- Cart 0
- English
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: ATP Detection in Diabetes-Related MI/R Pathogenesis
December 26, 2024
Clicks:397
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is a global threat affecting millions of people worldwide. T2D is a significant risk factor for myocardial infarction, leading to severe left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial revascularization, increasing the risk of ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury, and complicating disease progression. The reasons for the exacerbation of diabetic myocardial injury are yet to be fully understood, with mitochondrial dysfunction being a focal point of research.
Studies suggest that mechanisms by which T2D increases susceptibility to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (MI/R) injury include: ① T2D itself triggers hyperglycemia and insulin resistance; ② the release of oxidative stress and inflammation induced during ischemia and reperfusion. Both contribute to mitochondrial dysfunction. Although growing evidence indicates the association of mitochondrial dysfunction with its role in the pathophysiology of T2D MI/R, effective therapeutic strategies targeting mitochondria to combat this disease have not yet been implemented.
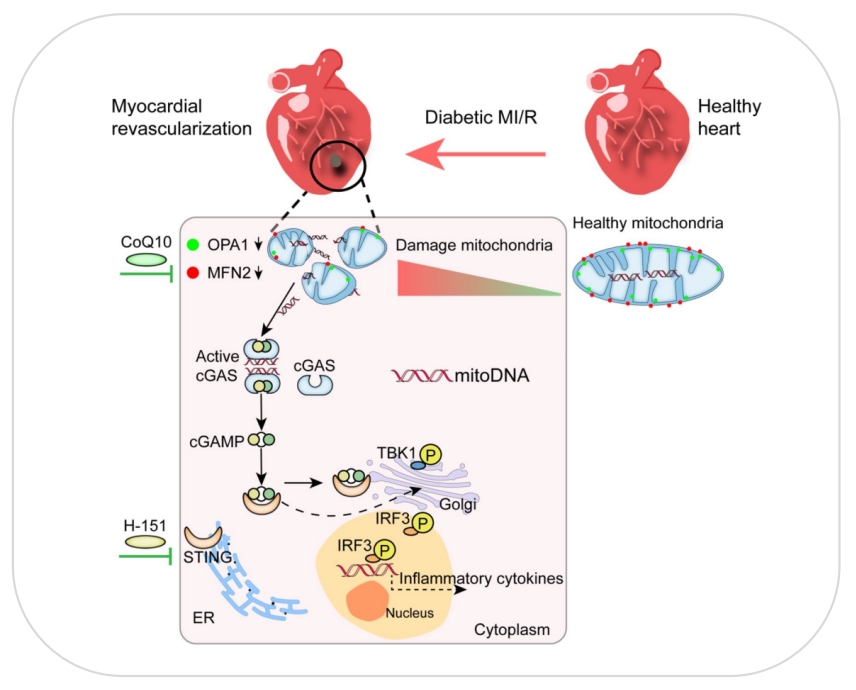
Figure 1: Graphical Abstract of Research on the Pathogenesis of Diabetes-Related MI/R Injury [1]
On August 3, 2023, Professor Xia Zhongyuan's team from Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University published a research paper titled "Decreased MFN2 activates the cGAS-STING pathway in diabetic myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion by triggering the release of mitochondrial DNA" in Cell Communication and Signaling. They established a diabetic mouse model using a high-fat diet (HFD) plus a low dose of streptozotocin (STZ), an MI/R model by inducing myocardial ischemia for 2 hours followed by 30 minutes of reperfusion, and a cellular model of glucolipotoxicity in H9C2 cells induced by high glucose (HG) and palmitic acid (PA). The study elucidated the key role of cGAS-STING activation in the pathogenesis of diabetes-related MI/R injury, which is triggered by an increase in cytosolic mitochondrial DNA due to reduced mitochondrial fusion.
