- Cart 0
- English
Agonist Inhibitors full recommendation -- Deubiquitination enzyme (DUB)
August 19, 2021
Clicks:554
|
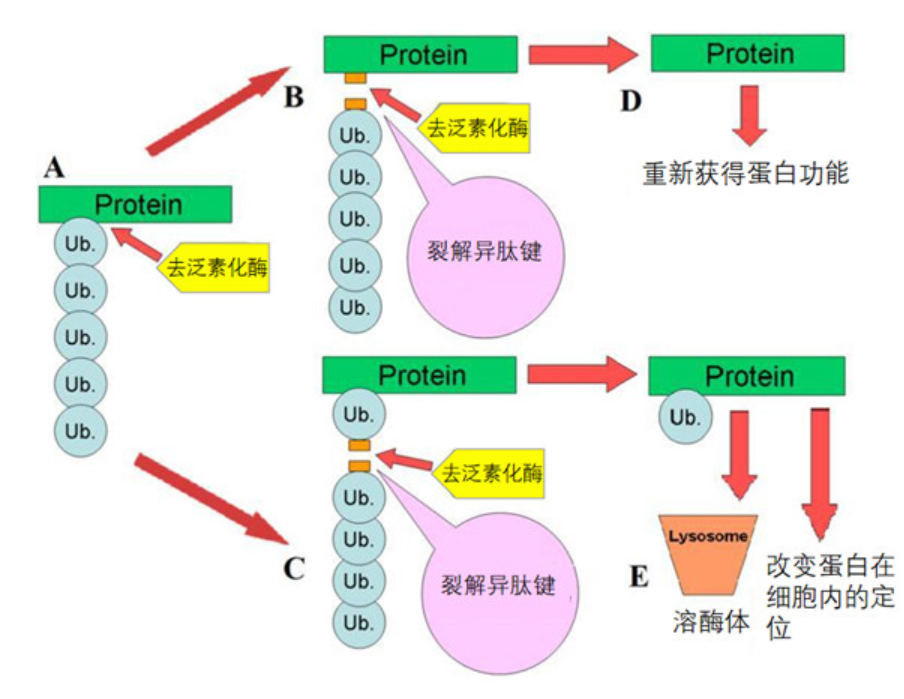
Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is an important protein degradation regulation system in cells. The ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of substrate proteins can affect or regulate a variety of cellular activities, including gene transcription, cell cycle regulation, immune response, cell receptor function, tumor growth, and inflammatory processes. The way is also a kind of dynamic modification of protein bidirectional regulation system, in the body by the ubiquitin ligase system (E1 and E2, E3) of the substrate and ubiquitin are modified, to family of ubiquitin digesting enzyme (DUB) is responsible for by hydrolysis of ubiquitin carboxyl terminal ester bond, peptide bond or peptide bond, specificity of ubiquitin molecules from links have ubiquitin protein or precursor protein hydrolysis, It has the effect of deubiquitination and reverse regulation of protein degradation, thus affecting the function of protein.
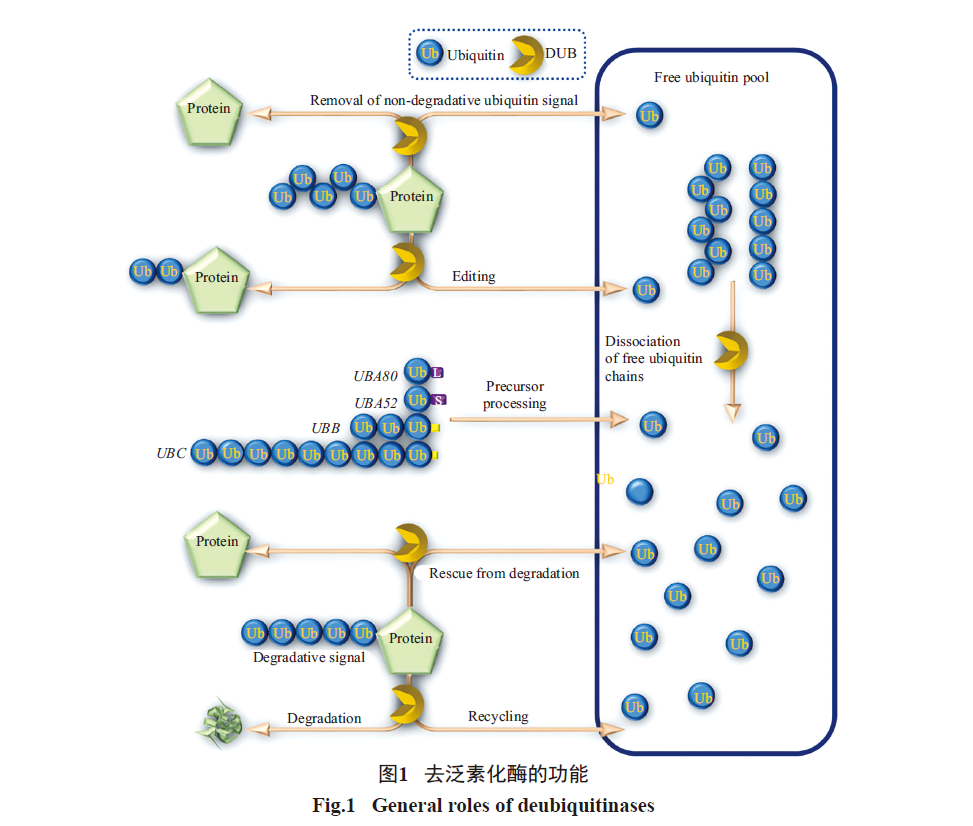
Deubiquitin enzymes are a large family of proteases, which can be divided into five families: ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase (UCH) family, ubiquitin specific protease (USP/UBP) family, Otubaim (OTU) family, Josephin domain protein family and JAMM family. The functions of deubiquitination enzymes in cells can be roughly divided into the following categories: (1) processing of ubiquitin precursors to produce free ubiquitin molecules; (2) Remove the ubiquitin chain on the protein to prevent the protein from being degraded by the proteasome, thus stabilizing the protein; (3) Remove the undegraded ubiquitination signal attached to the protein; (4) Ensure the homeostasis of ubiquitin molecules in cells by preventing them from being degraded together with substrate proteins; (5) Involved in the disintegration of cell-free ubiquitin chains; (6) Edit the type of ubiquitin chain by cutting the ubiquitin chain.
