- Cart 0
- English
mIHC Literature Interpretation:TAMs target MS4A4A to restore CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a malignant tumor originating from the mucosal epithelium of the colon and rectum, and it is one of the most common malignant tumors in clinical practice. Its incidence and mortality rates are second only to gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, and primary liver cancer among malignant tumors of the digestive system. Despite the new era where "immunotherapy has become an important treatment modality for early and advanced malignant tumors," realizing the benefits of immunotherapy in colorectal cancer patients remains an unmet clinical need.
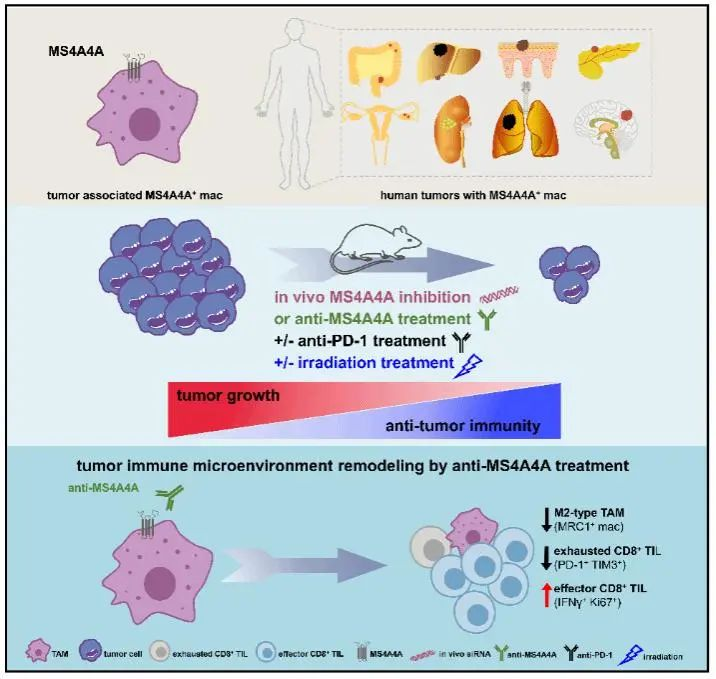
In July 2023, the team of Professors Li Guoxin and Deng Haijun from the Department of General Surgery at Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, published an original scientific paper titled "Targeting MS4A4A on tumor-associated macrophages restores CD8+ T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity" in the internationally renowned gastroenterology journal GUT. The article discovered for the first time that Membrane Spanning 4-Domains A4A (MS4A4A), a member of the 4-domain A subfamily, is specifically highly expressed by tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in various cancers, including colorectal cancer, and is associated with poor clinical outcomes in cancer patients. Inhibition of MS4A4A in vivo and treatment with anti-MS4A4A monoclonal antibodies can both suppress tumor growth and improve the therapeutic effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
The research findings indicate:
1. MS4A4A is selectively upregulated in TAMs and is associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients;2. MS4A4A can promote M2 macrophage polarization and induce CD8+ T cell dysfunction;
3. Inhibition of macrophage MS4A4A in vivo can slow down the progression of colorectal cancer;
4. MS4A4A promotes M2 macrophage polarization by activating the PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT6 pathways;
5. Anti-MS4A4A monoclonal antibody treatment delays the progression of colorectal cancer and alters the immune suppressive microenvironment;
6. MS4A4A-targeted therapy enhances the efficacy of PD-1 blockade;
7. Anti-MS4A4A monoclonal antibody treatment improves the efficacy against established colorectal cancer in rats.
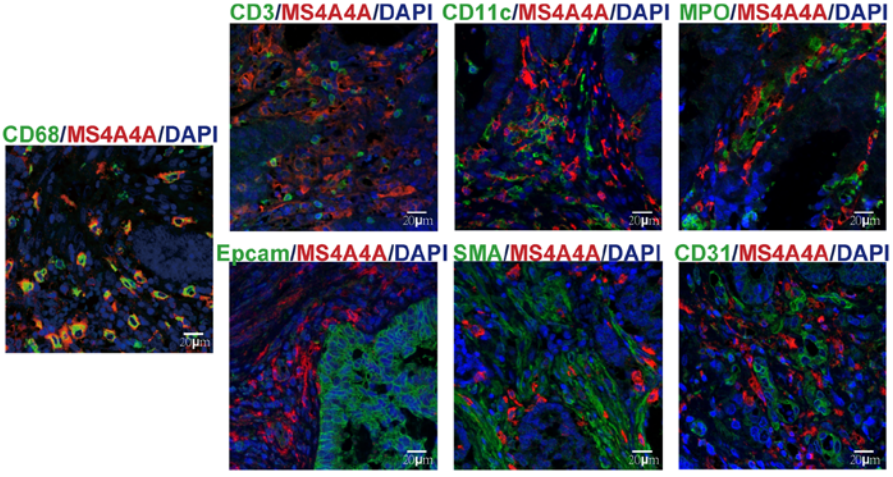
mIHC representative results figure
This study reveals the key role of MS4A4A+ TAMs in regulating tumor immune evasion, suggesting that anti-MS4A4A therapy may effectively enhance the efficacy of anti-PD-1 treatment. These findings provide a new perspective for understanding the role of TAMs in modulating antitumor immunity and offer a new direction for the development of effective immunotherapeutic strategies for CRC.
References
Li Y, Shen Z, Chai Z, Zhan Y, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Liu Y, Li Z, Lin M, Zhang Z, Liu W, Guan S, Zhang J, Qian J, Ding Y, Li G, Fang Y, Deng H. Targeting MS4A4A on tumour-associated macrophages restores CD8+ T-cell-mediated antitumour immunity. Gut. 2023 Jul 28:gutjnl-2022-329147. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-329147. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37507218.
|
Item NO. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
Antibody eluent (for mIHC) |
30ml |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
December 06, 2024
Clicks:169
