- Cart 0
- English
How can organoid technology be used to address drug screening issues?
September 26, 2024
Clicks:788
I. Current Pain Points in Drug Development
Data indicates that the development of new cancer drugs accounts for more than 50% of global new drug development. In 2020, the number of cancer clinical trials in China reached as high as 722, yet the failure rate of new cancer drugs is as high as 96%.
The main reasons are:
(1) 2D cell/cell line models cannot accurately reflect the in vivo situation;
(2) There are significant species differences between animal models and humans, leading to a large discrepancy between the results of the last batch of animal experiments and the first batch of patient clinical trials;
(3) The lack of targeting in patient enrollment in clinical trials, with the drug's efficacy not passing muster.
Therefore, there is a need for a disease model that closely resembles human conditions to reduce the cost and time of drug development. Organoid models, derived from human tissue, can enable clinical trials in the laboratory, improving the success rate of development, shortening the development cycle, and reducing development costs, which will be highly attractive to pharmaceutical companies.
II. How to Use Organoid Technology for Drug Screening?
It mainly includes three aspects: organoid culture, organoid identification, and organoid drug screening.
1. Organoid Culture
It can be divided into two categories based on the source of the sample: tissue-derived organoids and pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids.
Currently, we use tissue-derived tumor organoid models more frequently for drug screening. The conventional method is to construct them using the Matrigel method, which is relatively simple to operate.
 Figure 1: Organoid Construction Using Matrigel Matrix Method
Figure 1: Organoid Construction Using Matrigel Matrix Method
For drug combinations, various tumor organoid models can be used for assessment, such as conducting high-throughput screening drug combination analysis for the combined effects of two drugs (synergy, antagonism, etc.). The following figure shows the brightfield images of organoids from different cancer types cultured by our company, with a 4x objective for observing the quantity and a 10x objective for observing the morphology.
 Figure 2: Brightfield Image Display of Organoids
Figure 2: Brightfield Image Display of Organoids
2. Organoid Identification
Organoid identification primarily involves assessing the consistency between organoids and the original tumor tissue. The identification methods mainly include multiplex fluorescence immunohistochemistry, routine histology, single-cell sequencing, and various other methods for evaluation. Validation is performed from multiple perspectives, including morphology, histopathology, and molecular genetics.
The following figure shows the multiplex fluorescence immunohistochemistry identification performed by our company on the constructed lung cancer organoids (abs9443, Organotial lung cancer organoid culture medium kit) using the six-color multiplex fluorescence immunohistochemistry staining kit—universal for mouse and rabbit second antibodies (abs50014).
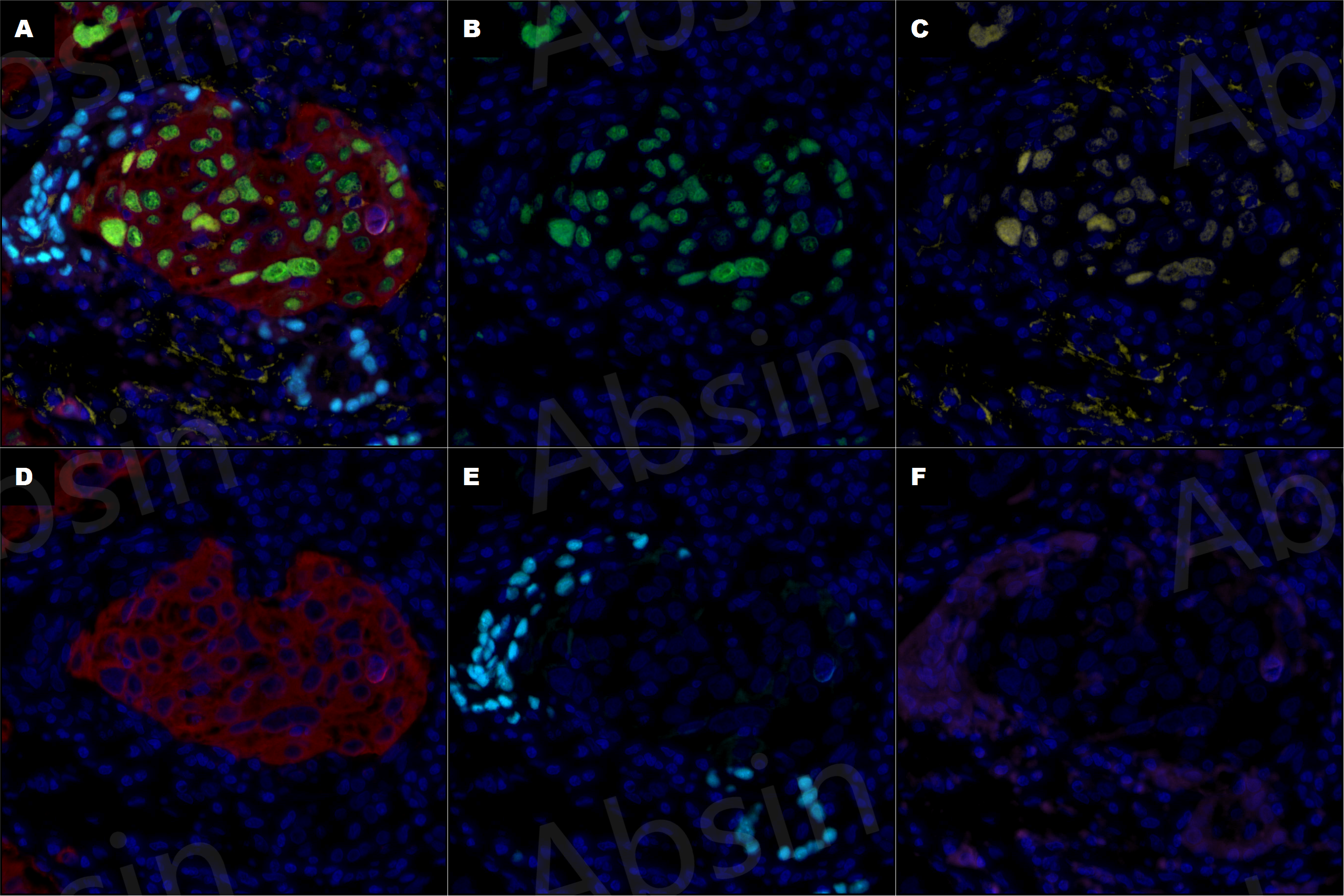
Figure 3: Multiplex Fluorescence Immunohistochemistry Identification of Lung Cancer Organoids
3. Organoid Drug Screening
After the organoid identification work is completed, the next step of drug screening can be initiated. The drugs that can be screened with organoids mainly include chemotherapeutic agents, small molecule targeted drugs, antibody drugs, etc. The core indicators for drug screening are usually the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and the cell plating inhibition rate. When conducting drug sensitivity experiments, it is important to pay attention to the selection of plating density and the passage number of the plating.
The following figure shows the sensitivity test of Sorafenib drug on hepatocellular carcinoma organoids studied by our company (partial experimental results), with an IC50 value of 2.26 μM, indicating that the drug is sensitive, and the results are consistent with clinical controls.

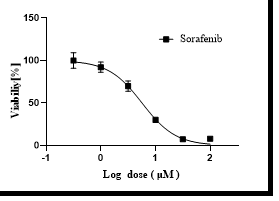
Figure 4: Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocyte Organoids to Different Concentrations of Sorafenib
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |