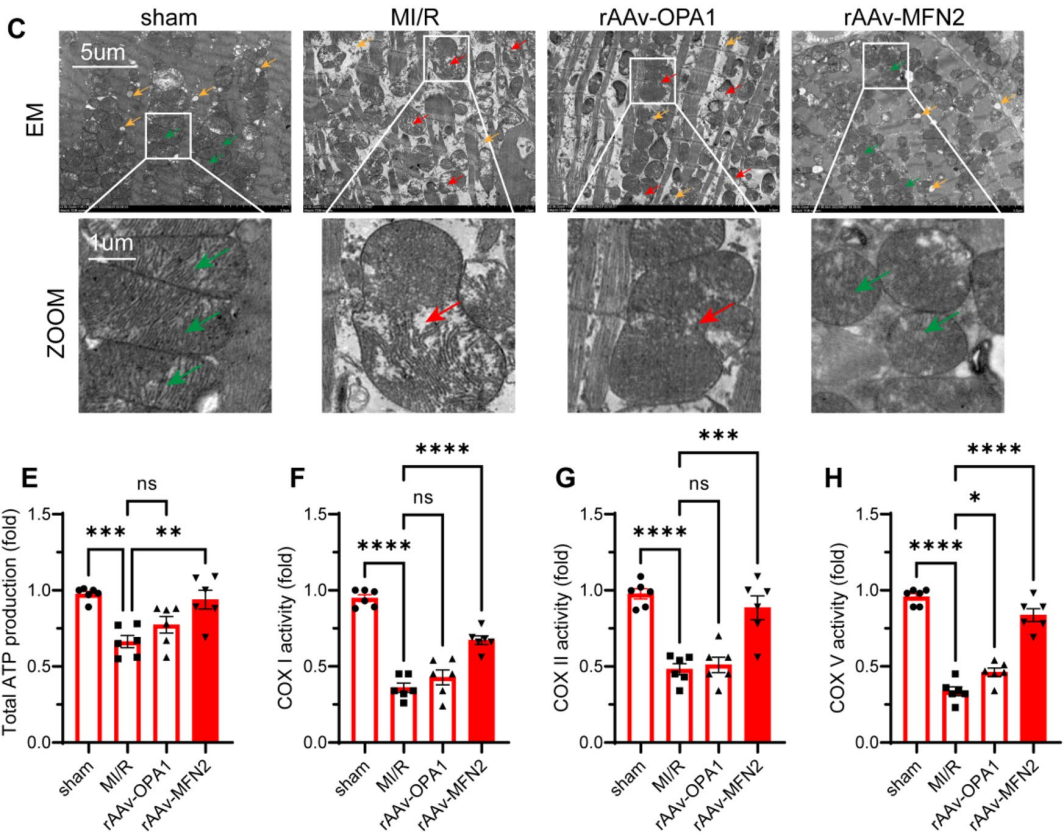
Figure 2: rAAV-MFN2 Overexpression Modulates Mitochondrial Dynamics and Function in Diabetic MI/R Mice. C: Mitochondrial Morphology; E-H: ATP Production and COX Activities in Cardiomyocytes [1]
Professor Xia Zhongyuan's team's research provides preclinical insights into the treatment of diabetes-related MI/R injury. In the study, the detection and quantification of total ATP in cardiomyocytes were performed using the ATP Microplate Assay Kit provided by Absin (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Introduction to the Use of ATP Detection Kit (abs580117)
Applicable Range: Urine, serum, plasma, tissue extracts, cell lysates, cell culture supernatants, and other biological fluid samples.
Detection Principle:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the chemical energy of cellular metabolism, often referred to as the "energy currency" of cells. ATP is produced only during photosynthesis and cellular respiration and is consumed in cellular processes such as biosynthetic reactions, movement, and cell division. It is a key indicator of cellular activity and is used as a measure of cell viability and cytotoxicity in research and drug development.
The ATP Detection Kit is a sensitive method for determining adenosine triphosphate in various samples. The ATP concentration is determined by creatine kinase and creatine. The reaction product can be measured at a colorimetric reading of 660 nm.
|
Components |
Size |
Storage |
|
96-Well Microplate |
1 plate |
— |
|
Assay Buffer |
30mL × 4 |
4 ℃ |
|
Enzyme |
Powder × 1 |
-20 ℃,keep in dark |
|
Reaction Buffer |
1mL × 1 |
4 ℃ |
|
Substrate |
Powder × 1 |
-20 ℃,keep in dark |
|
Dye Reagent Ⅰ |
Powder × 1 |
4 ℃ |
|
Dye Reagent Ⅱ |
Powder × 1 |
4 ℃ |
|
Dye Reagent Ⅲ |
10mL × 1 |
4 ℃ |
|
Standard |
Powder × 1 |
-20℃ |
|
Plate Adhesive Strips |
3 Strips |
— |
|
Technical Manual |
1 Manual |
— |
Remarks:
1. After the reaction is complete, the solution should turn yellow. If there is no color, it indicates that the experiment has failed. If the solution is blue, it suggests that the solution is contaminated. To prevent phosphorus contamination, it is best to use disposable plastic containers for solution preparation.2. Enzyme: Add 1 mL of distilled water to dissolve before use.
