of signal molecules produced by autocrine or paracrine to be too low, which is not conducive to cell adhesion or proliferation. It is recommended to coat the plate with gelatin (abs9357) before plating, which can effectively promote cell adhesion.
Fourth, we discuss severe apoptosis of cells after viral transfection, as shown in Figure 5, which are 293T cells that have undergone apoptosis and are floating after viral transfection.

Figure 5 293T cells undergoing apoptosis and floating after viral transfection
Why do 293T cells undergo severe apoptosis after viral transfection? After ruling out methodological steps and transfection reagents and still not improving, one can investigate the nutritional system before transfection, especially the impact of serum batch variation. Many students say that the cell morphology was normal during the early culture, but cell morphology is only an external indicator for identifying whether the cells are healthy. Other indicators should also be combined to assess cell health (such as doubling time, survival rate). By changing the serum batch and then conducting the transfection experiment again, one can observe the effects after transfection and analyze the cause through comparison.
Note: Images sourced from the internet and customers, for reference and learning purposes only
Which cell culture strategy would you like to learn about next? Feel free to leave a comment. If you have any cell culture questions, welcome to join our WeChat group by scanning the code to discuss
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