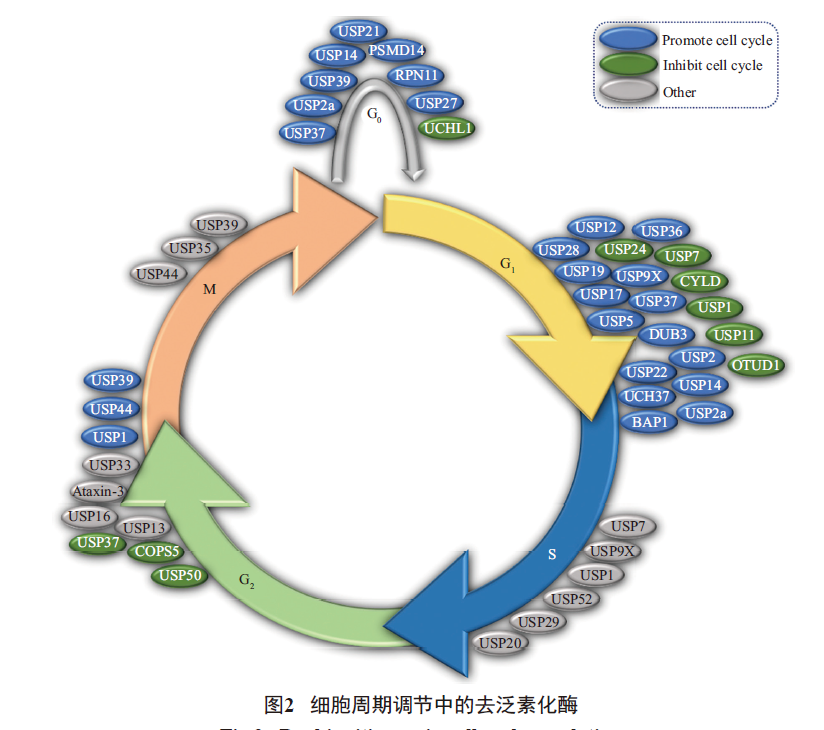
The process of cell cycle involves multiple levels of regulation, and deubiquitination enzymes, as a class of important hydrolases involved in the post-translational modification of proteins, play an important role in the regulation of cell cycle. Deubiquitination enzymes play different biological functions in different cycle regulation. For example, USP44 in G2/M phase and USP39 in G0/G1 and G2/M phases can promote cell cycle operation, while in M phase, USP39 can affect the process of cell cycle by regulating the separation process of chromosomes. USP9X and USP1 are mainly involved in THE DNA damage repair process in the S phase and affect the operation of the cell cycle in the S phase, while USP9X in the G1/S phase and USP1 in the G2/M phase promote the operation of the cell cycle through other ways.
The researchers found a significant increase in USP14 protein expression in obese mice. Using cell lines with stable expression and knockout of USP14, they found that fatty acid synthase (FASN), a key enzyme in triglyceride synthesis, was one of the target molecules of USP14 through the combined application of large-scale protein-protein interaction omics, quantitative proteomics and ubiquitination omics, and bioinformatics analysis. Studies have found that the increased expression of USP14 in obese mice can reduce the ubiquitination level of FASN, increase the stability of FASN protein, increase the synthesis of triglyceride, and ultimately lead to the increase of NAFLD level.