3. Substrate: Add 6 mL of distilled water and heat until dissolved before use.
4. Standard: Add 1 mL of distilled water to fully dissolve before use, then take 500 μL and add it to 500 μL of distilled water to obtain a standard solution with a concentration of 5 mmol/L.
5. Dye Reagent Working Solution: Take 5 mL of Dye Reagent Ⅲ and add it to Dye Reagent Ⅰ, and 1 mL of Dye Reagent Ⅲ and add it to Dye Reagent Ⅱ to fully dissolve. Transfer all of Dye Reagent Ⅱ into Dye Reagent Ⅲ and mix well, then transfer all of Dye Reagent Ⅰ into Dye Reagent Ⅲ (this step must be followed). The mixed dye reagent can be stored at 4°C for 2-3 days.
Experimental Procedure:
I. Reagents and Materials
1.Reagents to be provided: Distilled water
2. Materials to be provided: Microplate reader, pipettes and pipette tips, centrifuge tubes, centrifuge, timer, wet ice, etc.
II. Sample Processing
1. Cell/Bacterial Samples: Collect cells or bacteria (5×10^6) in a centrifuge tube, centrifuge to remove the supernatant, add 1 mL of Assay Buffer, sonicate (power 20%, 3 seconds on, 10 seconds off, repeat 30 times), then centrifuge at 4°C, 8000g for 10 minutes. Transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube and place on wet ice for detection;2. Tissue Samples: Take 1g of tissue and add 1 mL of Assay Buffer for sonication homogenization (power 20%, 3 seconds on, 10 seconds off, repeat 30 times), then centrifuge at 4°C, 8000g for 10 minutes. Transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube and place on wet ice for detection;
3. Serum/Plasma Samples: Place directly on wet ice for detection.
III. Preparation of the Standard Curve
Dilute the standard provided with the kit (2.5 mmol/L) with distilled water to create a continuous twofold dilution series to form the standard curve.
IV. Preliminary Experiment for Samples
For samples with unknown concentrations that may vary over a wide range, it is recommended to perform a preliminary experiment with several dilution gradients to ensure that the readings fall within the range of the standard curve.
V. Sample Detection
Heat all reagents to 37°C before use. Add samples and react fully as follows, then detect the absorbance at 660 nm using a microplate reader.
|
Reagent |
Sample Well |
Standard Well |
Blank Well |
|
Sample |
20μL |
— |
— |
|
Standard |
— |
20μL |
— |
|
Distilled Water |
— |
— |
20μL |
|
Substrate |
60μL |
60μL |
60μL |
|
Reaction Buffer |
10μL |
10μL |
10μL |
|
Enzyme |
10μL |
10μL |
10μL |
|
Mix well and incubate in a 37°C oven for 30 minutes. |
|||
|
Dye Reagent Working Solution |
100μL |
100μL |
100μL |
|
Mix well, incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes, and then measure the absorbance at 660 nm. |
|||
VI. Calculation of Sample Concentration
The instruction manual for the kit provides two methods for calculating the concentration of samples: ① Standard Curve Method; ② Formula Method.
For kits that come with both calculation formulas and standard curves, you can choose either method. The formula is a simplified calculation method. It is recommended to use the standard curve method for calculation, although it is more troublesome and consumes more reagents, the results will be more accurate. When using the standard curve method, a new standard curve must be prepared each time, as this reaction is a dynamic process, and the measured values can vary with reaction time, temperature, and other factors.
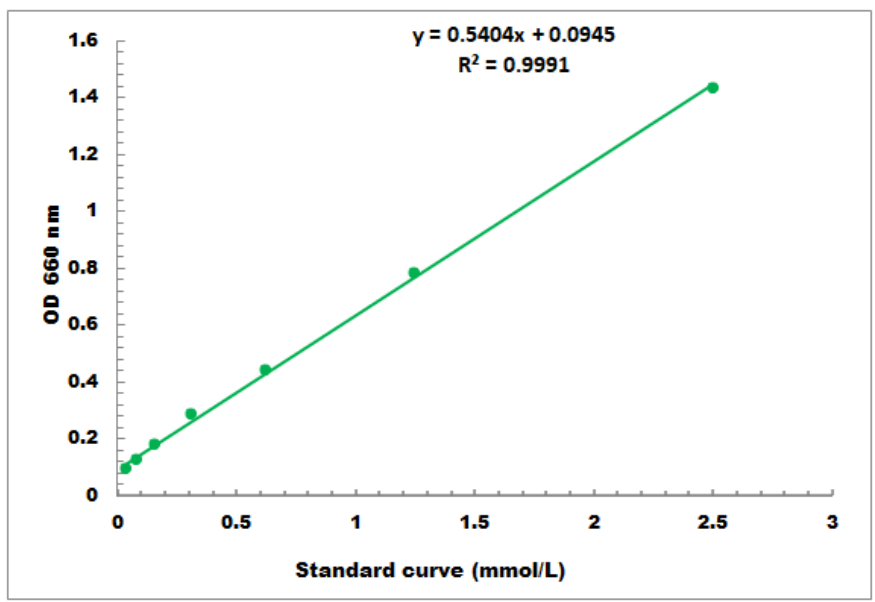
Figure 3: Example of an ATP Detection Standard Curve (Detection Limit: 0.02 mmol/L - 2.5 mmol/L)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: My sample is tissue. After following the sample processing method provided in the instruction manual to collect the supernatant for testing, how can I confirm the dilution factor of the supernatant?
A1: Since the ATP content of the sample to be tested is unknown, it is recommended to select appropriate sample points (2-3) for a preliminary experiment to determine the dilution factor.
Q2: The manual mentions that the mixed dye reagent can be stored at 4°C for 2-3 days. Do I have to complete the experiment within 2-3 days?
A2: The dye in the kit is prone to oxidation and degradation after dissolution, and may become ineffective if stored for a long time. It is suggested that you accumulate more samples for a one-time detection; if you must conduct the test in multiple sessions, you might consider purchasing the components separately.
Q3: Can the detection plate in the ATP Detection Kit be separated? Because if I want to do a preliminary experiment to explore the dilution factor, I might only need to use a few wells.
A3: The plate cannot be separated, but you can use a regular 96-well microplate as an alternative for the preliminary experiment.
References
[2] Xu J, Xiong A, Wang X,et al.Hyperoside attenuates pyrrolizidine alkaloids-induced liver injury by ameliorating TFEB-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2023, 46(8):694-712.
[3] CaoM J, Huang X W, Zou J L, et al. Attenuation of Microglial Activation and Pyroptosis by Inhibition of P2X7 Pathway Promotes Photoreceptor Survival in Experimental Retinal Detachment[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2023, 64(7):1-14.
[4] YeB, Pei Y T, Wang L J, et al. NAD+ supplementation prevents STING-induced senescence in CD8+ T cells by improving mitochondrial homeostasis[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2024,1-17.
ATP Series Assay Kits:
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
Detection Range |
|
Na+/K+ ATPase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
0.01μmol/L - 5μmol/L |
|
|
Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
0.01μmol/L - 5μmol/L |
Other Biochemical Detection Kits:
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
Detection Range |
|
Glutathione Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
0.01mmol/L - 0.5mmol/L |
|
|
Hydroxyproline Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
2μmol/L - 200μmol/L |
|
|
Hexokinase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
4μmol/L - 400μmol/L |
|
|
Pyruvate Kinase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
4μmol/L - 400μmol/L |
|
|
Phosphofructokinase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
4μmol/L - 400μmol/L |
|
|
Triglyceride Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
0.1mmol/L - 5mmol/L |
|
|
Phosphorus Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
0.01mmol/L - 0.4mmol/L |
|
|
α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
4μmol/L - 400μmol/L |
|
|
Copper Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
1μmol/L - 250μmol/L |
|
|
TBARS Microplate Assay Kit |
96T |
0.5μmol/L - 25μmol/L |
| Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us. |
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