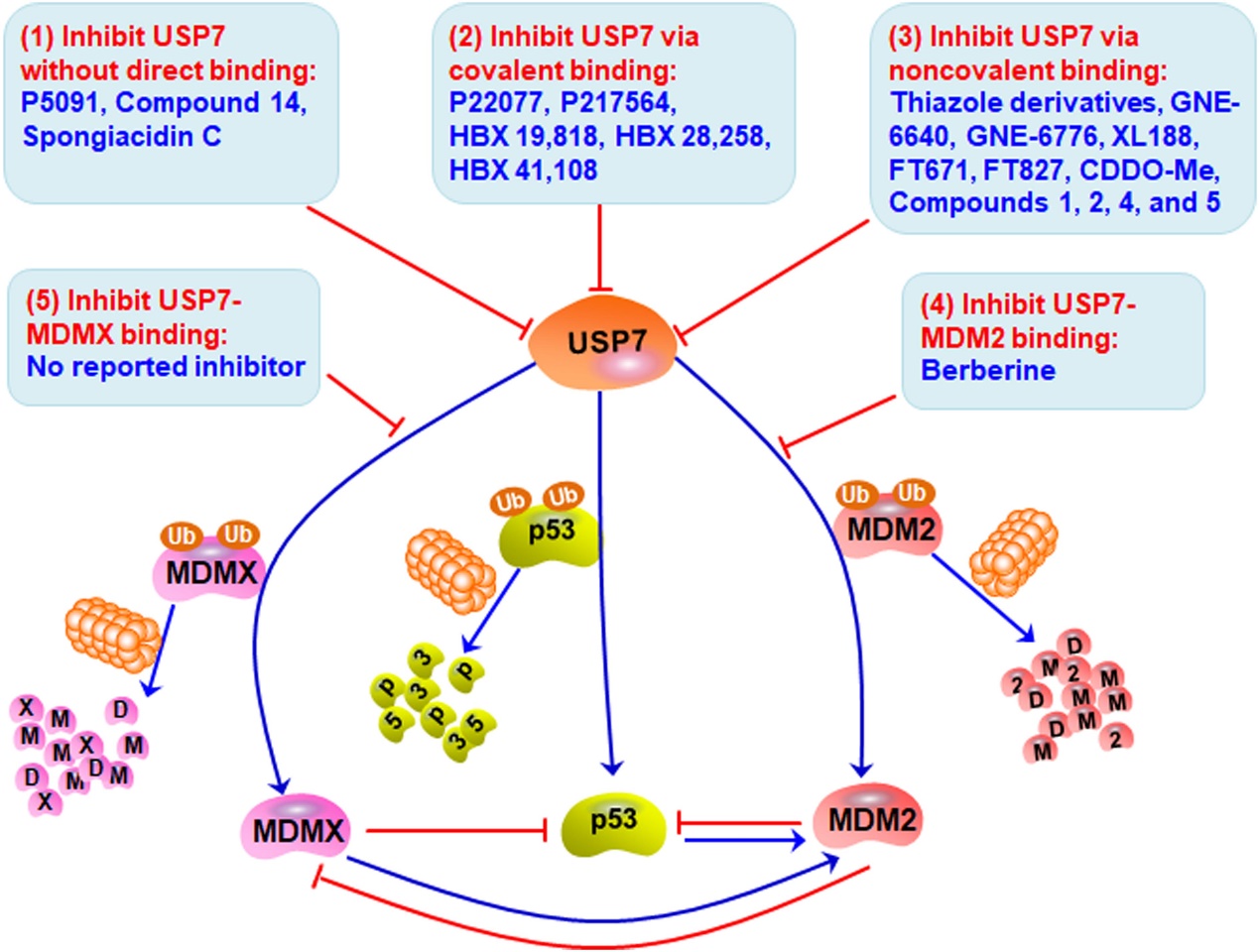
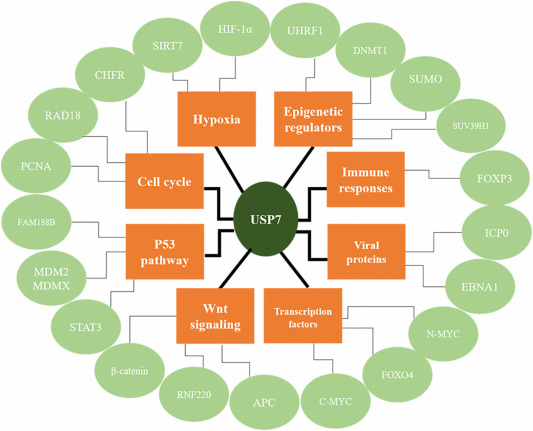
Several small molecule inhibitors have been developed that extensively inhibit the deubiquitination activity of USP7 without direct binding, covalent binding, or non-covalent binding, thereby inducing the degradation of MDM2 and MDMX and stabilizing and activating p53. These compounds have been shown to have anti-cancer properties both in vivo and in vitro. Direct inhibition of USP7 in combination with MDM2 and MDMX may be tested to develop safer and more effective cancer treatment inhibitors.
A summary of the role of USP7 in cancer and known interacting partners. The main known processes and pathways of USP7 functions are shown in orange, and the interactions of known targets corresponding to these functions are shown in green.
|